- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to Identify

Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to Identify
Table of Contents
A research gap is an essential concept in academic and scientific research, representing areas where existing knowledge is limited, contradictory, or absent. Identifying and addressing research gaps is critical for advancing knowledge, contributing new insights, and ensuring the relevance of research studies. This article provides an in-depth exploration of research gaps, their types, real-world examples, and methods for identifying them effectively.

Research Gap
A research gap refers to unexplored or underexplored areas within a research field, where questions remain unanswered, inconsistencies exist, or insufficient evidence is available. It signifies an opportunity for researchers to investigate and contribute new insights that address these deficiencies.
For instance, while there might be substantial research on the effects of exercise on physical health, a gap may exist regarding its impact on mental health among specific demographics, such as elderly populations.
Types of Research Gaps
Research gaps can be categorized based on the nature of the knowledge deficit. Below are the primary types:
1. Knowledge Gap
A knowledge gap occurs when there is insufficient or outdated information on a topic. This may arise in rapidly evolving fields or subjects that have not been extensively studied.
- Example : Limited research on the long-term environmental impact of biodegradable plastics.
2. Evidence Gap
This gap exists when research findings are inconclusive, contradictory, or lack sufficient empirical evidence to support claims.
- Example : Conflicting studies on the effectiveness of mindfulness meditation in reducing anxiety.
3. Methodological Gap
Methodological gaps occur when existing research uses inadequate or outdated methods, leaving room for new approaches to yield more reliable or comprehensive results.
- Example : Most studies on workplace productivity rely on self-reported surveys, but few use objective performance metrics.
4. Contextual Gap
This type of gap arises when research focuses on a general context but neglects specific settings, populations, or regions.
- Example : Extensive studies on e-learning effectiveness in urban areas but limited research on rural schools.
5. Theoretical Gap
A theoretical gap occurs when existing frameworks or theories fail to explain certain phenomena, or when no theory has been developed for a particular topic.
- Example : Lack of a unified theory explaining the psychological impact of social media use across different age groups.
6. Practical Gap
Practical gaps exist when research does not address real-world applications or fails to provide actionable recommendations.
- Example : Studies on renewable energy technologies often lack insights into cost-effective implementation strategies for small businesses.
7. Population Gap
This gap occurs when certain groups, such as minorities, children, or elderly populations, are underrepresented in research.
- Example : Limited studies on the effectiveness of digital health interventions for individuals with disabilities.
Examples of Research Gaps
Example 1: climate change.
- Knowledge Gap : Insufficient understanding of microplastic accumulation in polar ecosystems.
- Evidence Gap : Contradictory findings on the role of cloud seeding in mitigating global warming.
Example 2: Health Sciences
- Methodological Gap : Most studies on diabetes management rely on short-term data, with few examining long-term adherence to lifestyle changes.
- Contextual Gap : A lack of research on healthcare disparities in low-income countries.
Example 3: Education
- Practical Gap : Studies highlight the benefits of technology-enhanced learning but rarely address challenges such as accessibility and cost.
- Population Gap : Limited research on the impact of remote learning on neurodiverse students.
How to Identify Research Gaps
Identifying research gaps requires a systematic approach to reviewing existing literature, analyzing trends, and understanding the needs of the field. Below are the key steps:
Step 1: Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Review
Review existing research, focusing on:
- Published journal articles.
- Books and book chapters.
- Conference proceedings.
- Theses and dissertations.
Tools to Use :
- Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science.
- University library databases.
What to Look For :
- Areas with limited studies.
- Contradictory findings.
- Repeated conclusions suggesting opportunities for further research.
Step 2: Analyze Recent Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses often highlight research gaps by summarizing current knowledge and identifying areas needing further investigation.
Example : A meta-analysis on exercise and cognitive health may conclude that additional research is needed on specific age groups, such as children or elderly populations.
Step 3: Consult Field Experts
Engage with academics, practitioners, or professionals to identify pressing questions or challenges in the field. Experts often provide insights into practical or theoretical gaps not yet addressed in the literature.
Tip : Attend conferences, workshops, and seminars to stay updated on ongoing discussions in your area of research.
Step 4: Evaluate Methodological Limitations
Examine the methodologies used in existing studies to identify weaknesses or opportunities for improvement.
Example : Many behavioral studies rely on self-reported data, which may introduce bias. A gap exists for research using objective measures or triangulated methods.
Step 5: Identify Trends and Emerging Topics
Stay informed about trends and emerging issues in your field through news articles, blogs, and industry reports. Emerging technologies, policies, or global challenges often create new research opportunities.
Example : The rise of AI in healthcare creates gaps related to ethical considerations, patient privacy, and long-term impact.
Step 6: Examine Underrepresented Populations or Contexts
Focus on populations, regions, or contexts that have received less attention in the literature.
Example : Most studies on remote work focus on developed countries, leaving a contextual gap in understanding its impact in developing economies.
Step 7: Use Citation Analysis
Examine highly cited papers to identify areas where researchers frequently call for further studies. The “limitations” or “future research” sections in articles often highlight research gaps.
Example : A study on social media marketing may conclude with recommendations for further exploration of its impact on small businesses versus large corporations.
Best Practices for Addressing Research Gaps
- Be Specific : Clearly define the gap you intend to address and explain its significance.
- Use Robust Methods : Select methodologies that improve upon previous studies and produce reliable results.
- Collaborate : Engage with multidisciplinary teams to explore gaps from different perspectives.
- Propose Practical Solutions : Where possible, offer actionable recommendations or applications for your findings.
Research gaps represent opportunities for innovation and advancement in any field. By identifying and addressing these gaps, researchers contribute new knowledge, solve pressing problems, and influence practice or policy. Whether through comprehensive literature reviews, expert consultations, or analyzing emerging trends, a systematic approach to finding research gaps ensures the relevance and impact of scholarly work.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Machi, L. A., & McEvoy, B. T. (2021). The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success (4th ed.). Corwin Press.
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., & Papaioannou, D. (2016). Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review (2nd ed.). Sage.
- Cooper, H. (2016). Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis: A Step-by-Step Approach (5th ed.). Sage Publications.
- Ridley, D. (2012). The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . Sage Publications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing...

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Thesis – Outline, Structure and Writing Guide

Research Gap
Ai generator.

A research gap is an area within a field that lacks sufficient information or understanding, highlighting opportunities for further investigation. Identified through literature review, it guides researchers to explore new questions and develop innovative theories. Addressing these gaps advances knowledge and solves real-world problems. In areas like Marketing Gap Analysis , identifying research gaps leads to more effective strategies and improved market performance.
What is a Research Gap?
A research gap is an area within a field of study that lacks sufficient information or understanding, presenting an opportunity for further investigation. It is identified through a thorough review of existing literature and highlights areas where more research is needed. Recognizing these gaps is essential for advancing knowledge, guiding researchers to explore new questions, develop innovative theories, and improve methodologies.
Examples of Research Gap
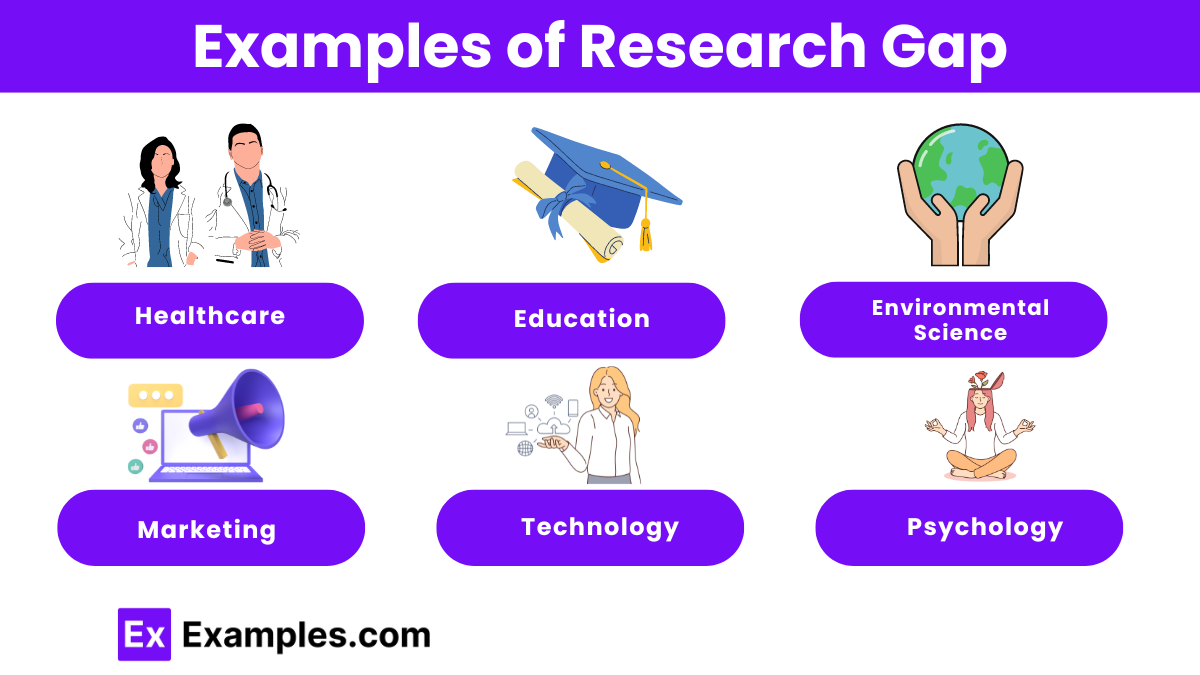
- Healthcare : Limited studies on the long-term effects of telemedicine on patient outcomes, especially in rural areas.
- Education : Insufficient research on the impact of virtual reality in improving student engagement and learning outcomes in primary education.
- Environmental Science : Lack of comprehensive data on the effects of microplastics on marine ecosystems.
- Marketing : Few studies exploring the influence of social media influencers on consumer behavior in emerging markets.
- Technology : Sparse research on the ethical implications of artificial intelligence in workplace decision-making processes.
- Psychology : Limited understanding of the mental health impacts of prolonged social media use among teenagers.
- Economics : Insufficient analysis of the effects of cryptocurrency adoption on traditional banking systems.
- Sociology : Lack of in-depth studies on the long-term effects of remote work on family dynamics and work-life balance.
- Public Health : Few studies examining the effectiveness of community-based interventions in reducing obesity rates among children.
- Renewable Energy : Limited research on the integration of renewable energy sources into existing power grids and their economic impacts.
Different Types of Research Gaps
Research gaps are areas where knowledge is lacking or where existing research could be expanded. Identifying and addressing these gaps is crucial for advancing knowledge in any field. Here are the different types of research gaps:
1. Evidence Gap
Definition : An evidence gap occurs when there is a lack of empirical data to support conclusions or theories. This gap signifies areas where more research is needed to provide solid evidence for or against a hypothesis.
Example : Limited studies on the long-term effects of a new medication.
2. Knowledge Gap
Definition : A knowledge gap refers to a lack of understanding or awareness about a specific topic. This gap often highlights areas where research has not yet been conducted or where findings are inconsistent.
Example : Insufficient knowledge about the impact of social media on mental health among teenagers.
3. Practical-Knowledge Gap
Definition : This gap arises when there is a disconnect between theoretical research and practical application. It points to areas where findings from research have not been implemented in real-world settings or where practical challenges are not addressed by existing research.
Example : Theoretical models for disaster management that are not tested in actual disaster scenarios.
4. Methodological Gap
Definition : A methodological gap is identified when current research methods are inadequate to address certain research questions. This gap indicates the need for new or improved research methods.
Example : The need for longitudinal studies to better understand the progression of chronic diseases.
5. Policy Gap
Definition : A policy gap occurs when research does not inform policy or when there is a lack of research supporting existing policies. This gap often highlights the need for research that can influence or evaluate policy decisions.
Example : Lack of research on the effectiveness of policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
6. Population Gap
Definition : This gap is present when certain populations or demographic groups are underrepresented in research. It calls attention to the need for more inclusive research that considers diverse populations.
Example : Underrepresentation of elderly populations in clinical trials for new medications.
7. Theory Gap
Definition : A theory gap is found when there is a lack of theoretical framework to explain certain phenomena. This gap suggests the need for developing or refining theories to better understand specific issues.
Example : Incomplete theoretical explanations for the rise of extremism in modern societies.
8. Contextual Gap
Definition : A contextual gap exists when research does not take into account the context in which a phenomenon occurs. This gap highlights the need for studies that consider environmental, cultural, or situational factors.
Example : Studies on education methods that do not consider cultural differences in learning styles.
9. Perspective Gap
Definition : This gap arises when certain perspectives or viewpoints are missing from the research. It emphasizes the need for more diverse viewpoints to provide a comprehensive understanding of a topic.
Example : Limited perspectives from minority groups in research on workplace diversity.
10. Data Gap
Definition : A data gap is identified when there is a lack of available data or when existing data is insufficient to support research conclusions. This gap indicates the need for more extensive data collection and analysis.
Example : Insufficient data on climate change impacts in specific geographic regions.
How to write Research Gap
Identifying and articulating a research gap is a crucial step in academic research. It highlights the need for your study and sets the stage for your research question and objectives. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write a research gap:
1. Literature Review
Conduct a thorough literature review to understand the current state of research in your field. Look for recent studies, key theories, and significant findings. Take note of any inconsistencies, unanswered questions, or areas that have not been explored.
2. Identify the Gap
After reviewing the literature, pinpoint the specific areas where research is lacking. This could be due to insufficient evidence, outdated studies, contradictory findings, or unaddressed issues.
3. Justify the Gap
Explain why this gap is important. Discuss the implications of not addressing this gap and how filling it could advance knowledge in your field or solve a practical problem.
4. Formulate Your Research Question
Based on the identified gap, formulate a clear and focused research question. This question should aim to address the gap and guide your study.
5. Contextualize the Gap
Place your research gap within the broader context of your field. Explain how your study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and why it is timely and relevant.
6. Use Clear and Concise Language
When writing about the research gap, be clear and concise. Avoid jargon and ensure that your explanation is understandable to readers outside your immediate field.
How to Identify Research Gap?
Identifying a research gap is essential for developing a relevant and impactful research question. Here are the steps to effectively identify a research gap:
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Review
Start by thoroughly reviewing existing literature in your area of interest. Use academic databases, journals, books, and conference papers to gather information. Focus on:
- Recent studies and their findings
- Key theories and models
- Methodologies used
- Areas of consensus and disagreement
2. Analyze the Literature Critically
While reviewing the literature, critically evaluate the studies. Look for:
- Inconsistencies : Contradictory findings or conclusions
- Outdated Information : Studies that need updating due to new data or advancements
- Methodological Flaws : Weaknesses or limitations in research methods
- Unanswered Questions : Questions that previous studies have raised but not answered
3. Identify Trends and Patterns
Identify trends and patterns in the existing research. Consider:
- Common themes and topics
- Frequently used methodologies
- Populations and settings studied
- Gaps in data and analysis
4. Look for Understudied Areas
Identify topics or subtopics that have not been extensively researched. Pay attention to:
- Emerging fields or new technologies
- Neglected populations or regions
- Interdisciplinary research opportunities
5. Consult Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Review articles and meta-analyses can provide a summary of the current state of research and highlight areas where further research is needed. They often suggest future research directions and gaps.
6. Analyze Research Agendas and Funding Opportunities
Research agendas and funding calls from academic institutions, government agencies, and private organizations can highlight priority areas and identify gaps that need addressing.
7. Discuss with Experts and Peers
Engage in discussions with experts, mentors, and peers in your field. They can provide insights into current research trends and gaps that you might have overlooked.
8. Examine Conference Proceedings
Conference proceedings often contain the latest research and can indicate emerging trends and gaps. Attend conferences and review the abstracts and presentations.
9. Evaluate the Practical Relevance
Consider the practical implications of existing research. Identify areas where research findings have not been applied or where practical challenges remain unaddressed.
10. Formulate Research Questions
Based on the identified gaps, develop specific research questions. These questions should address the gaps and guide your research towards filling them.
Research Gap Uses
1. advancing knowledge.
Filling a research gap helps in advancing the overall knowledge within a field. It allows researchers to build upon existing studies and contribute new insights, theories, or methods.
2. Innovative Solutions
Addressing a research gap can lead to the development of innovative solutions to existing problems. Researchers can explore new approaches, technologies, or applications that have not been previously considered.
3. Funding and Support
Identifying a significant research gap can attract funding and support from academic institutions, government bodies, and private organizations. Funders are often interested in supporting projects that promise new discoveries and advancements.
4. Publishing Opportunities
Research that addresses a gap is often seen as valuable and original, increasing the chances of publication in reputable academic journals. This can enhance the researcher’s profile and credibility within the academic community.
5. Educational Development
For educators and students, identifying research gaps can guide the development of curricula and educational programs. It ensures that teaching materials are up-to-date and relevant to current academic and industry trends.
FAQ’s
Why is identifying a research gap important.
Identifying a research gap helps focus efforts on unexplored areas, advancing knowledge and contributing to the field.
How can I identify a research gap?
Review current literature, analyze findings, and note areas lacking comprehensive studies or conflicting results.
What are the types of research gaps?
Types include evidence gaps, knowledge gaps, practical gaps, theoretical gaps, and methodological gaps.
What is an evidence gap?
An evidence gap exists when there is a lack of empirical data supporting a particular hypothesis or theory.
How does a theoretical gap differ from a practical gap?
A theoretical gap involves missing or underdeveloped concepts, while a practical gap involves real-world issues needing solutions.
What is a methodological gap?
A methodological gap arises when certain methods have not been applied to study a specific problem.
How can conflicting results indicate a research gap?
Conflicting results suggest inconsistencies in findings, pointing to areas needing further investigation.
What is the role of a literature review in identifying research gaps?
A literature review helps identify gaps by summarizing existing studies and highlighting areas needing further research.
Can technology advancements create research gaps?
Yes, new technologies can reveal gaps by enabling studies that were previously impossible or overlooked.
What is the impact of research gaps on funding opportunities?
Identifying significant gaps can attract funding by demonstrating the need for research in unexplored areas.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Call for Articles
- Login

Identifying Research Gaps to Pursue Innovative Research
This article is an excerpt from a lecture given by my Ph.D. guide, a researcher in public health. She advised us on how to identify research gaps to pursue innovative research in our fields.
What is a Research Gap?
Today we are talking about the research gap: what is it, how to identify it, and how to make use of it so that you can pursue innovative research. Now, how many of you have ever felt you had discovered a new and exciting research question , only to find that it had already been written about? I have experienced this more times than I can count. Graduate studies come with pressure to add new knowledge to the field. We can contribute to the progress and knowledge of humanity. To do this, we need to first learn to identify research gaps in the existing literature.
A research gap is, simply, a topic or area for which missing or insufficient information limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question. It should not be confused with a research question, however. For example, if we ask the research question of what the healthiest diet for humans is, we would find many studies and possible answers to this question. On the other hand, if we were to ask the research question of what are the effects of antidepressants on pregnant women, we would not find much-existing data. This is a research gap. When we identify a research gap, we identify a direction for potentially new and exciting research.


How to Identify Research Gap?
Considering the volume of existing research, identifying research gaps can seem overwhelming or even impossible. I don’t have time to read every paper published on public health. Similarly, you guys don’t have time to read every paper. So how can you identify a research gap?
There are different techniques in various disciplines, but we can reduce most of them down to a few steps, which are:
- Identify your key motivating issue/question
- Identify key terms associated with this issue
- Review the literature, searching for these key terms and identifying relevant publications
- Review the literature cited by the key publications which you located in the above step
- Identify issues not addressed by the literature relating to your critical motivating issue
It is the last step which we all find the most challenging. It can be difficult to figure out what an article is not saying. I like to keep a list of notes of biased or inconsistent information. You could also track what authors write as “directions for future research,” which often can point us towards the existing gaps.
Different Types of Research Gaps
Identifying research gaps is an essential step in conducting research, as it helps researchers to refine their research questions and to focus their research efforts on areas where there is a need for more knowledge or understanding.
1. Knowledge gaps
These are gaps in knowledge or understanding of a subject, where more research is needed to fill the gaps. For example, there may be a lack of understanding of the mechanisms behind a particular disease or how a specific technology works.
2. Conceptual gaps
These are gaps in the conceptual framework or theoretical understanding of a subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand the relationship between two concepts or to refine a theoretical framework.
3. Methodological gaps
These are gaps in the methods used to study a particular subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to develop new research methods or to refine existing methods to address specific research questions.
4. Data gaps
These are gaps in the data available on a particular subject. For example, there may be a need for more research to collect data on a specific population or to develop new measures to collect data on a particular construct.
5. Practical gaps
These are gaps in the application of research findings to practical situations. For example, there may be a need for more research to understand how to implement evidence-based practices in real-world settings or to identify barriers to implementing such practices.
Examples of Research Gap
Limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms of a disease:.
Despite significant research on a particular disease, there may be a lack of understanding of the underlying mechanisms of the disease. For example, although much research has been done on Alzheimer’s disease, the exact mechanisms that lead to the disease are not yet fully understood.
Inconsistencies in the findings of previous research:
When previous research on a particular topic has inconsistent findings, there may be a need for further research to clarify or resolve these inconsistencies. For example, previous research on the effectiveness of a particular treatment for a medical condition may have produced inconsistent findings, indicating a need for further research to determine the true effectiveness of the treatment.
Limited research on emerging technologies:
As new technologies emerge, there may be limited research on their applications, benefits, and potential drawbacks. For example, with the increasing use of artificial intelligence in various industries, there is a need for further research on the ethical, legal, and social implications of AI.
How to Deal with Literature Gap?
Once you have identified the literature gaps, it is critical to prioritize. You may find many questions which remain to be answered in the literature. Often one question must be answered before the next can be addressed. In prioritizing the gaps, you have identified, you should consider your funding agency or stakeholders, the needs of the field, and the relevance of your questions to what is currently being studied. Also, consider your own resources and ability to conduct the research you’re considering. Once you have done this, you can narrow your search down to an appropriate question.
Tools to Help Your Search
There are thousands of new articles published every day, and staying up to date on the literature can be overwhelming. You should take advantage of the technology that is available. Some services include PubCrawler , Feedly , Google Scholar , and PubMed updates. Stay up to date on social media forums where scholars share new discoveries, such as Twitter. Reference managers such as Mendeley can help you keep your references well-organized. I personally have had success using Google Scholar and PubMed to stay current on new developments and track which gaps remain in my personal areas of interest.
The most important thing I want to impress upon you today is that you will struggle to choose a research topic that is innovative and exciting if you don’t know the existing literature well. This is why identifying research gaps starts with an extensive and thorough literature review . But give yourself some boundaries. You don’t need to read every paper that has ever been written on a topic. You may find yourself thinking you’re on the right track and then suddenly coming across a paper that you had intended to write! It happens to everyone- it happens to me quite often. Don’t give up- keep reading and you’ll find what you’re looking for.
Class dismissed!
How do you identify research gaps? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Frequently Asked Questions
A research gap can be identified by looking for a topic or area with missing or insufficient information that limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question.
Identifying a research gap is important as it provides a direction for potentially new research or helps bridge the gap in existing literature.
Gap in research is a topic or area with missing or insufficient information. A research gap limits the ability to reach a conclusion for a question.
Thank u for your suggestion.
Very useful tips specially for a beginner
Thank you. This is helpful. I find that I’m overwhelmed with literatures. As I read on a particular topic, and in a particular direction I find that other conflicting issues, topic a and ideas keep popping up, making me more confused.
I am very grateful for your advice. It’s just on point.
The clearest, exhaustive, and brief explanation I have ever read.
Thanks for sharing
Thank you very much.The work is brief and understandable
Thank you it is very informative
Thanks for sharing this educative article
Thank you for such informative explanation.
Great job smart guy! Really outdid yourself!
Nice one! I thank you for this as it is just what I was looking for!😃🤟
Thank you so much for this. Much appreciated
Thank you so much.
Thankyou for ur briefing…its so helpful
Thank you so much .I’ved learn a lot from this.❤️
Very exciting and useful piece for researchers.
Your are awesome, it’s a great article.
Thanks alot. It is very useful
The kind of article I have been looking for. Thanks for this
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications
10 Ways to Help Students Restore Focus on Learning
Switching Your Major As a Researcher: Things to Consider Before Making the Decision

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Plagiarism Checker
- AI Content Detector
- Academic Editing
- Publication Support Services
- Thesis Editing
- Enago Reports
- Journal Finder
- Thought Leadership
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Industry News
- Al in Academia
- Other Resources
- Infographics
- Enago Learn
- On-Demand Webinar
- Open Access Week
- Peer Review Week
- Publication Integrity Week
- Conference Videos
- Call for speakers
- Author Training
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What features do you prefer in a plagiarism detector? (Select all that apply)

🚀 Work With Us
Private Coaching
Language Editing
Qualitative Coding
✨ Free Resources
Templates & Tools
Short Courses
Articles & Videos
How To Find A Research Gap, Quickly
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | April 2023

Overview: Finding Research Gaps
- What exactly is a research gap?
- Research gap vs research topic
- How to find potential research gaps
- How to evaluate research gaps (and topics)
- Key takeaways
What is a research gap?
As a starting point, it’s useful to first define what we mean by research gap, to ensure we’re all on the same page. The term “research gap” gets thrown around quite loosely by students and academics alike, so let’s clear that up.
Simply put, a research gap is any space where there’s a lack of solid, agreed-upon research regarding a specific topic, issue or phenomenon. In other words, there’s a lack of established knowledge and, consequently, a need for further research.
Let’s look at a hypothetical example to illustrate a research gap.
Within the existing research regarding factors affect job satisfaction , there may be a wealth of established and agreed-upon empirical work within a US and UK context , but very little research within Eastern nations such as Japan or Korea . Given that these nations have distinctly different national cultures and workforce compositions compared to the West, it’s plausible that the factors that contribute toward job satisfaction may also be different. Therefore, a research gap emerges for studies that explore this matter.
This example is purely hypothetical (and there’s probably plenty of research covering this already), but it illustrates the core point that a research gap reflects a lack of firmly established knowledge regarding a specific matter . Given this lack, an opportunity exists for researchers (like you) to go on and fill the gap.
So, it’s the same as a research topic?
Not quite – but they are connected. A research gap refers to an area where there’s a lack of settled research , whereas a research topic outlines the focus of a specific study . Despite being different things, these two are related because research gaps are the birthplace of research topics. In other words, by identifying a clear research gap, you have a foundation from which you can build a research topic for your specific study. Your study is unlikely to resolve the entire research gap on it’s own, but it will contribute towards it .
If you’d like to learn more, we’ve got a comprehensive post that covers research gaps (including the different types of research gaps), as well as an explainer video below.
How to find a research gap
Now that we’ve defined what a research gap is, it’s time to get down to the process of finding potential research gaps that you can use as a basis for potential research topics. Importantly, it’s worth noting that this is just one way (of many) to find a research gap (and consequently a topic). We’re not proposing that it’s the only way or best way, but it’s certainly a relatively quick way to identify opportunities.
Step 1: Identify your broad area of interest
The very first step to finding a research gap is to decide on your general area of interest . For example, if you were undertaking a dissertation as part of an MBA degree, you may decide that you’re interested in corporate reputation, HR strategy, or leadership styles. As you can see, these are broad categories – there’s no need to get super specific just yet. Of course, if there is something very specific that you’re interested in, that’s great – but don’t feel pressured to narrow it down too much right now.
Equally important is to make sure that this area of interest is allowed by your university or whichever institution you’ll be proposing your research to. This might sound dead obvious, but you’ll be surprised how many times we’ve seen students run down a path with great excitement, only to later learn that their university wants a very specific area of focus in terms of topic (and their area of interest doesn’t qualify).

Step 2: Do an initial literature scan
Once you’ve pinned down your broad area (or areas) of interest, the next step is to head over to Google Scholar to undertake an initial literature scan . If you’re not familiar with this tool, Google Scholar is a great starting point for finding academic literature on pretty much any topic, as it uses Google’s powerful search capabilities to hunt down relevant academic literature. It’s certainly not the be-all and end-all of literature search tools, but it’s a useful starting point .
Within Google Scholar, you’ll want to do a few searches using keywords that are relevant to your area of interest. Sticking with our earlier example, we could use the key phrase “job satisfaction”, or we may want to get a little more specific – perhaps “job satisfaction for millennials” or “job satisfaction in Japan”.
It’s always a good idea to play around with as many keywords/phrases as you can think up. Take an iterative approach here and see which keywords yield the most relevant results for you. Keep each search open in a new tab, as this will help keep things organised for the next steps.
Once you’ve searched for a few different keywords/phrases, you’ll need to do some refining for each of the searches you undertook. Specifically, you’ll need to filter the results down to the most recent papers . You can do this by selecting the time period in the top left corner (see the example below).

Filtering to the current year is typically a good choice (especially for fast-moving research areas), but in some cases, you may need to filter to the last two years . If you’re undertaking this task in January or February, for example, you’ll likely need to select a two-year period.
Need a helping hand?
Step 3: Review and shortlist articles that interest you
Once you’ve run a few searches using different keywords and phrases, you’ll need to scan through the results to see what looks most relevant and interesting to you. At this stage, you can just look at the titles and abstracts (the description provided by Google Scholar) – don’t worry about reading the actual article just yet.
Next, select 5 – 10 articles that interest you and open them up. Here, we’re making the assumption that your university has provided you with access to a decent range of academic databases. In some cases, Google Scholar will link you directly to a PDF of the article, but in most cases, you’ll need paid access. If you don’t have this (for example, if you’re still applying to a university), you can look at two options:
Open-access articles – these are free articles which you can access without any journal subscription. A quick Google search (the regular Google) will help you find open-access journals in your area of interest, but you can also have a look at DOAJ and Elsevier Open Access.
DeepDyve – this is a monthly subscription service that allows you to get access to a broad range of journals. At the time of shooting this video, their monthly subscription is around $50 and they do offer a free trial, which may be sufficient for your project.
Step 4: Skim-read your article shortlist
Now, it’s time to dig into your article shortlist and do some reading. But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the articles from start to finish – you just need to focus on a few key sections.
Specifically, you’ll need to pay attention to the following:
- The abstract (which you’ve probably already read a portion of in Google Scholar)
- The introduction – this will give you a bit more detail about the context and background of the study, as well as what the researchers were trying to achieve (their research aims)
- The discussion or conclusion – this will tell you what the researchers found
By skimming through these three sections for each journal article on your shortlist, you’ll gain a reasonable idea of what each study was about, without having to dig into the painful details. Generally, these sections are usually quite short, so it shouldn’t take you too long.
Step 5: Go “FRIN hunting”
This is where the magic happens. Within each of the articles on your shortlist, you’ll want to search for a few very specific phrases , namely:
- Future research
- Further research
- Research opportunities
- Research directions
All of these terms are commonly found in what we call the “FRIN” section . FRIN stands for “further research is needed”. The FRIN is where the researchers explain what other researchers could do to build on their study, or just on the research area in general. In other words, the FRIN section is where you can find fresh opportunities for novel research . Most empirical studies will either have a dedicated FRIN section or paragraph, or they’ll allude to the FRIN toward the very end of the article. You’ll need to do a little scanning, but it’s usually pretty easy to spot.
It’s worth mentioning that naturally, the FRIN doesn’t hand you a list of research gaps on a platter. It’s not a silver bullet for finding research gaps – but it’s the closest thing to it. Realistically, the FRIN section helps you shortcut the gap-hunting process by highlighting novel research avenues that are worth exploring.
This probably sounds a little conceptual, so let’s have a look at a few examples:
The impact of overeducation on job outcomes: Evidence from Saudi Arabia (Alzubaidi, 2020)
If you scroll down to the bottom of this article, you’ll see there’s a dedicated section called “Limitations and directions for future research”. Here they talk about the limitations of the study and provide suggestions about how future researchers could improve upon their work and overcome the limitations.
Perceived organizational support and job satisfaction: a moderated mediation model of proactive personality and psychological empowerment (Maan et al, 2020)
In this article, within the limitations section, they provide a wonderfully systematic structure where they discuss each limitation, followed by a proposal as to how future studies can overcome the respective limitation. In doing so, they are providing very specific research opportunities for other researchers.
Medical professionals’ job satisfaction and telemedicine readiness during the COVID-19 pandemic: solutions to improve medical practice in Egypt (El-Mazahy et al, 2023)
In this article, they don’t have a dedicated section discussing the FRIN, but we can deduct it based on the limitations section. For example, they state that an evaluation of the knowledge about telemedicine and technology-related skills would have enabled studying their independent effect on the perception of telemedicine.
Follow this FRIN-seeking process for the articles you shortlisted and map out any potentially interesting research gaps . You may find that you need to look at a larger number of articles to find something interesting, or you might find that your area of interest shifts as you engage in the reading – this is perfectly natural. Take as much time as you need to develop a shortlist of potential research gaps that interest you.
Importantly, once you’ve developed a shortlist of potential research gaps, you need to return to Google Scholar to double-check that there aren’t fresh studies that have already addressed the gap. Remember, if you’re looking at papers from two years ago in a fast-moving field, someone else may have jumped on it . Nevertheless, there could still very well be a unique angle you could take – perhaps a contextual gap (e.g. a specific country, industry, etc.).
Ultimately, the need for originality will depend on your specific university’s requirements and the level of study. For example, if you’re doing an undergraduate research project, the originality requirements likely won’t be as gruelling as say a Masters or PhD project. So, make sure you have a clear understanding of what your university’s expectations are. A good way to do this is to look at past dissertations and theses for your specific programme. You can usually find these in the university library or by asking the faculty.
How to evaluate potential research gaps
Once you’ve developed a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant potential research topics) that interest you, you’ll need to systematically evaluate them to choose a winner. There are many factors to consider here, but some important ones include the following:
- Originality and value – is the topic sufficiently novel and will addressing it create value?
- Data access – will you be able to get access to the sample of interest?
- Costs – will there be additional costs involved for data collection and/or analysis?
- Timeframes – will you be able to collect and analyse the data within the timeframe required by your university?
- Supervisor support – is there a suitable supervisor available to support your project from start to finish?
To help you evaluate your options systematically, we’ve got a topic evaluation worksheet that allows you to score each potential topic against a comprehensive set of criteria. You can access the worksheet completely free of charge here .

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered quite a lot of ground in this post. Here are the key takeaways:
- A research gap is any space where there’s a lack of solid, agreed-upon research regarding a specific topic/issue/phenomenon.
- Unique research topics emerge from research gaps , so it’s essential to first identify high-quality research gaps before you attempt to define a topic.
- To find potential research gaps, start by seeking out recent journal articles on Google Scholar and pay particular attention to the FRIN section to identify novel opportunities.
- Once you have a shortlist of prospective research gaps and resultant topic ideas, evaluate them systematically using a comprehensive set of criteria.
If you’d like to get hands-on help finding a research gap and research topic, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey, step by step.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
Very useful for me, but i am still confusing review of literature review, how to find out topic related previous research.
Powerful notes! Thanks a lot.
This is helpful. Thanks a lot.
Thank you very much for this. It is really a great opportunity for me to learn the research journey.
Very Useful
It nice job
You have sharpened my articulations of these components to the core. Thanks so much.
It’s educative and an inspiring way of impacting research knowledge…
Thanks to the writer
Excellent professional advice on the research gap. This is crucial because it highlights the need for research. Without it, there is no need to proceed.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

How to identify research gap in literature review?
How to Identify a Research Gap in a Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide
Identifying a research gap is a crucial step in the research process, as it helps researchers to identify an area that needs further investigation. A literature review is a comprehensive and systematic analysis of the existing research on a particular topic, and it is essential to identify the gaps in the existing knowledge to determine the direction of future research. In this article, we will discuss how to identify a research gap in a literature review.
Understanding the Importance of Identifying a Research Gap
- To address research questions : A research gap helps to focus research questions and provide a clear direction for future studies.
- To avoid duplication of work : Identifying a research gap ensures that research does not duplicate existing work, thus avoiding wasting resources.
- To make a meaningful contribution : A research gap helps to make a meaningful contribution to the field by addressing a crucial knowledge gap.
Identifying a Research Gap: A Step-by-Step Approach
Table of Contents
Step 1: Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Review
- Search for relevant articles : Search for articles in academic databases, journals, and books.
- Assess the relevance of articles : Evaluate the relevance of articles to the research topic and focus on the most significant and recent studies.
Step 2: Analyze and Synthesize the Literature
- Identify research questions and themes : Identify the research questions and themes that emerge from the literature review.
- Identify gaps and inconsistencies : Identify gaps and inconsistencies in the existing literature.
- Synthesize the findings : Synthesize the findings to identify patterns, trends, and relationships.
Step 3: Identify the Research Gap
- Use a conceptual framework : Use a conceptual framework to analyze the literature and identify the research gap.
- Use a theoretical framework : Use a theoretical framework to analyze the literature and identify the research gap.
- Use a meta-analysis : Use a meta-analysis to synthesize the results of previous studies and identify the research gap.
Significant Points to Consider
- Quality of the studies : The quality of the studies should be high to ensure that the results are reliable and valid.
- Relevance of the topics : The topics should be relevant to the research question and focus on the most significant and recent studies.
- Methodological limitations : The methodological limitations of the studies should be considered when identifying the research gap.
Tools and Techniques to Identify a Research Gap
- Formal research protocol : Use a formal research protocol to guide the search and analysis of the literature.
- Research mapping software : Use research mapping software to visualize the relationships between studies and identify the research gap.
- Table and figures : Use tables and figures to summarize the findings and identify the research gap.
Case Study: Identifying a Research Gap in Literature Review
- Topic : The impact of social media on mental health in young adults
- Search strategy : A comprehensive search of academic databases, journals, and books using relevant keywords and MeSH terms.
- More studies on the impact of social media on mental health in young adults
- More research on the role of social media in exacerbating mental health issues in young adults
- More investigation into the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health in young adults
In conclusion, identifying a research gap in a literature review is a critical step in the research process. By following the step-by-step approach outlined in this article, researchers can identify the gaps in existing knowledge and make a meaningful contribution to the field.
- How do I sell my crypto on robinhood?
- Where is university of marquette located?
- How to block search results on Google?
- Does alexa record your conversations?
- How to block porn on iPad?
- How to hide birthday on LinkedIn?
- Why canʼt I open Facebook messenger?
- How to play YouTube on Apple carplay?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Identify Gaps in Research: Tips to Speed Up the Process
If you have ever wondered how to identify research gaps, well, you’re not alone. All researchers looking to make a solid contribution to their field need to start by identifying a topic or issue that hasn’t been tackled before and coming up with possible solutions for it. This is where learning what is a research gap, knowing about some research gap examples, and knowing how to identify research gaps becomes important. Through this article, we will try answering these questions for you.
Table of Contents
What is a research gap ?
Research gaps are areas requiring more studies or research. 1 They can be:
- an unsolved question or problem within your field.
- a case where inconclusive or contradictive results exist.
- a new concept or idea that hasn’t been studied.
- a new/updated research to replace the outdated existing research.
- a specific demographic or location that has not been well studied.
Why is it important to identify research gaps ?
Identifying and prioritizing research gaps is an essential part of any research for the following reasons. 2 This can help you:
- ensure the rapid generation of subsequent research that is informed by input from previous research studies.
- understand areas of uncertainty within the research problem.
- establish the research problem and scope of the study.
- determine the scope of funding opportunities.
Identifying research gaps : A challenge for early researchers
Coming up with original, innovative ideas in your chosen area of research can be tricky, especially if you are an early career researcher, for the following reasons: 3,4
- Enormous information available : The introduction, discussion, and future research sections in published research articles provide information about gaps in the research field. It is easy to get overwhelmed and feel confused about which one to address. Using digital tools can help you seek out popular topics or the most cited research papers.
- Difficulty in organizing the data : One can quickly lose ideas if not appropriately noted. Mapping the question to the resource and maintaining a record can help narrow research gap s.
- Fear of challenging the existing knowledge : Beginner researchers may not feel confident to question established norms in their field. A good plan of action would be discussing such ideas with your advisor and proceeding according to their feedback or suggestions.
- Lack of direction and motivation : Early researchers have reported negative emotions regarding academic research, including feeling directionless or frustrated with the effort required in identifying research topics. Again a good advisor can help you stay focused. Mentors can help novice researchers avoid cases with a high risk of failure, from misunderstanding the literature, weak design, or too many unknowns. Talking with other fellow researchers can also help overcome some of the anxiety.

How to identify research gaps in the literature
More than 7 million papers get published annually. 5 Considering the volume of existing research, identifying research gaps from existing literature may seem a daunting task. While there are no hard rules for identifying research gaps, the literature has provided some guidelines for identifying problems worth investigating.
1. Observe : Personal interests and experiences can provide insight into possible research problems. For example, a researcher interested in teaching may start with a simple observation of students’ classroom behavior and observe the link with learning theories. Developing the habit of reading literature using smart apps like R Discovery can keep you updated with the latest trends and developments in the field.
2. Search : Exploring existing literature will help to identify if the observed problem is documented. One approach is identifying the independent variables used to solve the researcher’s topic of interest (i.e., the dependent variable). Databases such as Emerald, ProQuest, EbscoHost, PubMed, and ScienceDirect can help potential researchers explore existing research gaps. The following steps can help with optimizing the search process once you decide on the key research question based on your interests.
-Identify key terms.
-Identify relevant articles based on the keywords.
-Review selected articles to identify gaps in the literature.
3. Map : This involves mapping key issues or aspects across the literature. The map should be updated whenever a researcher comes across an article of interest.
4. Synthesize : Synthesis involves integrating the insights of multiple but related studies. A research gap is identified by combining results and findings across several interrelated studies. 6
5. Consult: Seeking expert feedback will help you understand if the research gaps identified are adequate and feasible or if improvements are required.
6. Prioritize : It is possible that you have identified multiple questions requiring answers. Prioritize the question that can be addressed first, considering their relevance, resource availability, and your research strengths.
7. Enroll : Research Skills Development Programs, including workshops and discussion groups within or outside the research institution, can help develop research skills, such as framing the research problem. Networking and corroborating in such events with colleagues and experts might help you know more about current issues and problems in your research domain.
While there is no well-defined process to identify gaps in knowledge, curiosity, judgment, and creativity can help you in identifying these research gaps . Regardless of whether the research gaps identified are large or small, the study design must be sufficient to contribute toward advancing your field of research.
References
- Dissanayake, D. M. N. S. W. (2013). Research, research gap and the research problem.
- Nyanchoka, L., Tudur-Smith, C., Porcher, R., & Hren, D. Key stakeholders’ perspectives and experiences with defining, identifying and displaying gaps in health research: a qualitative study. BMJ open , 10 (11), e039932 (2020).
- Müller-Bloch, C., & Kranz, J. (2015). A framework for rigorously identifying research gaps in qualitative literature reviews.
- Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. P. (2017). Designing and conducting mixed methods research . Sage publications.
- Fire, M., & Guestrin, C. Over-optimization of academic publishing metrics: observing Goodhart’s Law in action. GigaScience , 8 (6), giz053 (2019).
- Ellis, T. J., & Levy, Y. Framework of problem-based research: A guide for novice researchers on the development of a research-worthy problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline Volume 11, 2008 ).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Question: How can research gaps be addressed?
Research gaps can be addressed by conducting further studies, experiments, or investigations that specifically target the areas where knowledge is lacking or incomplete. This involves conducting a thorough literature review to identify existing gaps, designing research methodologies to address these gaps, and collecting new data or analyzing existing data to fill the void. Collaboration among researchers, interdisciplinary approaches, and innovative research designs can also help bridge research gaps and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field.
Question: Can research gaps change over time?
Yes, research gaps can change over time. As new studies are conducted, technologies advance, and societal needs evolve, gaps in knowledge may be identified or existing gaps may become more pronounced. Research gaps are dynamic and subject to shifts as new discoveries are made, new questions arise, and priorities change. It is crucial for researchers to continuously assess and update their understanding of the field to identify emerging research gaps and adapt their research efforts accordingly.
Question: Are research gaps specific to a particular discipline or field?
Research gaps can exist within any discipline or field. Each discipline has its own unique body of knowledge and areas where understanding may be limited. Research gaps can arise from unanswered questions, unexplored phenomena, conflicting findings, practical challenges, or new frontiers of knowledge. They are not limited to a specific discipline or field, as gaps can exist in natural sciences, social sciences, humanities, engineering, or any other area of study.
Question: How can research gaps contribute to the research proposal?
Research gaps play a significant role in the development of research proposals. They help researchers identify a clear rationale and justification for their study. By addressing identified gaps in knowledge, researchers can demonstrate the significance and relevance of their proposed research. Research proposals often include a literature review section that highlights existing gaps and positions the proposed study as a contribution to the field. By explicitly addressing research gaps, researchers can strengthen the credibility and importance of their research proposal, as well as its potential impact on advancing knowledge and addressing critical questions or challenges.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

4 Types of Essays in Academic Writing

What is Analytical Research? Importance and Examples

How to find and fill gaps in the literature [Research Gaps Made Easy]
As we dive deeper into the realm of research, one term repeatedly echoes in the corridors of academia: “gap in literature.”
But what does it mean to find a gap in the literature, and why is it so crucial for your research project?
A gap in the literature refers to an area that hasn’t been studied or lacks substantial inquiry in your field of study. Identifying such gaps allows you to contribute fresh insights and innovation, thereby extending the existing body of knowledge.
It’s the cornerstone for every dissertation or research paper, setting the stage for an introduction that explicitly outlines the scope and aim of your investigation.
This gap review isn’t limited to what has been published in peer-reviewed journals; it may also include conference papers, dissertations, or technical reports, i.e., types of papers that provide an overview of ongoing research.
This step is where your detective work comes in—by spotting trends, common methodologies, and unanswered questions, you can unearth an opportunity to explore an unexplored domain, thereby finding a research gap.
Why Looking for Research Gaps is Essential
Looking for research gaps is essential as it enables the discovery of novel and unique contributions to a particular field.
By identifying these gaps, found through methods such as analyzing concluding remarks of recent papers, literature reviews, examining research groups’ non-peer-reviewed outputs, and utilizing specific search terms on Google Scholar, one can discern the trajectory of ongoing research and unearth opportunities for original inquiry.
These gaps highlight areas of potential innovation, unexplored paths, and disputed concepts, serving as the catalyst for valuable contributions and progression in the field. Hence, finding research gaps forms the basis of substantial and impactful scientific exploration.
Then your research can contribute by finding and filling the gap in knowledge.
Method 1: Utilizing Concluding Remarks of Recent Research
When embarking on a quest to find research gaps, the concluding remarks of recent research papers can serve as an unexpected treasure map.
This section of a paper often contains insightful comments on the limitations of the work and speculates on future research directions.
These comments, although not directly pointing to a research gap, can hint at where the research is heading and what areas require further exploration.
Consider these remarks as signposts, pointing you towards uncharted territories in your field of interest.
For example, you may come across a conclusion in a recent paper on artificial intelligence that indicates a need for more research on ethical considerations. This gives you a direction to explore – the ethical implications of AI.
However, it’s important to bear in mind that while these statements provide valuable leads, they aren’t definitive indicators of research gaps. They provide a starting point, a clue to the vast research puzzle.
Your task is to take these hints, explore further, and discern the most promising areas for your investigation. It’s a bit like being a detective, except your clues come from scholarly papers instead of crime scenes!
Method 2: Examining Research Groups and Non-peer Reviewed Outputs
If concluding remarks are signposts to potential research gaps, non-peer reviewed outputs such as preprints, conference presentations, and dissertations are detailed maps guiding you towards the frontier of research.
These resources reflect the real-time development in the field, giving you a sense of the “buzz” that surrounds hot topics.
These materials, presented but not formally published, offer a sneak peek into ongoing studies, providing you with a rich source of information to identify emerging trends and potential research gaps.
For instance, a presentation on the impact of climate change on mental health might reveal a new line of research that’s in its early stages.
One word of caution: while these resources can be enlightening, they have not undergone the rigorous peer review process that published articles have.
This means the quality of research may vary and the findings should be interpreted with a critical eye. Remember, the key is to pinpoint where the research is heading and then carve out your niche within that sphere.
Exploring non-peer reviewed outputs allows you to stay ahead of the curve, harnessing the opportunity to investigate and contribute to a burgeoning area of study before it becomes mainstream.
Method 3: Searching for ‘Promising’ and ‘Preliminary’ Results on Google Scholar
With a plethora of research at your fingertips, Google Scholar can serve as a remarkable tool in your quest to discover research gaps. The magic lies in a simple trick: search for the phrases “promising results” or “preliminary results” within your research area. Why these specific phrases? Scientists often use them when they have encouraging but not yet fully verified findings.
To illustrate, consider an example. Type “promising results and solar cell” into Google Scholar, and filter by recent publications.
The search results will show you recent studies where researchers have achieved promising outcomes but may not have fully developed their ideas or resolved all challenges.
These “promising” or “preliminary” results often represent areas ripe for further exploration.
They hint at a research question that has been opened but not fully answered. However, tread carefully.
While these findings can indeed point to potential research gaps, they can also lead to dead ends. It’s crucial to examine these leads with a critical eye and further corroborate them with a comprehensive review of related research.
Nevertheless, this approach provides a simple, effective starting point for identifying research gaps, serving as a launchpad for your explorations.
Method 4: Reading Around the Subject
Comprehensive reading forms the bedrock of effective research. When hunting for research gaps, you need to move beyond just the preliminary findings and delve deeper into the context surrounding these results.
This involves broadening your view and reading extensively around your topic of interest.
In the course of your reading, you will start identifying common themes, reoccurring questions, and shared challenges in the research.
Over time, patterns will emerge, helping you recognize areas where research is thin or missing.
For instance, in studying autonomous vehicles, you might find recurring questions about regulatory frameworks, pointing to a potential gap in the legal aspects of this technology.
However, this method is not about scanning through a huge volume of literature aimlessly. It involves strategic and critical reading, looking for patterns, inconsistencies, and areas where the existing literature falls short.
It’s akin to painting a picture where some parts are vividly detailed while others remain sketchy. Your goal is to identify these sketchy areas and fill in the details.
So grab your academic reading list, and start diving into the ocean of knowledge. Remember, it’s not just about the depth, but also the breadth of your reading, that will lead you to a meaningful research gap.
Method 5: Consulting with Current Researchers
Few methods are as effective in uncovering research gaps as engaging in conversations with active researchers in your field of interest.
Current researchers, whether they are PhD students, postdoctoral researchers, or supervisors, are often deeply engaged in ongoing studies and understand the current challenges in their respective fields.
Start by expressing genuine interest in their work. Rather than directly asking for research gaps, inquire about the challenges they are currently facing in their projects.
You can ask, “What are the current challenges in your research?”
Their responses can highlight potential areas of exploration, setting you on the path to identifying meaningful research gaps.
Moreover, supervisors, particularly those overseeing PhD and Master’s students, often have ideas for potential research topics. By asking the right questions, you can tap into their wealth of knowledge and identify fruitful areas of study.
While the act of discovering research gaps can feel like a solitary journey, it doesn’t have to be.
Engaging with others who are grappling with similar challenges can provide valuable insights and guide your path. After all, the world of research thrives on collaboration and shared intellectual curiosity.
Method 6: Utilizing Online Tools
The digital age has made uncovering research gaps easier, thanks to a plethora of online tools that help visualize the interconnectedness of research literature.
Platforms such as:
- Connected Papers,
- ResearchRabbit, and
allow you to see how different papers in your field relate to one another, thereby creating a web of knowledge.
Upon creating this visual web, you may notice that many papers point towards a certain area, but then abruptly stop. This could indicate a potential research gap, suggesting that the topic hasn’t been adequately addressed or has been sidelined for some reason.
By further reading around this apparent gap, you can understand if it’s a genuine knowledge deficit or merely a research path that was abandoned due to inherent challenges or a dead end.
These online tools provide a bird’s eye view of the literature, helping you understand the broader landscape of research in your area of interest.
By examining patterns and relationships among studies, you can effectively zero in on unexplored areas, making these tools a valuable asset in your quest for research gaps.
Method 7: Seeking Conflicting Ideas in the Literature
In scientific research, areas of conflict can often be fertile ground for finding research gaps. These are areas where there’s a considerable amount of disagreement or ongoing debate among researchers.
If you can bring a fresh perspective, a new technique, or a novel hypothesis to such a contentious issue, you may well be on your way to uncovering a significant research gap.
Take, for instance, an area in psychology where there is a heated debate about the influence of nature versus nurture.
If you can introduce a new dimension to the debate or a method to test a novel hypothesis, you could potentially fill a significant gap in the literature.
Investigating areas of conflict not only opens avenues for exploring research gaps, but it also provides opportunities for you to make substantial contributions to your field. The key is to be able to see the potential for a new angle and to muster the courage to dive into contentious waters.
However, engaging with conflicts in research requires careful navigation.
Striking the right balance between acknowledging existing research and championing new ideas is crucial.
In the end, resolving these conflicts or adding significant depth to the debate can be incredibly rewarding and contribute greatly to your field.
The Right Perspective Towards Research Gaps
The traditional understanding of research gaps often involves seeking out a ‘bubble’ of missing knowledge in the sea of existing research, a niche yet to be explored. However, in today’s fast-paced research environment, these bubbles are becoming increasingly rare.
The paradigm of finding research gaps is shifting. It’s no longer just about seeking out holes in existing knowledge, but about understanding the leading edge of research and the directions it could take. It involves not just filling in the gaps but extending the boundaries of knowledge.
To identify such opportunities, develop a comprehensive understanding of the research landscape, identify emerging trends, and keep a close eye on recent advancements.
Look for the tendrils of knowledge extending out into the unknown and think about how you can push them further. It might be a challenging task, but it offers the potential for making substantial, impactful contributions to your field.
Remember, every great innovation begins at the edge of what is known. That’s where your research gap might be hiding.
Wrapping up – Literature and research gaps
Finding and filling a gap in the literature is a task crucial to every research project. It begins with a systematic review of existing literature – a quest to identify what has been studied and more importantly, what hasn’t.
You must delve into the rich terrain of literature in their field, from the seminal, citation-heavy research articles to the fresh perspective of conference papers. Identifying the gap in the literature necessitates a thorough evaluation of existing studies to refine your area of interest and map the scope and aim of your future research.
The purpose is to explicitly identify the gap that exists, so you can contribute to the body of knowledge by providing fresh insights. The process involves a series of steps, from consulting with faculty and experts in the field to identify potential trends and outdated methodologies, to being methodological in your approach to identify gaps that have emerged.
Upon finding a gap in the literature, we’ll ideally have a clearer picture of the research need and an opportunity to explore this unexplored domain.
It is important to remember that the task does not end with identifying the gap. The real challenge lies in drafting a research proposal that’s objective, answerable, and can quantify the impact of filling this gap.
It’s important to consult with your advisor, and also look at commonly used parameters and preliminary evidence. Only then can we complete the task of turning an identified gap in the literature into a valuable contribution to your field, a contribution that’s peer-reviewed and adds to the body of knowledge.
To find a research gap is to stand on the shoulders of giants, looking beyond the existing research to further expand our understanding of the world.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


Don't know where to start? 6 Tips on identifying research gaps
Statement of the Problem
Fatima Qureshi

The first step of conducting a study is identifying a previously unexplored area of research. Choosing an untapped area in your research field will improve your chances of getting published. But the big question is: how to decide which research problem should you study? Some researchers have clear ideas about the research problem they want to pursue. However, researchers, particularly those who are at an early stage of their career, find themselves in a fix when they have to zero down on a research topic that is original and innovative. The best way to do this is to identify a gap in existing research in the field, i.e., finding a research gap!
This article presents some tips to help you identify a knowledge gap or an unexplored area on which you can base your research.
What is a research gap?

Let us begin with understanding what a research gap means. When you read papers or books on topics of your interest, you may realize there are some areas that have significant scope for more research but they have not been tapped by other researchers. In other words, no one has picked up or worked on these ideas. A research gap or a literature gap refers to such unexplored or underexplored areas that have scope for further research.

Why is it important to identify a unique research gap?
Assume that you have completed your research work and published the findings only to find out that another researcher has already published something similar. How devastating would that be! Therefore, it is necessary to find out those problems in your research field which have not been addressed before. Not only would you be investing your funds and resources in the right project but also increasing the chances of your research findings getting published.
Challenges you may face while identifying research gaps
Finding gaps and coming up with original and innovative topics can be tricky for more than one reason. Here’s a list of challenges that you might face while identifying research gaps in your chosen area of study:
1. Effort of dealing with an enormous amount of information: There could be a lot of unanswered questions in an area of your interest. So you might get overwhelmed with the number of research gaps you stumble upon and feel confused about which one you should focus on.
2. Difficulty of searching in an organized manner: Some researchers may find it difficult to organize the information they have gathered. One can easily lose ideas if they are not noted properly.
3. Hesitation in questioning established norms: Some researchers are not confident enough to challenge the existing knowledge in their field and may hesitate to question what others have claimed in their work.
How to identify gaps in literature
You may wonder what would be the best way to come up with some innovative research questions. Though there is no well-defined process to find a gap in existing knowledge, your curiosity, creativity, imagination, and judgment can help you identify it.
Here are 6 tips to identify research gaps:
1. Look for inspiration in published literature
- What is the significance of this research to my work or the broader field?
- How can this article help me formulate my research questions?
- Does the author’s argument require more clarification?
- What issues or questions has the author not addressed?
- Is there a different perspective that I can consider?
- What other factors could have influenced the results?
- Are the methods or procedures used outdated or no longer considered valid in your field? Is there scope for you to test the findings using more a current approach?
- While reading research articles, you can focus on the Introduction section where the authors explain the importance of their research topic and the gaps they have identified and attempted to fill through their research. Also, look at the directions or suggestions for further research that the authors have made as that could be highly inspiring.
- Read meta-analyses and review papers to learn more about the developments and trends in research over the years in the area of your liking. This will help you get acquainted with the problems that have been researched upon in the past as well as trending queries on those topics that you find interesting.
2. Seek help from your research advisor
Discuss the issues and problems in your field with your research advisor to generate ideas for research. Articulating your ideas and knowing what others think and are working on may help you identify your study area or even identify mistakes in your approach. If you think a question would be interesting to work on, you can discuss it with your advisor and get their suggestions.
3. Use digital tools to seek out popular topics or most cited research papers
To familiarize yourself with the trending queries in your field, you can use digital tools as they can save time and help you cast a wider net in your search for a research gap. Websites like Essential Science Indicator that identify the most cited papers in a field along with the emerging branches, influential contributors, publications, and countries in that field can be immensely useful to know which topics are considered important. You can also use Google Trends to learn more about the popular questions related to your research area. This will ease your search for an untapped area in your research field.
4. Check the websites of influential journals
The websites of prominent journals often have a section called ‘key concepts’ where experts in an area highlight the central ideas in that field. Reading through this section can help you gain a lot of insights and generate new ideas as well. Moreover, you should also look through the reference section of these papers as it can lead you to important resources on the topic.
5. Make a note of your queries
It is a good practice to note all the questions that cross your mind while reading any published literature. If possible, you should map the question to the resource it is based on. " Keep track of what the authors told you and the questions that occur to you whenever you read anything - an article, a book, a book chapter, a dissertation, etc. " advises Nadine Anderson, Behavioral Sciences and Women's and Gender Studies Librarian at the University of Michigan. She says that this will also help in ensuring that there is no unintended plagiarism in your research paper. You can use tables, charts, pictures, or tools to maintain a record. This can help you in the long run when you are developing your idea into a research problem or even when writing your manuscript.
6. Research each question
Once you have a list of questions that could be explored, you must conduct thorough research on them. What does this mean? Read more about each doubt or query that you have. Find out if other researchers have had similar questions and whether they have found answers to them. This will help you avoid duplication of work.
Your research project is something that you will invest a lot of time in, so make sure it is something that arouses your interest and passion. While you finalize an unprecedented research idea, make sure you consider the time frame available to complete the project as well as other important aspects such as the availability of funds, equipment, and infrastructure. An over-ambitious project may be difficult to accomplish due to time and resources restraints, while research that makes an insufficient contribution may fail to get the approval of your funding committee or the journal’s editorial board.
Since there is no specific method to pick out exceptional or interesting research problems, you can use the tips presented in this article and figure out what works for you. Keep reading and asking questions until you find the extraordinary problem you’ve been looking for!
Good luck with your research!
Related reading:
- How to choose a research question
- Finding the right research question is the first step to successful publication
- How to write the literature review of your research paper
- Tips for effective literature searching and keeping up with new publications
References:
Steps for identifying research gaps in the literature
Ph.D. Thesis Research: Where do I Start?
6 (very useful!) Approaches to identify research gaps and generate research questions

for this article
Published on: Feb 25, 2019
- Problem Statement
You're looking to give wings to your academic career and publication journey. We like that!
Why don't we give you complete access! Create a free account and get unlimited access to all resources & a vibrant researcher community.
One click sign-in with your social accounts

Sign up via email
1536 visitors saw this today and 1210 signed up.
Subscribe to Conducting Research
Confirm that you would also like to sign up for free personalized email coaching for this stage.
Related Reading

The basics of writing a statement of the problem for your research…

7 Biases to avoid in qualitative research

Types of qualitative research methods
Don't know where to start? 6 Tips on identifying research gaps 8 min read
Evaluating research methodology, studying the literature, and innovating - Tips from an expert 10 min read
Literature review 101: Purpose and how to write one 7 min read
5 Tips to write a great literature review 9 min read
11 Commonly confused elements of a research paper 16 min read
Trending Searches
- Statement of the problem
- Background of study
- Scope of the study
- Types of qualitative research
- Rationale of the study
- Concept paper
- Literature review
- Introduction in research
- Under "Editor Evaluation"
- Ethics in research
Recent Searches
- Review paper
- Responding to reviewer comments
- Predatory publishers
- Scope and delimitations
- Open access
- Plagiarism in research
- Journal selection tips
- Editor assigned
- Types of articles
- "Reject and Resubmit" status
- Decision in process
- Conflict of interest
scholarsedge.in

What is Research Gap? How to Identify Research Gap?

Identifying research gaps is crucial for advancing knowledge and fostering innovation. A research gap is an area where existing studies and knowledge are insufficient or inconclusive, providing opportunities for new research. Recognising these gaps can significantly enhance the relevance and impact of your research. This guide will explore what research gaps are, why they matter, and how to identify them effectively.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Gap?
A research gap is a topic or area for which missing or insufficient information limits the ability to conclude a question. In research methodology, this gap represents areas where little or no research has been done or where the existing studies are outdated or have methodological flaws. Understanding and addressing these gaps is fundamental to advancing knowledge and developing innovative solutions.
Understanding Research Gaps in Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are systematic summaries of previous research on a topic. They identify what is known, what is unknown, and what needs further exploration. Research gaps in literature reviews often emerge as:
- Inconsistent Findings: Different studies produce conflicting results.
- Outdated Studies: Older studies that may not account for recent developments or methodologies.
- Methodological Flaws: Studies with significant limitations in design, sample size, or analysis.
- Unexplored Areas: Topics that have not been studied extensively or at all.
Steps to Identify a Research Gap
Identifying research gaps involves several steps:
Step 1: Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Review
A thorough literature review is the foundation for identifying research gaps. Use academic databases like Google Scholar , PubMed , and JSTOR to find relevant studies. Search using a variety of keywords and phrases related to your topic.
Step 2: Analyze and Synthesize Findings
Critically analyse the studies you find. Look for patterns, inconsistencies, and limitations. Synthesise the information to understand the current state of knowledge in your field.
Step 3: Formulate Research Questions
Based on your analysis, develop research questions that address the identified gaps. Ensure your questions are clear, focused, and researchable.
Practical Examples of Research Gaps
Here are some practical examples of research gaps across different fields:
- Healthcare: Despite numerous studies on the efficacy of a particular drug, there may be a lack of research on its long-term effects.
- Technology: In the field of artificial intelligence, there might be gaps in understanding the ethical implications of AI in specific industries.
- Social Sciences: In studies of social behaviour, there may be a need for more research on the impact of social media on mental health in teenagers.
For detailed case studies and more examples, refer to these research gap examples in PDF.
Tools and Resources for Finding Research Gaps
Various tools can aid in identifying research gaps:
Keyword Generators and Databases
- Google Scholar: Use it to search for scholarly articles and track citations.
- PubMed: A free resource for searching biomedical and life sciences literature.
- JSTOR: Provides access to thousands of academic journals, books, and primary sources.
Research Gap Analysis Tools
- Research Gap Analyzer: Tools designed to analyse existing literature and highlight gaps.
- Citation Analysis: Identify frequently cited papers and see what areas are often discussed or overlooked.
Identifying research gaps is a critical step in the research process. It ensures that your research is relevant, innovative, and impactful. By conducting a comprehensive literature review, analysing existing studies, and formulating precise research questions, you can uncover significant gaps in knowledge. Utilise the tools and resources discussed to aid your search and contribute valuable new insights to your field.
By focusing on these steps, researchers can position themselves to make meaningful contributions to their disciplines. Remember, every research gap you fill brings the scientific community one step closer to a deeper understanding of the world.
FAQs on Research Gap
What is the meaning of the research gap.
A research gap refers to an area within the existing literature that lacks sufficient information, knowledge, or previous research. It signifies an issue or problem that has not been adequately explored, providing an opportunity for further investigation. Identifying a research gap is essential for advancing a field by contributing new insights and understanding. Researchers aim to find these gaps through thorough literature reviews, which help highlight areas that need more exploration, thus guiding future research efforts.
How do you answer a research gap?
Answering a research gap involves several steps: first, clearly defining the gap through a comprehensive literature review and next, formulating specific research questions that address this gap—then, designing and conducting a study to collect and analyse data pertinent to these questions and finally, interpreting the results in the context of existing literature and communicating the findings through publications or presentations to contribute new knowledge and fill the identified gap.
How to identify research gap?
Identifying a research gap involves conducting a comprehensive literature review to understand the current state of research in a field. Analyse existing studies to find patterns and limitations. Note areas with conflicting results or insufficient coverage. Look for trends and emerging topics that may lack extensive research. Consult experts and use research tools like citation analysis to refine your search. Develop specific research questions based on these gaps. This systematic approach helps ensure your research will contribute valuable new insights to the field, addressing previously underexplored areas.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The four most common types of research gaps are the classic literature gap, the disagreement gap, the contextual gap and the methodological gap. To find potential research gaps, start by reviewing recent journal articles in your area of interest, paying particular attention to the FRIN section .
Mar 25, 2024 · Evidence Gap: Contradictory findings on the role of cloud seeding in mitigating global warming. Example 2: Health Sciences. Methodological Gap: Most studies on diabetes management rely on short-term data, with few examining long-term adherence to lifestyle changes. Contextual Gap: A lack of research on healthcare disparities in low-income ...
Jun 24, 2024 · 5. Contextualize the Gap. Place your research gap within the broader context of your field. Explain how your study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and why it is timely and relevant. 6. Use Clear and Concise Language. When writing about the research gap, be clear and concise.
Jul 21, 2023 · What is a Research Gap? Today we are talking about the research gap: what is it, how to identify it, and how to make use of it so that you can pursue innovative research. Now, how many of you have ever felt you had discovered a new and exciting research question, only to find that it had already been written about? I have experienced this more ...
Learn a step-by-step process to identify research gaps and topics for your dissertation, thesis or project. Use Google Scholar to scan literature, filter by time period and select articles that interest you.
Nov 27, 2024 · To avoid duplication of work: Identifying a research gap ensures that research does not duplicate existing work, thus avoiding wasting resources. To make a meaningful contribution: A research gap helps to make a meaningful contribution to the field by addressing a crucial knowledge gap. Identifying a Research Gap: A Step-by-Step Approach
Oct 11, 2022 · Learn what a research gap is, why it is important, and how to find one in the literature. Follow the steps and guidelines to identify, prioritize, and address research gaps in your field.
Jul 4, 2023 · By further reading around this apparent gap, you can understand if it’s a genuine knowledge deficit or merely a research path that was abandoned due to inherent challenges or a dead end. These online tools provide a bird’s eye view of the literature, helping you understand the broader landscape of research in your area of interest.
Feb 25, 2019 · Learn what a research gap is and why it is important to find one for your study. Get tips on how to locate gaps in literature, seek help from advisors, use digital tools, and record your queries.
Jul 5, 2024 · Answering a research gap involves several steps: first, clearly defining the gap through a comprehensive literature review and next, formulating specific research questions that address this gap—then, designing and conducting a study to collect and analyse data pertinent to these questions and finally, interpreting the results in the context of existing literature and communicating the ...