- Electric Currents and Its Effects Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10

Last Updated on October 22, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 7 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 7 science chapter 10 Electric Currents and Its Effects.

Table of Contents

Case Study Questions on Electric Currents and Its Effects
Question 1:
Read the given passage below and answer the question:
Electricity is the form of energy which we use electricity for many purposes to make our tasks easier. Electricity makes it possible to light our homes, roads, offices, markets and factories even after sunset. A bulb has a thin wire that gives off light. The wire of an electric bulb gets heated to such a high temperature that it starts glowing. Nowadays The fluorescent CFLs and LED bulbs are being used for lighting as they are considered to much better than incandescent electric bulbs. However, damaged CFLs need to be disposed off safely. It is advised to use electrical appliances and gadgets, which are electricity efficient. It also advisable to use ISI marked electrical appliances and gadgets
Q.1. What is the name of thin wire in the electric bulb? (a) Element (b) Coil (c) Filament (d) Fuse
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: An electric bulb has a filament that is connected to its terminals. The filament of an electric bulb gets heated to such a high temperature that it starts glowing.
Q.2. CFLs and LED stand for: (a) Compact fluorescent lamps and light emitting diode. (b) Composed fluorescent lamps and light emitting diode. (c) Compact fluorescent lamps and light emission diode. (d) Composed fluorescent lamps and light emission diode.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: CFLs – Compact fluorescent lamps, LED – light emitting diode.
Q.3. Fluorescent tubes and CFLs contain toxic gas: (a) carbon monoxide (b) water vapour (c) mercury vapours (d) Chlorofluorocarbons
Difficulty Level: Hard
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Fluorescent tubes and CFLs contain mercury vapour, toxic in nature. Therefore, damaged fluorescent tubes or CFLs need to be disposed off safely.
Q.4. What is a disadvantage of using incandescent electric bulbs? How LED bulbs are better than incandescent bulbs and CFLs?
Ans. Incandescent electric bulbs give heat therefor, a part of electricity consumed is used in producing heat which results in the wastage of electricity. LED bulbs consume less electricity as compared to incandescent bulbs or CFLs. Thus, LED bulbs are much electricity efficient.
Q.5. Who assigns ISI mark? Why is it suggested to use ISI mark products?
Ans. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi assigns a Standard Mark on products, called ISI mark. The ISI mark is an assurance of conformity to the specifications given on the products. It is therefore suggested to use ISI mark products.
- Wastewater Story Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 13
- Forests Our Lifelines Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- Light Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Motion and Time Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 9
- Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Transpirations in Animals and Plants Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
- Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 5
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
- Heat Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Nutrition in plants class 7 case study questions science chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Define electric current.
- Define electricity.
- Discuss electric circuits and its components.
- Describe the heating effect of electric current.
- Explain the magnetic effect of electric current.
We use electrical appliances in everyday life from morning to night. We use electric bulbs, air conditioners, refrigerators, etc., They run with the help of electrical energy.
- Electricity is the form of energy, which is used to run appliances, move things and to do work using these appliances.
- Electricity can be generated naturally through lightning or artificially through the generator.
- Electric circuit is a continuous and closed circuit of electric current.
Components of electric circuit: Bulb, electric cell, switch (key), conductors, bulb and other devices which are used .
For further practice on case study questions related to Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Currents and Its Effects, we recommend exploring the link given below.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Electric Currents and Its Effects Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 7 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How do case study questions differ from other question types?
A3: Unlike direct questions that test specific knowledge, case study questions involve analyzing a scenario, understanding the context, and applying various scientific concepts to answer the questions. They test higher-order thinking skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 7 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. There is another website Physics Gurukul that offers a large collection of case study questions.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on Electric Currents and Its Effects for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Electric Currents and Its Effects class 7 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of Electric Currents and Its Effects.
Q7: What steps should I follow to correctly answer case study questions?
A7: Follow these steps: Read the case study carefully. Understand the scenario and the information provided. Identify the key concepts. Determine which scientific principles or concepts are relevant to the case study. Analyze the information. Break down the information, identify relationships, and note any data or facts given. Answer the questions. Apply your knowledge to answer the questions, ensuring that your responses are based on the case study and the relevant scientific concepts.
Q8: What should I check when reading a case study?
A8: Check the following: Context and background: Understand the setting and context of the case study. Key facts and data: Identify important details, data points, and observations mentioned. Relevant concepts: Recognize which scientific concepts and principles are applicable. Questions asked: Carefully read each question to understand what is being asked and how it relates to the case study.
Q9: What are common mistakes to avoid when answering case study questions?
A9: Common mistakes include: Not reading the case study carefully: Missing important details and context. Ignoring key concepts: Failing to identify and apply relevant scientific principles. Superficial analysis: Providing answers that lack depth and do not fully address the questions. Making assumptions: Adding information not provided in the case study or making unsupported assumptions.
Q10: How can I ensure my answers are thorough and well-structured?
A10: Ensure your answers are thorough and well-structured by: Organizing your thoughts: Structure your answer logically with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Using evidence: Support your answers with specific information from the case study. Applying relevant concepts: Clearly explain how scientific principles relate to the case study. Reviewing your answers: Check for completeness and accuracy, ensuring all parts of the question are addressed.
Q11: What are the important keywords from the chapter “Electric Currents and Its Effects”?
A11: Important keywords from the chapter “Electric Currents and Its Effects” are given below: Appliances: A machine or device designed to perform a specific task or function. Generator: A machine which generates something for example electricity. Circuit: A circular path in which electricity flows. Resistance: An electrical component which resists or opposes the flow of electric current. Fuse: A safety device used in electric circuits. Coil: A long thin piece of wire spiralled into circles.

Related Posts

A to Z Classes
Cbse, ncert and icse solution online, class 7 science case study question, case study question class 7 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 7 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 7 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 7 Science.
There are total 18 chapter Nutrition in Plants, Nutrition in Animals, Fibre to Fabric, Heat, Acids, Bases and Salts, Physical and Chemical Changes, Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate, Winds, Storms and Cyclones, Soil, Respiration in Organisms, Transportation in Animals and Plants, Reproduction in Plants, Motion and Time, Electric Current and Its Effects, Light, Water: A Precious Resource, Forests: Our Lifeline, Wastewater Story
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 7 Science Case Study Question
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Case Study Question
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question
- Chapter 4 Heat Case Study Question
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Case Study Question
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Case Study Question
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Case Study Question
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones Case Study Question
- Chapter 9 Soil Case Study Question
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms Case Study Question
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants Case Study Question
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants Case Study Question
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time Case Study Question
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
- Lakhmir Singh Class 7 Solution
- NCERT Class 7 Math Solution
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 5 Minutes
Question 1:
Read the case/passage and answer the questions given below.
To carry out a simple function such as eating food there has to be coordination of the eyes, hands and the mouth. The eyes have to focus on the food, the hands have to pick it up and take it to the mouth where it will be chewed. All these actions have to be coordinated in such a manner that they follow a particular sequence and the action is completed. A similar mechanism is also needed for internal functions of the body. This function is carried out by the nervous system. It is composed of (a) Specialised cells which can detect, receive and transmit different kinds of stimuli. These are called neurons. (b) Nerve fibres which are certain bundles of extended processes of nerve cells.
The individuals also have to adjust to the changing conditions around them and vary their responses. At the same time, the internal conditions of the body should be maintained constant. This is called homeostasis. The internal conditions of the body are maintained at a constant by controlling the physiology of the organisms.
(i) What will the correct sequence in which conduction of information through nerves take place? (ii) How homeostasis is said to maintain the equilibrium of the body? (iii) What function does the central nervous system perform? (iv) What happens when the dendrite tip of a nerve cell receives a signal?
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Extra Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration In Organisms
Extra questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration In Organisms with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Respiration In Organisms Class 7 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short extra questions and answers.
1. Where does cellular respiration take place?
Answer: Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms.
2. What is aerobic respiration?
Answer: The process of breakdown of glucose with the use of oxygen is called aerobic respiration.
3. What are some common uses of Yeast?
Answer: Some common uses of Yeast are bread, wine and beer.
4. Name an organism that can survive in the absence of air.
Answer: Yeast can survive in the absence of air.
5. How do earthworms breathe?
Answer: Earthworms breathe through their skins.
6. What does a breath mean?
Answer: A breath means one inhalation plus one exhalation.
7. What is cell?
Answer: A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism.
8. What are all organisms made up of?
Answer: All organisms are made of small microscopic units called cells.
9. Name the respiratory organ of birds.
Answer: They have lungs in their chest cavities like the human beings.
10. What forms the floor of the chest cavity?
Answer: A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity.
11. What are the end products of anaerobic respiration?
Answer: The end products of anaerobic respiration are alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy.
12. What is produced during anaerobic respiration in muscles that causes cramps?
Answer: Lactic acid is produced during anaerobic respiration in muscles that causes cramps.
13. What is cellular respiration?
Answer: The process of breakdown of food in the cell with the release of energy is called cellular respiration.
14. What is breathing rate?
Answer: The number of times a person breathes in a minute is termed as the breathing rate.
15. Why smoking should be avoided?
Answer: Smoking damages lungs. Smoking is also linked to cancer. So, it must be avoided.
16. What are spiracles?
Answer: Insects have small openings on their body that allow them to breathe. These openings are called spiracles.
17. Why we should eat regularly?
Answer: We should eat regularly because food has stored energy, which is released during respiration.
18. What is a stomata and what is its function?
Answer: Leaves of the plants have tiny pores called stomata for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
19. What is breathing?
Answer: Breathing means taking in air rich in oxygen and giving out air rich in carbon dioxide with the help of respiratory organs.
20. What is inhalation and exhalation?
Answer: The taking in of air rich in oxygen into the body is called inhalation and giving out of air rich in carbon dioxide is known as exhalation.
Short Extra Questions and Answers
1. How do frogs breathe?
Answer: Frogs have a pair of lungs like human beings to breathe air. They can also breathe through their skin, which is moist and slippery.
2. Name some animals that breathe through lungs.
Answer: Animals such as elephants, lions, cows, goats, frogs, lizards, snakes, birds, have lungs in their chest cavities like the human beings.
3. Why do mountaineers carry oxygen with them?
Answer: Mountaineers carry oxygen with them because the amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
4. Why should we cover our nose while sneezing?
Answer: When we sneeze, we should cover our nose so that the foreign particles we expel are not inhaled by other persons.
5. How does respiration occur in earthworms?
Answer: Earthworms breathe through their skins. The skin of an earthworm feels moist and slimy on touching. Gases can easily pass through them.
6. What role does hair present in the nasal cavity play in the process of respiration?
Answer: When we inhale, the particles get trapped in the hair present in our nasal cavity. Thus, the hairs present in the nasal cavity filters the air.
7. What is normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest?
Answer: On an average, an adult human being at rest breathes in and out 15ñ18 times in a minute.
8. Why do we get muscle cramps after heavy exercise?
Answer: The cramps occur when muscle cells respire anaerobically. The partial breakdown of glucose produces lactic acid. The accumulation of lactic acid causes muscle cramps.
9. What happens during exhalation?
Answer: During exhalation, ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves up to its former position. This reduces the size of the chest cavity and air is pushed out of the lungs.
10. What happens during inhalation?
Answer: During inhalation, ribs move up and outwards and diaphragm moves down. This movement increases space in our chest cavity and air rushes into the lungs. The lungs get filled with air.
11. What happens to the air we breathe in?
Answer: The air we breathe in is transported to all parts of the body and ultimately to each cell. In the cells, oxygen in the air helps in the breakdown of food and energy is released.
12. How does respiration work in yeast?
Answer: Yeasts are single-celled organisms. They get energy through anaerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, glucose breaks down into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
13. Why are yeasts used to make wine and beer?
Answer: Yeasts are single-celled organisms. They respire anaerobically and during this process yield alcohol. They are, therefore, used to make wine and beer.
14. What is the function of gills in fish?
Answer: Gills in fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water. Gills are projections of the skin and are well supplied with blood vessels for exchange of gases.
15. How do plant roots respire?
Answer: Like all other living cells of the plants, the root cells also need oxygen to generate energy. Roots take up air from the air spaces present between the soils particles.
Long Extra Questions and Answers
1. Why do we feel hungry after a physical activity?
Answer: When we need extra energy, we breathe faster. As a result more oxygen is supplied to our cells. It speeds up the breakdown of food and more energy is released. Due to rapid breakdown of food we feel hungry.
2. What is anaerobic respiration?
Answer: Food can also be broken down, without using oxygen. This is called anaerobic respiration. Breakdown of food releases energy.
3. Do the plants also respire?
Answer: Like other living organisms, plants also respire for their survival. They also take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. In the cells oxygen is used to break down glucose into carbon dioxide and water as in other organisms.
4. When we release our breath after holding it for some time, we had to breathe heavily. Why it was so?
Answer: This is so, because whenever we need extra energy, we breathe faster. As a result more oxygen is supplied to our cells. It speeds up the breakdown of food and more energy is released.
5. How does exchange of gases take place in insects? Or Explain respiration in insects.
Answer: Insects have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange.
Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles.
6. When and where does anaerobic respiration occur in humans?
Answer: During heavy exercise, fast running, cycling, walking for many hours or heavy weight lifting, the demand for energy is high. But the supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. Then anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscle cells to fulfill the demand of energy.
7. What is the percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in inhaled and exhaled air?
Answer: When we exhale, we breathe out less oxygen but more carbon dioxide than we inhale.
Inhaled air: Oxygen 21% and Carbon dioxide 0.04%
Exhaled air: Oxygen 16.4 % and Carbon dioxide 4.4%
8. Why do we get relief from cramps after a hot water bath or a massage?
Answer: Hot water bath or massage improves circulation of blood. As a result, the supply of oxygen to the muscle cells increases. The increase in the supply of oxygen results in the complete breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water. Thus, we get relief from cramps after a hot water bath or a massage.
9. Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
Answer: When we inhale a lot of dust-laden air, the particles get trapped in the hair present in our nasal cavity. However, sometimes these particles may get past the hair in the nasal cavity. Then they irritate the lining of the cavity, as a result of which we sneeze. Sneezing expels these foreign particles from the inhaled air and a dust free, clean air enters our body.
10. How does respiration occur in plants? Or How do the plants breathe in oxygen?
Answer: In plants each part can independently take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. Roots take in air present in the soil. Leaves have tiny pores called stomata through which they exchange gases. The breakdown of glucose in the plant cells is similar to that in other living beings.
11. What parts of the human body are involved in respiration?
Answer: We take in air through our nostrils. When we inhale air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air reaches our lungs through the windpipe. Lungs are present in the chest cavity. This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides. A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Breathing involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage.
12. How do the cockroaches breathe?
Answer: A cockroach has small openings on the sides of its body. These openings are called spiracles. They have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange. Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles.
13. Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Answer: During fast running the demand for energy is high. But the supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. Our muscle cells can also respire anaerobically, but only for a short time, when there is a temporary deficiency of oxygen. Thus, an athlete breathes faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race so that more oxygen is supplied to the cells. This speed up the breakdown of food and more energy is released.
14. Why do we respire?
Answer: All organisms are made of small microscopic units called cells. A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Each cell of an organism performs certain functions such as nutrition, transport, excretion and reproduction. To perform these functions, the cell needs energy. Even when we are eating, sleeping or reading we require energy. The food has stored energy, which is released during respiration. Therefore, we respire to get energy from food.
15. List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer: Similarities
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respirations are types of cellular respiration.
- Both generate energy by breaking down glucose and produces byproducts.
Differences
16. How do we breathe?
Answer: Normally we take in air through our nostrils. When we inhale air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air reaches our lungs through the windpipe. Lungs are present in the chest cavity. This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides. A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Breathing involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage. During inhalation, ribs move up and outwards and diaphragm moves down. This movement increases space in our chest cavity and air rushes into the lungs. The lungs get filled with air. During exhalation, ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves up to its former position. This reduces the size of the chest cavity and air is pushed out of the lungs.
17. Take three test-tubes. Fill ¾ th of each with water. Label them A, B and C. Keep a snail in test-tube A, a water plant in test-tube B and in C, keep snail and plant both. Which test-tube would have the highest concentration of CO 2 ?
Answer: Snail breathes in oxygen and breathes out carbon dioxide. Hence concentration of CO 2 increases in the test tube. Therefore, test tube A will have high concentration of carbon dioxide.
In test tube B water plant uses carbon dioxide for synthesizing food and hence there will be less concentration of carbon dioxide compared to test tube A.
In test tube C, carbon dioxide produced by snail is utilized by plant for synthesis of food and oxygen released by plant is utilized by snail for respiration. Hence, concentration of carbon dioxide is least in test tube C.
18. Whales and dolphins often come up to the water surface. They even release a fountain of water sometimes while moving upwards. Why do they do so?
Answer: Whales and dolphins are mammals and breathe air into their lungs, just like we do. They cannot breathe under water like fish can as they do not have gills. They breathe through a nostril, called a blowhole, located right on top of their heads. This allows them to take breaths by exposing just the top of their heads to the air while they are swimming or resting under the water. After each breath, the blowhole is sealed tightly by strong muscles that surround it, so that water cannot get into the dolphin’s lungs.
When they surfaces for air, they breathes out (exhales) first and then breathes in (inhales) fresh air. The water spray is not coming from theirs lungs; it is just water sitting on top of their head around the blowhole being blown away before they inhale.
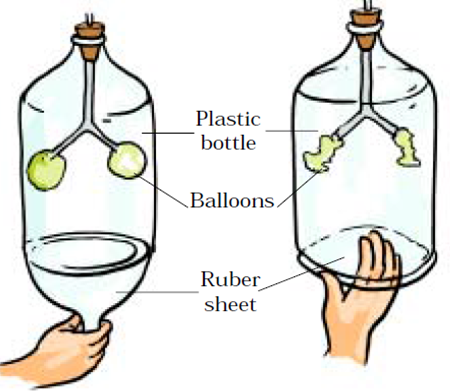
19. Explain the mechanism of breathing with the help of an activity.
Answer: Take a wide plastic bottle. Remove the bottom. Get a Y-shaped glass or plastic tube. Make a hole in the lid so that the tube may pass through it. To the forked end of the tube fix two deflated balloons. Introduce the tube into the bottle. Now cap the bottle. Seal it to make it airtight. To the open base of the bottle tie a thin rubber or plastic sheet using a large rubber band. To understand the expansion of the lungs, pull the rubber sheet from the base downwards. The volume of the cavity increases. This causes the pressure to decrease. Air rushes in to equalize the pressure, causing the balloons to inflate. Next, push the rubber/plastic sheet up. The volume of the cavity decreases. This causes an increase in pressure within the bottle, the air rushes out of the balloons causing them to deflate.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10
Home » CBSE » Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus
Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 – Respiration in Organisms
Science is a complex subject with a wide range of topics. Each concept requires a unique approach. Learning and understanding more about a specific topic in an orderly manner would help in gaining expertise in this subject. To be a good performer in Science, students need to have a strong hold on the basic concepts required to grasp further complex topics that will be introduced in higher classes.
Quick Links
Chapter 10 of Class 7 Science is about ‘Respiration in Organisms’. In this chapter, students will learn about various topics that will around understanding respiration, different types of respiration, and the respiration process in plants, animals, and humans.
Extramarks is a trusted online learning platform which is used by lakhs of students from Class 1 to Class 12. Our expert Science teachers have developed comprehensive study materials such as NCERT solutions, chapter notes, CBSE revision notes, and so on.
For providing practice materials for our students, our teachers have collated questions from various sources including the NCERT textbook, NCERT exemplar book, CBSE past years’ question papers, CBSE sample papers, and other reference books. Students can refer to our Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 to get access to all these questions which will help them to revise the full chapter while solving the questions.
By practising from Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Important Questions, students will be able to have strong foundational knowledge with all the important fundamental topics to cover for excelling in the CBSE exams.
Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 – With Solutions
For the overall preparation of students for exams, we suggest students refer to our Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10. This question bank includes questions from various sources and comprises step-by-step solutions that are guaranteed to improve the students’ performance and their grades.
It is advised that students solve these questions to understand their preparedness for the exams.
Below is a list of a few questions and answers taken from our question bank of Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10:
Question 1: List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration are:
- In both respirations, the food particles are broken down into smaller, digestible pieces to release energy.
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration occur inside the cell.
- Both respiration processes produce byproducts.
Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration are:
Question 2: Take three test tubes. Fill ¾th of each with water. Label them A, B and C. Keep a snail in test tube A, a water plant in test tubes B and C, and keep the snail and plant both. Which test tube would have the highest concentration of CO 2 ?
Answer 2: We are now aware that plants photosynthesis in the presence of CO 2 to produce glucose and by-product oxygen. Therefore, test tube B and test tube C contain plants that will have no concentration of CO 2 as plants use up the CO 2 , present. In test tube A, where a snail is placed, there will be a high concentration of CO 2 due to aerobic respiration taking place.
Question 3: Tick the correct answer:
(a) In cockroaches, air enters the body through:
(i) lungs (ii) gills (iii) spiracles (iv) skin.
(b) During heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation of:
(i) carbon dioxide (ii) lactic acid (iii) alcohol (iv) water.
(c) Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest is:
(i) 9–12 (ii) 15–18 (iii) 21–24 (iv) 30–33.
(d) During exhalation, the ribs:
(i) move outwards (ii) move downwards (iii) move upwards (iv) do not move at all.
- (iii) spiracles
- (ii)lactic acid
- (ii)move downwards
Question 4: Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Answer 4 : Athletes require a lot of oxygen during the race to form and release energy; thus, the athlete breathes faster and deeper than usual after the race to release energy; additionally, if the oxygen does not reach the cell, there is a chance of cramping after the race due to the formation of lactic acid.
Question 5: Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
Answer 5: When we inhale a lot of dust-laden air, the nasal cells get irritated as a reflex response; therefore, dust is thrown out through sneezing.
Question 6: Sometimes, when we do heavy exercise, anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells. What is produced during this process ?
(a) alcohol and lactic acid
(b) alcohol and CO 2
(c) lactic acid and CO 2
(d) lactic acid only
Answer 6 : (d) lactic acid only
During exercise, the body uses oxygen for aerobic respiration at a higher rate; since oxygen is at a limited amount, the body shifts to anaerobic respiration, which gives lactic acid as a by-product.
Question 7: During the process of exhalation, the ribs move
(a) down and inwards.
(b) up and inwards.
(c) down and outwards.
(d) up and outward.
Answer 7: (a) Down and inwards
During exhalation, the diaphragm moves up, and the ribs move downwards and inwards, decreasing the
Space in the chest cavity increases the air pressure inside the lungs, which forces the air out of the lungs.
Question 8: Breathing is a process that
(i) provides O 2 to the body.
(ii) breaks down food to release energy.
(iii) helps the body to get rid of CO 2 .
(iv) produces water in the cells.
Which of the following gives the correct combination of functions of breathing?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer 8 : (c) (i) and (iii)
Breathing is a process that requires the intake of oxygen-rich air and the exhalation of carbon dioxide air, which is expelled from the body with the help of respiratory organs.
Question 9: Which gas present in the air is essential for aerobic respiration? What is the role of oxygen during respiration?
Answer 9: Atmospheric oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration and to help break down food to release energy.
Question 10: Whenever we feel drowsy or sleepy, we start yawning. Does yawning help us in any way?
Answer 10: Whenever we feel drowsy or sleepy, we start yawning, and our respiration rate slows down. As our lungs do not get enough oxygen, we yawn, bringing an extra supply of oxygen-rich air to the lungs and delivering it to the brain, helping us to stay awake.
Question 11: A food stall owner was preparing dough for making bhaturas. He added a pinch of yeast and sugar to the dough and left it in a warm place. After a few hours, the dough had risen. There was a sour smell too.
(a) Why did the dough rise?
(b) Why did the dough smell sour?
(c) Why was sugar added to the dough?
(d) What would have happened if the dough was kept in the refrigerator soon after it was prepared?
Answer 11:
- Yeast is present in the dough during respiration to produce CO2, which makes the dough rise.
- Yeast undergoing anaerobic respiration produces alcohol, which gives a sour smell to the dough.
- Sugar acts as a food source for the yeast present in the dough.
- If the dough is kept in the refrigerator, then the yeast will not multiply, hence not releasing alcohol and co2, making the dough rise and have a sour smell.
Question 12:Paheli participated in a 400 m race competition at her school and won the race. When she came home, she had mixed feelings of joy and pain as she had cramps in her leg muscles. She was relieved of the pain after a massage. Answer the following questions related to the situation.
(a) What could be the possible reasons for the pain in her legs?
(b) Why did she feel comfortable after a massage?
Answer 12 :
- Pain in her legs is caused by an accumulation of lactic acid in her muscles, formed due to anaerobic respiration during her intense physical exercise.
- She felt comfortable after the massage as the massage improves blood circulation, thereby increasing the blood flow and eliminating the lactic acid, breaking it down into CO2 and water.
Question 13: Insects and the leaves of a plant have pores through which they exchange gases with the atmosphere. Can you write two points of differences between these pores with respect to their position, number and extension into the body?
Answer 13: Two points of difference between these pores with respect to their position, number, and extension into the body are:
- The spiracles in insects can be found on the sides of the insect’s body, while the stomata in plants are present on the lower surface of the leaves in plants.
- Insects’ spiracles are lesser in number as compared to stomata in plants.
- Spiracles are a part of an extensive network of a tracheal system which is absent in the leaves.
Question 14: Explain the process of breathing.
Answer 14: The air inhaled is transported to every part of the body and ultimately is transported to every cell in the body. The oxygen in the air helps in the breakdown of food in the cells to release energy. This process is called cellular respiration.
Question 15: Define cellular respiration.
Answer 15: The oxygen in the air we inhale is transported to every part of the body and every cell through capillaries. Oxygen is needed in the breakdown of food. This process of breakdown of food in the cell for the release of energy is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration occurs in the cells of every organism.
Question 16: Define respiration in plants.
Answer 16: Plants take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide through tiny pores called stomata, situated in the back of the leaves. Oxygen is used to break down glucose into carbon dioxide and water inside the cell.
Question 17: What is the total percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the inhaled air and exhaled air?
Answer 17: The percentage of oxygen in inhaled air is 21% and carbon dioxide is 0.04%, respectively, and the percentage of oxygen in exhaled air is 16.4% and carbon dioxide is 4.4%, respectively.
Question 18: Explain respiration in
1) Cockroach
2) Earthworm
Answer 18:
- Cockroach: Cockroaches have a small opening on the side of their bodies known as spiracles. Through spiracles, oxygen-rich air rushes through the tracheal tube and diffuses into the body tissue to reach every cell in the body. In the same way, carbon dioxide-rich blood from a cell enters tracheal tubes and exits the body through spiracles through the process of diffusion.
- Earthworm: The earthworm breathes through the skin. The skin of earthworms is moist and slimy. Oxygen enters the body of the earthworm through diffusion and exits in a similar way.
Question 19: Explain respiration in aquatic animals.
Answer 19: Aquatic animals have special projections of the skin (organs ) called gills that help them use oxygen dissolved in water. Gills are rich in blood vessels to help in the diffusion of gases.

Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10
The topics covered in Science Chapter 10 Class 7 Important Questions will be the foundation for the concepts that will be covered in the chapters of Class 11. Therefore, it is advised for students to practise Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 to ensure a strong conceptual understanding of all the concepts covered in Class 7 Science.
A few of the benefits of solving questions from our list of Important Questions Class 7 Chapter 10 are listed below:
- The question bank contains questions from the NCERT textbook, NCERT exemplar, past years’ question papers, and various other reference books. While going through these questions, students will get to access their knowledge about different topics in the chapter. While solving these questions, students will be able to revise the whole chapter, covering the entire syllabus.
- Important Questions Class 7 Chapter 10 is a set of questions created by subject experts solely for the purpose of assisting students in their exam preparation. There is a good possibility of these questions appearing in exams. It makes it easier for the students to answer problems by practising these questions in advance.
- Chapter 10 Class 7 Science Important Questions contains questions in various formats through which students can get access to various materials required for exam preparation based on their needs. They can work on understanding concepts in terms of a broader spectrum of topics by searching across the Extramarks website after registration.
- Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 includes MCQs, short answer type questions, long answer type questions and reasoning type questions which enables students with a wider variety of ways to strengthen their preparation during exams.
Extramarks provides comprehensive learning solutions for students from Class 1 to Class 12. We have abundant resources available on our website, along with essential questions and answers. Students can click on the links given below to access some of these resources:
- NCERT books
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question paper
- Important Formula from Mathematics and Science
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Why does a muscle cramp occurs ?
Muscle cramp occurs due to the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles.
Q.2 How many pairs of spiracles are present in cockroaches?
In cockroaches, the number of spiracles is 20 (10 pairs).
Q.3 Choose the CORRECT match pair(s). I. Roots of a mango tree – Stomata II. Herbaceous plants – Lenticels III. Woody plants – Lenticels IV. Frogs– Skin
The roots of the mango tree take air present in between the particles of soil. Herbaceous plants take air through stomata present on the surface of leaves.
Q.4 Give a brief account of respiratory system of humans.
The respiratory system of humans includes following parts: I. Nostrils: Our nose have two nostrils. These connect the external environment with the internal parts of body. They are involved in taking in the air. II. Nasal cavity: The passage in the nose behind the nostrils is called nasal cavity. III. Trachea: Nasal cavity leads into the trachea which is a long, tubular structure that leads into the lungs. IV. Lungs: These are the major respiratory organs of humans. Lungs contain tiny, round cells called alveoli. Through these cells, the process of gaseous exchange takes place.
Please register to view this section
Faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. what are the three components of respiration.
The three components are molecular oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water.
2. What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is when the cells break down glucose to extract energy and release carbon dioxide as a by-product.
3. How can we overcome exam fear?
To get rid of exam fear, you should get the basics of the chapter, that is, conceptual knowledge. Students can improve their understanding of the chapter by revising and also by solving chapter-specific questions. The more questions a student can solve, the more familiar they become with the concepts covered in those questions.
The next step is to practise solving Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 to get used to writing answers with accuracy to help gain good scores on exams. Students can further refer to CBSE revision notes by Extramarks to help them revise the whole chapter and get all the important topics at their fingertips.
4. List all the chapters from Class 7 Science.
Below is a complete list of all chapters covered in the CBSE syllabus from Class 7 Science:
- Chapter-1 Nutrition In Plants
- Chapter-2 Nutrition In Animals
- Chapter-3 Fibre To Fabric
- Chapter-4 Heat
- Chapter-5 Acids Bases And Salts
- Chapter-6 Physical And Chemical Changes
- Chapter-7 Weather Climate And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate
- Chapter-8 Winds Storms And Cyclones
- Chapter-9 Soil
- Chapter-10 Respiration In Organisms
- Chapter-11 Transportation In Animals And Plants
- Chapter-12 Reproduction In Plants
- Chapter-13 Motion And Time
- Chapter-14 Electric Current And Its Effects
- Chapter-15 Light
- Chapter-16 Water A Precious Resource
- Chapter-17 Forests Our Lifeline
- Chapter-18 Wastewater Story
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Current and Its Effects
- 7th June 2023
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Current and Its Effects are provided here to help students in understanding the topic thoroughly. All these solutions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation. Class 7 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 10 includes all the textbook exercise questions and answers. These solutions will help students complete their assignments & homework.
Class 7 Science Electric Current and Its Effects Questions and Answers
Exercise Questions
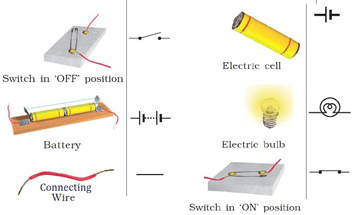
Question 1: Draw in your notebook the symbols to represent the following components of electrical circuits: connecting wires, switch in the ‘OFF’ position, bulb, cell, switch in the ‘ON’ position, and battery
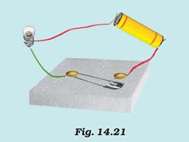
Question 2: Draw the circuit diagram to represent the circuit shown in Fig.14.21.
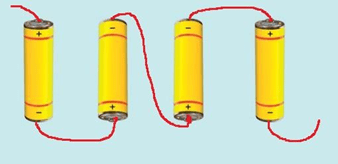
Question 3: Fig.14.22 shows four cells fixed on a board. Draw lines to indicate how you will connect their terminals with wires to make a battery of four cells.

Answer: To make a battery of cells, the positive terminal (+) of one cell always be connected to negative terminal (-) of another cell.
Question 4: The bulb in the circuit shown in Fig.14.23 does not glow. Can you identify the problem? Make necessary changes in the circuit to make the bulb glow.
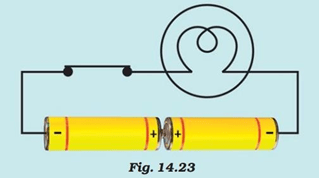
Answer: The positive terminal (+) of one cell always be connected to the negative terminal (-) of another cell. Here the two positive terminals are connected to each other. The correct arrangement is as follows:
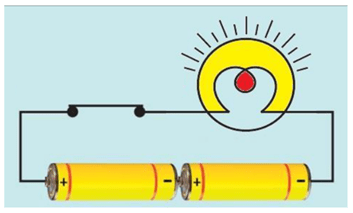
Question 5: Name any two effects of electric current.
Answer: The two effects of electric current are (i) Heating effect of electric current (ii) Magnetic effect of electric current
Question 6: When the current is switched on through a wire, a compass needle kept nearby gets deflected from its north-south position. Explain.
Answer: The current-carrying wire produces a magnetic field around it. When a compass is kept nearby this wire, the two magnetic field (magnetic field due to wire and magnetic field due to compass) interact with each other causing deflection in the magnetic needle. When the current is switched off, there is no magnetic field produced by the wire, the magnetic needle does not deflect from its north-south position.
Question 7: Will the compass needle show deflection when the switch in the circuit shown by Fig.14.24 is closed?
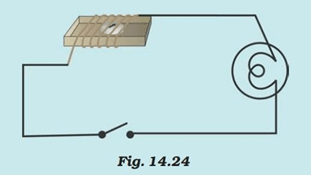
Answer: No. The given circuit does not have any current source. In the absence of current, the wire does not behave as a magnet and hence, the compass needle will not show any deflection.
Question 8: Fill in the blanks:
(a) Longer line in the symbol for a cell represents its ___________terminal (b) The combination of two or more cells is called a ____________. (c) When current is switched ‘on’ in a room heater, it ___________. (d) The safety device based on the heating effect of electric current is called a _____________.
Ans .(a) positive (b) battery (c) produces heat (d) fuse.
Question 9: Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ it is a false:
(a) To make a battery of two cells, the negative terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the other cell. [T/F] (b) When the electric current through the fuse exceeds a certain limit, the fuse wire melts and breaks. [T/F] (c) An electromagnet does not attract a piece of iron. [T/F] (d) An electric bell has an electromagnet. [T/F]
Answer: (a) False (b) True (c) False (d) True
Question 10: Do you think an electromagnet can be used for separating plastic bags from a garbage heap? Explain.
Answer: No, electromagnets can only attract magnetic materials. Plastic bag is a non-magnetic material and will not be attracted by an electromagnet. Hence, an electromagnet cannot be used for separating plastic bags from a garbage heap.
Question 11: An electrician is carrying out some repairs in your house. He wants to replace a fuse by a piece of wire. Would you agree? Give reasons for your response.
Answer: It is not a wise idea to replace fuse by a piece of wire, as it has very low melting point. In case of metal piece, melting point will be high and the circuit will be intact in case there is overload or overheat.
Question 12: Zubeda made an electric circuit using a cell holder, a switch and a bulb. When she put the switch in the ‘ON’ position, the bulb did not glow. Help Zubeda in identifying the possible defects in the circuit.
Answer 12: Possible reasons are as follows:
- The bulb may be fused or defective.
- Cells are not connected properly.
- There may be loose connections.
- The switch is not functioning well.
- The cells are dried up i.e. the power of the cell has been exhausted.
Question 13: In the circuit shown in Fig. 14.25
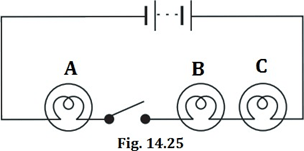
(i) Would any of the bulb glow when the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position?
(ii) What will be the order in which the bulbs A, B and C will glow when the switch is moved to the ‘ON’ position?
Answer: (i) None of the bulb will glow when the switch is in the OFF position, since the electric circuit is not closed.
(ii) When the switch is moved to ‘ON’ position, circuit is complete and electric current will flow immediately. All of the bulbs will glow instantly.
Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Current and Its Effects provided by CBSE Path help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in the exams. All the solutions provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10 - Electric Current and Its Effects
- Class 7 Important Question
- Chapter 14: Electric Current And Its Effects

CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter-10 Important Questions Electric Current and Its Effects - Free PDF Download
Chapter 10 Class 7 Science is based on the topic of electric current and its effects. It gives students the basic idea about the flow of electric current. Important questions include the function of electric fuse, Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB), symbols of electrical components, magnetic effect of electric current, the heating effect of electric current, electromagnet, electric bell, etc. These topics play an essential role in examinations. It is crucial to practice the symbols, circuit diagrams, formulae and problems to score good marks. Solving important questions on electric current helps in knowing essential topics in depth. It also helps in gaining critical concepts. Register Online for NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE board examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,they can download Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Study Important Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 – Electric Current and its Effect
Very short answer questions: 1 mark.
State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, correct the statement.
1. Cells connected in a series form a battery.
2. In a battery the positive terminal of one cell should connect to the positive terminal of the other cell.
Ans: False. We connect the positive terminal of one cell with the negative terminal of another cell.
3. The circuit shown in the picture above is correctly represented by the diagram.
4. The bulb will glow in the following circuit diagram.
Ans: False. In the given circuit switch is off and as a result the bulb will not glow.
5. The electric bulb contains a thin wire called the fuse which glows when electricity passes through it.
Ans: False. The thin wire present inside the bulb which glows is called filament.
6. A piece of nichrome wire will get heated when electricity passes through it.
7. The coil of wire in an electric room heater that gets heated is called the element.
8. The amount of heat produced in a wire is independent of its length, thickness and material.
Ans: False. Amount of heat produced is dependent on length, thickness and material.
9. Thomas Edison was the first person to notice that the compass needle deflected each time electric current was passed.
Ans: False. The first person to notice compass needle deflection was Hans Christian Oersted.
10. The electric bell works on the principle of electromagnetism.
Short Answer Questions: 3 Marks
11. Explain the function of the electrical fuse in a circuit.
Ans: Fuse is made up of material having low melting point. The main function of a fuse is to break the circuit if there is overflow of current and prevent fire. The fuse protects electrical wires and appliances from damage from excess current.
12. What is MCB? What is its Function?
Ans: MCB is the abbreviation for Miniature Circuit Breaker. It is a tool that is used in place of a fuse. MBC automatically breaks the circuit if it exceeds the safe limit of current passing through it to prevent fire and other damage. MCB can be turned on manually
13. Give an example to show that we use the heating effect of electric current in our daily lives.
Ans: The use of heaters and geysers is an example of the heating impact of electric current. These instruments contain a thick coil of wire called heating elements. When electricity is passed through them these wires start glowing red and produce heat. Hence, heat is generated with the help of electric current.
14. Why does an electric bulb get fused?
Ans: A filament is an extremely tiny wire found within an electric bulb. When electricity is passed through a filament, it heats up and glows, emitting light. The filament, on the other hand, is a thin wire. When too much electric current is passed through the filament, or when it is passed through the filament repeatedly, it becomes too hot and breaks. This results in fusing of the bulb.
15. Draw the circuit diagram for the following circuit.
Ans: Below is the circuit diagram:
Long Answer Questions: 5 Marks
16. What is an electromagnet?
Ans: An electromagnet is a temporary magnet that is formed because of the magnetic effect of electric current. When electric current passes through a wire it behaves like a magnet. The strength of an electromagnet depends on the amount of current passing through it. Electromagnets show all the property of a magnet such as:
Attractive Properties
Repulsive Properties
They also point in a north-south direction when suspended freely.
Electromagnets are used in large cranes in junkyards to separate iron or any other magnetic object from the garbage.
17. Explain the working of an electric bell.
The electric bell consists of a coil of wire wound around a magnetic material like iron. The iron material is connected to a hammer at one end and a screw at the other end.
When we press the switch electric current flows through the coil and iron core gets magnetised and behaves as electromagnet.
Magnetic field created by this iron pulls the clapper towards themselves.
As a response the clapper strikes the gong and we hear the ringing of a bell.
The striking of gong breaks the circuit and the magnetic field is lost.
The clapper returns to its original place.
This process is repeated every time we switch it on and current flows through the circuit.
Important Questions for Class 7 Science Electric Current and its Effects
The chapter Electric Current And Its Effects Class 7 Science is essential as it builds the concepts for higher classes and more advanced topics to be studied further. Concepts like representing electric components by symbols, drawing circuit diagrams, the heating effect of current and its applications, electric fuse and Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB), magnet-like behaviour of electric current while flowing through a wire, electromagnet, applications of electromagnets, etc. is discussed. Solving important questions is helpful from an exam point of view as it gives an overview of the problems and important topics of the chapter. It also helps students to know their weak parts, so that they can take special care in those topics.
In What Ways Solving Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Important Questions 14 Help You?
Class 7 Science Chapter 10 important questions help in the following ways:
It saves students from mugging up the entire chapter. Important questions consist of essential topics and concepts which are important from an exam point of view.
It helps students understand concepts in-depth and in a short period as students need not mug up the entire chapter.
It creates a perfect learning environment for the students to learn and understand topics in a better way.
By practising questions on crucial topics, students must understand essential points and concepts better.
Students can also analyse their weak parts or topics which need extra attention from them. They can understand these topics in the chapter.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Solved Examples
Following are some solved examples on Class 7 Science Chapter 10 important questions:
Q. Name any two effects that are caused due to electric current.
(i) Heating effect of electric current.
(ii) Magnetic effect of electric current.
Q. A compass needle kept near a wire gets deflected from its north-south position when the current is switched on through a wire. Explain.
Solution: When the current is passing through a wire around, the magnetic field deflects the compass needle kept nearby.
Q. Can an electromagnet be used for separating plastic bags from a garbage heap? Explain.
Solution: The property of attraction does not apply for plastics and therefore an electromagnet cannot separate them.
Q. Some repairs are carried out in your house by an electrician. A fuse is to be replaced by a piece of wire. Would you agree? Give reasons for your response.
Solution: As a wire has a shallow melting point, it is not wise to replace the fuse by a piece of wire. The melting point will be high for metal, and the circuit will be intact if there is overload or overheat.
Q. Fill in the blanks:
(a) _ _ _ is represented by the long line in the symbol of a cell.
(b) Two or more cells combined is called a _ _ _.
(c) In a room heater, when current is switched 'on', it _ _ _.
(d) The safety device is called a _ _ _ which is based on the heating effect of electric current.
(a) The positive terminal is represented by the long line in the symbol of a cell.
(b) Two or more cells combined is called a battery.
(c) In a room heater, when current is switched 'on', it produces heat.
(d) The safety device is called a fuse which is based on the heating effect of electric current.
What are the Benefits of Important Questions from Vedantu for Class 7 - Electric Current and Its Effects?
Discover the advantages of Important Questions from Vedantu for Class 7 - Electric Current and Its Effects Science! These targeted questions offer focused insights, enhancing your understanding and preparation for this key science topic.
Focus on key topics for efficient studying.
Prepares students for exams and reduces anxiety.
Reinforces understanding of fundamental concepts.
Teaches effective time management.
Enables self-assessment and progress tracking.
Strategic approach for higher scores.
Covers a wide range of topics for comprehensive understanding.
Supports exam preparation and boosts confidence.
Electric Current and Its Effects is an integral part of Class 7 Science and plays a crucial role from an examination perspective. The important questions for Class 7 Science, as discussed by NCERT, cover a wide range of topics within the subject. They also provide a concise guide to critical points and details related to the topic.
A solid understanding of each section of Class 7 Science is fundamental as it forms the basis for higher-level studies. However, this section primarily focuses on important questions within the context of Class 7 Science.
FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10 - Electric Current and Its Effects
1. What is an Electromagnet?
A temporary magnet formed because of the magnetic effect of the electric current is known as an electromagnet. A wire behaves like a magnet only when an electric current passes through it. This property is used in making strong magnets called an electromagnet. Coils of wires show magnetic properties when electricity is passed through them. A magnetic field is produced around them. Magnet's strength depends upon the power of the electric current passed through it.
They are used in large cranes to lift large loads. They are also used in separating iron and other magnetic particles from a mixture. Doctors also use tiny electromagnets to take out pieces of magnetic particles from the body or the eye during surgery.
2. Explain the Working of an Electric Bell's Components, that is, the Iron Material, the Screw, and the Hammer.
A coil of wire when wound around a magnetic material like iron, it shows the basic structure of an electric bell. The iron material has a hammer at one end and a screw at the other. When the iron material is in contact with the screw, electricity passes through the wire coil, causing it to become an electromagnet. This electromagnet then pulls the iron material, which then strikes the hammer of the gong to produce a sound. During the process, when the iron material strikes the gong, it breaks contact with the screw and the circuit breaks. Thus, the electricity stops flowing, and the material returns to its original position.
3. Why does an electric bulb get fused?
A filament is a very small wire that is present inside an electric bulb. A filament warms up and illuminates as energy is delivered through it, generating light. On the other side, the filament is a thin wire. The filament grows too warm and breaks when excess electricity is put through it, or when it is passed through it continually. The bulb will fuse as a result of this. To know more and practice questions students can download the vedantu app.
4. What is an electromagnet?
An electromagnet is a transient magnet created by the magnetic action of electric discharge. The flow of electric current through a coil encircling a soft metal core turns it into an electromagnet. A wire acts as a magnet when electric current flows through it. The total current flowing through an electromagnet determines its strength. Large excavators in scrapyards utilize electromagnets to remove iron or any other magnetic item from the rubbish. For a detailed explanation of Class 7 Science Chapter 10, visit Vedantu website (vedantu.com).
5. What is the magnetic effect of current?
The current-carrying wire acts as a magnet when electric current travels through it. The magnetic effect of current is what it's called. The magnetic effect of current is the basis for the operation of an electric motor. When put in a magnetic field, a current-carrying conductor receives force and spins. Fleming's Left-Hand Rule can be used to identify the direction of the conductor's rotation. There are many appliances that use the magnetic effect of electricity such as:
Loudspeakers
Electric fan
Telephone instruments
6. What is a compass in a magnetic field?
A compass is a watch-like gadget that uses the magnetic field created within the earth to display direction. The needle of a compass is a small magnet that always points north-south. When a compass is placed closer to a magnet or a current-carrying circuit, the pointer is diverted by the magnetic field created by both. When the current is reversed, the magnetic field is reversed as well. To know more, solve the important questions by visiting the page Important questions for Class 7 Science and download a free PDF of the same.
7. Is chapter Electric Current And Its Effects Class 7 Science important?
Electric Current And Its Consequences is a chapter in the book Electric Current and Its Effects in Science for Class 7 and is important since it lays the foundation for higher classes and more sophisticated topics to be studied subsequently. Electric components are represented by symbols and circuit diagrams. The Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB), the heating impact of current, and its implementations are discussed. Electric fuses and electromagnets are also discussed. It has also given an overview of the magnet-like actions of electric charge while flowing through a cable.


- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Control and Coordination
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 7 control and coordination.

CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Control and Coordination. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Control and Coordination.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 7
Case study : 1.
If the body design in the squirrel relied only on electrical impulses via nerve cells, the range of tissues instructed to prepare for the coming activity would be limited. On the other hand, if a chemical signal were to be sent as well, it would reach all cells of the body and provide the wideranging changes needed. This is done in many animals, including human beings, using a hormone called adrenaline that is secreted from the adrenal glands.
i) which is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone?
Ans: Heart is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone which increases the heartbeat rate.
ii) Which hormone is released by thyroid gland?
Ans: Thyroxine is released by thyroid gland.
iii) What is the function of thyroxine hormone?
Ans: It regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body and promote the best balance for growth.
iv) Name the hormone released by ovary?
Ans: Estrogen and progesterone
V) Name the three hormonal glands located in the brain?
Ans: Pineal, pituitary and hypothalamus
CASE STUDY : 2
Some plants like the pea plant climb up other plants or fences by means of tendrils. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it. More commonly, plants respond to stimuli slowly by growing in a particular direction. Because this growth is directional, it appears as if the plant is moving.
i) How many type of tropism are shown by plants? Name them.
Ans: Generally there are 6 type of tropism namely phototropism, gravitropism, chemotropism, thigmotropism, thermotropism and hydrotropism.
ii) The touch me not plant is an example of which tropism?
Ans: it is an example of thigmotropism.
iii) give one example of chemotropism?
Ans: growth of pollen tubes to wheels is one example of chemotropism.
iv) Name the plants hormone which promotes cell division?
Ans: Cytokinins promotes cell division in plants.
v) Name the plant hormone which inhibits growth?
Ans: Abscisic acid
CASE STUDY : 3
We also think about our actions. Writing, talking, moving a chair, clapping at the end of a programme are examples of voluntary actions which are based on deciding what to do next. So, the brain also has to send messages to muscles. This is the second way in which the nervous system communicates with the muscles. The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial nerves arising from the brain and spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord. The brain thus allows us to think and take actions based on that thinking.
i) what are the three major parts of the brain?
Ans: Forebrain, Midbrain and hindbrain.
ii) what are the function of medulla?
Ans: It controls all the involuntary action such as blood pressure, salivation, vomiting, etc.
iii) Which fluid is present in our brain?
Ans: Cerebrospinal fluid.
iv) What is the function of hypothalamus?
Ans: It regulates homeostasis, releases hormones.
v) What is the function of mid brain?
Ans: The mid brain connects the forebrain and hindbrain.
CASE STUDY : 4
Body consists of dense networks of intricately arranged neurons. It sits in the forward end of the skull, and receives signals from all over the body which it thinks about before responding to them. Obviously, in order to receive these signals, this thinking part of the brain in the skull must be connected to nerves coming from various parts of the body.
i) What is reflex?
Ans: It is the sudden action done in response to something in the environment.
ii) How does the nervous tissue cause action?
Ans: When a nerve impulse reaches the muscles, the muscles fibres move by changing their shape and their arrangements in the cell.
iii) What is the function of the motor neuron?
Ans: It transmits the impulses from spinal cord to skeletal muscles.
iv) What is reflex arc?
Ans: It is the neural pathway that controls reflex starting from a sensory neuron and end at effector.
v) What is the role of sensory neuron?
Ans: It carry signals from outer part of body to central nervous system.
CASE STUDY : 5
In animals, such control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Touching a hot object is an urgent and dangerous situation for us. We need to detect it, and respond to it. How do we detect that we are touching a hot object? All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells. These receptors are usually located in our sense organs, such as the inner ear, the nose, the tongue, and so on. So gustatory receptors will detect taste while olfactory receptors will detect smell.
i) What are the parts of neuron?
Ans: Dendrite, nucleus, axon, nerve ending and a cell body.
ii) Which part of neuron receive the information first?
Ans: Dendritic tip receive the information first.
iii) At which place the electrical impulse get converted to a chemical impulse?
Ans: At synapse or a gap between nerve ending and a dendritic tip.
iv) What is neuromuscular junction?
Ans: The neuromuscular is made up of two words neuron & muscles, so it is the place where neuron and muscle fibre meet.
v) Draw the picture of neuron?
For more update follow net explanations page
Thnx for more confidence
Tomorrow I having my science exam and I am having 7 ch pending… please pray for me… that the paper has to be too easy for me….
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Kerala scert class 5 science sky near at hand question answer, kerala scert class 5 english arya in the cockpit question answer, kerala scert class 5 ict let’s search the internet question answer, the disk class 12 mcq | paradise elective english.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jul 22, 2023 · [Download] Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 7 science chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms. Case Study/Passage Based Questions Passage-1 Respiration is a basic characteristics of all living beings. It is an energy releasing reaction. The living cells break … Continue reading Case ...
Oct 22, 2024 · Reading Time: 10 minutes Last Updated on October 22, 2024 by XAM CONTENT. Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board.
CBSE Class 7 Science Case Study Question. Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Case Study Question; Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Case Study Question; Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric Case Study Question; Chapter 4 Heat Case Study Question; Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Case Study Question; Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Case Study Question
Case Study Questions Class 7 Science Respiration in Organisms
Jul 12, 2022 · Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: Read the case/passage and answer the questions given below. To carry out a simple function such as eating food there has to be coordination of the eyes, hands and the mouth. The eyes have to focus on the food, the hands … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and ...
Extra questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration In Organisms with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by ...
The topics covered in Science Chapter 10 Class 7 Important Questions will be the foundation for the concepts that will be covered in the chapters of Class 11. Therefore, it is advised for students to practise Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 to ensure a strong conceptual understanding of all the concepts covered in Class 7 Science.
Jun 7, 2023 · NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Current and Its Effects are provided here to help students in understanding the topic thoroughly. All these solutions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation. Class 7 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 10 includes all the textbook exercise questions and answers.
Free PDF download of Important Questions with solutions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 10 - Electric Current and Its Effects prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register online for Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in your examination.
Oct 14, 2022 · At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 7 CASE STUDY : 1