

Non-Experimental Research Designs
Sep 12, 2014
321 likes | 1.35k Views
Non-Experimental Research Designs. Farzin Madjidi, Ed.D. Pepperdine University G.S.E.P. Non-Experimental Designs. Descriptive Relationships Surveys Causal Comparative Qualitative. 2. Research Design looks tough!. But its really easy!. Descriptive Studies.
Share Presentation
- causal comparative
- cross sectional
- relationship studies
- variable predictor variable
- variable criterion variable based

Presentation Transcript
Non-Experimental Research Designs Farzin Madjidi, Ed.D. Pepperdine University G.S.E.P.
Non-Experimental Designs • Descriptive • Relationships • Surveys • Causal Comparative • Qualitative 2
Research Design looks tough!
But its really easy!
Descriptive Studies • Intended to examine and describe an issue • Especially effective when the area has been previously studied • Ex: a study of organizational climate • Ex: a study of salaries in an industry • Typical analysis • Descriptive statistics (graphs, charts, tables, etc.) • Textual analyses (content analysis) 3
Descriptive Studies Important Issues: • Cannot make conclusions about relationships studied • Subjects (AUs) and instrumentation MUST be clearly identified • Watch for “Graphic Distortions” 4
Relationship Studies • Investigate the degree to which differences or variation in one variable are related to differences or variation in another variable • They allow us to examine/discover characteristics that can predict other characteristics • Can lead to further investigation of other variables 5
Relationship Studies • Ex: What is the relationship between leadership styles and tenure as a leader? • Ex: Is there a difference in job satisfaction based on Work Locus of Control? • Typical Analysis • Correlation • Bivariate Regression • Inferential Techniques 6
Predictive Studies • Correlation coefficients only show associations • Predictive studies allow you to calculate the value of one variable (Criterion variable) based on the values of another variable (Predictor variable) • They allow you to make estimates • They allow you to devise forecasting models 7
Predictive Studies • Ex: Determining factors that lead to attrition at high level management positions • Ex: Forecasting property values based on a number of property variables • Typical Analysis includes: • Regression • Multiple Regression • Discriminant Analysis 8
Predictive Studies Important Issues: • Cannot infer Cause-and-Effect • Practical Significance vs. Statistical Significance (low, yet significant correlation; r vs. r-squared) • Reliability and Validity of instruments used • Assumptions/Limitations of statistical techniques used 9
Survey Research • A very popular methodology • Although mostly used in descriptive studies, can be used as part of both descriptive and predictive/relationship studies • Two different types: • Cross-Sectional • Longitudinal 10
Survey ResearchCross-Sectional Surveys • Studies a phenomenon as it occurs at one point in time (e.g., political surveys, attitude surveys, etc.) • Studies a phenomenon through subjects that are along different timelines of the phenomenon (e.g., attitudes of managers in different age groups, surveyed at the same time) 11
7-98 Cross-Sectional (Mgrs w/ 3 to 5 yrs of exp) Longitudinal 7-96 7-97 7-98 (mgrs w/ 1 yr of exp) (mgrs w/ 2 yr of exp) (mgrs w/ 3 yr of exp) Survey ResearchLongitudinal Surveys • The same group of subjects are studied over a period of time • Avoids some of the limitations of cross-sectional designs Convenience vs. Resources 12
Causal-Comparative Studies Go beyond relationships/associations to examine cause-and-effects. Two types of these studies: • Ex Post Facto • Correlational 13
Causal-Comparative StudiesEx Post Facto • Applied when seeking cause-and-effect relationships, but cannot do experiments • One or more independent variables are used to study their effects on one dependent variable • Ex: What is the impact of a particular training on job performance 14
Causal-Comparative StudiesEx Post Facto (cont’d) Ex. Continued: • Approach 1: Select two groups, one group is trained, the other is not. Next their job performance is measured (experimental design) • Approach 2: Look for groups with pre-existing conditions and compare their job performance. e.g., select a group that is already trained and one that is not trained and compare their job performance. • The groups selected must be as close as possible except for the independent variable 15
Causal-Comparative StudiesCorrelational These studies use more sophisticated versions of correlation analysis to investigate cause-and-effects • Path Analysis:A causal model is developed from theory which shows by arrows the causal sequence that is expected. Correlation between these variables is used as empirical evidence of the proposed links. • Newer, more sophisticated methods: • Structural Equation Modeling • Latent Variable Causal Modeling 16
Causal-Comparative Studies Important Issues: • Primary purpose should be developing cause-and-effect relationships when experimentation is not possible • The “intervention” must have already occurred • Must identify and consider extraneous variables • Differences between the groups not due to the independent variable should be controlled • Be careful with causal conclusions 17
- More by User

Experimental Research Designs
Experimental Design. AdvantagesBest establishes cause-and-effect relationshipsDisadvantagesArtificiality of experimentsFeasibilityUnethical. Causality. Temporal precedenceCovariation between IV and DVEliminate alternative explanations. Types of Experimental Designs. Simple True Experimental Complex True ExperimentalQuasi-Experimental.
1.04k views • 31 slides

Experimental RESEARCH DESIGNS
Experimental RESEARCH DESIGNS. This presentation was prepared by Del Siegle. Some of the material is from an earlier presentation by Scott Brown. Experimental Research Designs have Two Purposes:. …to provide answers to research questions ...to control variance (differences).
1.77k views • 50 slides

Research Methods – Experimental & Non-Experimental
Research Methods – Experimental & Non-Experimental. Higher Psychology. What is psychology?. the scientific study of thought, feeling and behavior. What do psychologists do ?. Help people with problems Measure and test Teach SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH. Where do psychologists work ?.
941 views • 44 slides

Non-experimental Designs
Non-experimental Designs. Psyc 231: Research Methods. Non-experimental Designs. Surveys Developmental Designs Small N Designs Quasi-experiments. Developmental Designs. Used to study development or changes in behavior Describe relationship between age and other variables Three main types
1.49k views • 32 slides
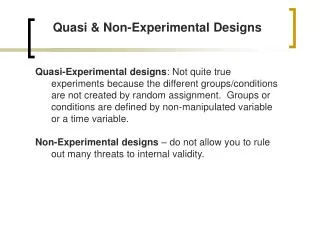
Quasi & Non-Experimental Designs
Quasi & Non-Experimental Designs. Quasi-Experimental designs : Not quite true experiments because the different groups/conditions are not created by random assignment. Groups or conditions are defined by non-manipulated variable or a time variable.
497 views • 22 slides

Non-Experimental designs: Correlational & Quasi-experimental designs
Non-Experimental designs: Correlational & Quasi-experimental designs. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Sometimes you just can’t perform a fully controlled experiment Because of the issue of interest Limited resources (not enough subjects, observations are too costly, etc).
247 views • 20 slides

Non-experimental Quantitative Research Designs (NEQDs)
Non-experimental Quantitative Research Designs (NEQDs). What Are They?. A research design in which the researcher measures or observes subjects or variables without attempting to introduce a treatment. How Could I Use NEQDs for Program Evaluation ?.
529 views • 13 slides


Non-Experimental designs
Non-Experimental designs. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. It was a difficult exam (I have adjusted scores by 5%, an error and a bad question were tossed out) Mean = 70.6 Max = 100 Min = 47.5. Exam 2. Most common area of errors between/within manipulations
467 views • 26 slides
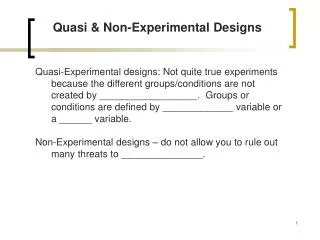
Quasi & Non-Experimental Designs. Quasi-Experimental designs: Not quite true experiments because the different groups/conditions are not created by __________________. Groups or conditions are defined by _____________ variable or a ______ variable.
455 views • 14 slides

Non-Experimental designs. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Sometimes you just can ’ t perform a fully controlled experiment Because of the issue of interest Limited resources (not enough subjects, observations are too costly, etc). Surveys Correlational Quasi-Experiments
570 views • 22 slides

Non-Experimental designs. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Mean = 76 Max = 94 Min = 48. Exam 2. Most common area of errors between/within manipulations interactions/main effects validity/reliability
382 views • 36 slides

Non-Experimental Designs: Survey Methods
Non-Experimental Designs: Survey Methods. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. I will aim to have the exams graded and entered into ReggieNet by Monday Remember that piloting is happening in labs this week, so be prepared with everything that you need, and attendance is important.
227 views • 21 slides

Non-Experimental designs: Surveys
Non-Experimental designs: Surveys. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Sometimes you just can’t perform a fully controlled experiment Because of the issue of interest Limited resources (not enough subjects, observations are too costly, etc). Surveys Correlational studies
178 views • 16 slides

Non-Experimental designs: Surveys & Correlational
Non-Experimental designs: Surveys & Correlational. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Quiz 8 is due Friday at midnight Running your group projects in labs this week. Please be there, your participation is important!. Reminders. Mean = 71.6 Median = 74 Max = 94 Min = 35.
545 views • 52 slides

Non-Experimental designs: Correlational & Quasi-experimental
Non-Experimental designs: Correlational & Quasi-experimental. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Non-Experimental designs: Correlational & Quasi-experimental. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology.
415 views • 38 slides

Experimental Research – Group Designs
Experimental Research – Group Designs. Population and Sample. Sampling. Sample should be representative of population How representative must a sample be? How does one recruit a representative sample? What is the rationale for the selection of a sample?
1.52k views • 150 slides

Chapter 4 Experimental Research Designs
Chapter 4 Experimental Research Designs. AIMS To outline deductive logic; To illustrate (laboratory) experimental research design; To give a management example of experimental design; To indicate why experimental logic is taken out of the laboratory; To illustrate quasi-experimental design.
228 views • 15 slides

Non-Experimental designs: Surveys & Correlational. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Mean = 74.14 Median = 77 Max = 94 Min = 50. Most common errors. Between vs. within designs Independent vs. dependent vars Scales of measurement. Confounds vs. extraneous variables
540 views • 53 slides

275 views • 23 slides

Non-Experimental designs. Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology. Sometimes you just can’t perform a fully controlled experiment Because of the issue of interest Limited resources (not enough subjects, observations are too costly, etc). Surveys Correlational Quasi-Experiments
260 views • 22 slides

Myers chapter 1 (B): Non-Experimental Research Designs
Myers chapter 1 (B): Non-Experimental Research Designs. A.P. Psychology. Do-Now (In Journal). Think of a psychological phenomenon that you would be interested to research (a behavior, habit, disorder, etc.) Briefly describe how you could hypothetically carry out your research.
206 views • 17 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Non-Experimental designs: Surveys & Correlational
Published by Teresa Sampaio Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Non-Experimental designs: Surveys & Correlational"— Presentation transcript:

Non-Experimental designs: Developmental designs & Small-N designs

Increasing your confidence that you really found what you think you found. Reliability and Validity.

Non-experimental Designs

Non-Experimental designs: Surveys & Quasi-Experiments

Non-Experimental designs

Non-true-experimental Designs PSY 231 Research Methods in Psychology.

Non-Experimental Designs: Surveys Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology.

Experiment Basics: Variables Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology.

Non-Experimental designs: Surveys Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology.

Non-Experimental designs: Surveys

Statistics Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology.

Non-Experimental designs: Correlational and Quasi-experiments Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology.

Non-Experimental designs Psych 231: Research Methods in Psychology.

Chapter 10 Finding Relationships Among Variables: Non-Experimental Research.

About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO