Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper

Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![abstract on a research paper “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![abstract on a research paper “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![abstract on a research paper “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Academic Programs within an Undergraduate College
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Diversity Statements
Professional Emails
Advice for Students Writing a Professional Email
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents
The abstract of a research paper is a concise summary that provides an overview of the study’s purpose, methodology, results, and conclusions. Positioned at the beginning of the paper, the abstract serves as the first impression for readers, helping them quickly decide whether the research is relevant to their interests. Writing an effective abstract requires clarity, precision, and an understanding of the study’s key points.
This guide explores the purpose of a research abstract, offers a step-by-step writing process, and provides practical examples to illustrate best practices.

Research Paper Abstract
An abstract is a brief summary of a research paper that typically ranges from 150 to 300 words. It succinctly describes the key components of the study, including its objectives, methods, findings, and implications.
Key Characteristics of an Abstract:
- Concise: Provides a complete overview within a limited word count.
- Self-Contained: Can be understood independently of the full paper.
- Structured or Unstructured: May follow specific sections (structured) or flow as a single paragraph (unstructured).
Example: An abstract for a study on the effects of exercise on mental health might summarize the research question, methods used, results indicating reduced anxiety levels, and implications for mental health interventions.
Purpose of a Research Abstract
- Attracts Readers: Helps potential readers quickly determine the relevance of the study.
- Facilitates Indexing: Allows easy discovery in databases and search engines.
- Provides Overview: Summarizes the key elements of the research for quick understanding.
- Enhances Accessibility: Serves as a standalone summary for those unable to access the full paper.
Types of Abstracts
1. descriptive abstract.
- Focuses on the purpose and scope of the research without detailed results.
- Example: Common in humanities and theoretical studies.
2. Informative Abstract
- Includes key details about methods, findings, and conclusions.
- Example: Widely used in scientific and technical research papers.
3. Critical Abstract
- Evaluates the study’s validity and reliability along with summarizing it.
- Example: Used in advanced reviews or critique papers.
4. Highlight Abstract
- Focuses on intriguing or unique aspects of the study to attract attention.
- Example: Found in conference proceedings or promotional materials.
How to Write a Research Paper Abstract
Step 1: understand the requirements.
- Review the target journal or institution’s guidelines for abstract length, format, and style.
Step 2: Identify Key Elements
- Background: What is the research about?
- Objective: What is the purpose or main question of the study?
- Methods: How was the research conducted?
- Results: What were the significant findings?
- Conclusion: What is the study’s implication or contribution?
Step 3: Write a Draft
- Create a rough draft summarizing each section of the paper.
Step 4: Refine for Clarity and Precision
- Use concise language to eliminate redundancy. Avoid technical jargon unless necessary.
Step 5: Verify Accuracy
- Ensure all details in the abstract accurately reflect the content of the paper.
Step 6: Edit for Style and Grammar
- Proofread to ensure clarity, coherence, and adherence to formatting requirements.
Best Practices for Writing an Abstract
- Write the Abstract Last: Compose the abstract after completing the full paper to ensure it captures all key points.
- Focus on Clarity: Avoid vague language or overly complex sentences.
- Use Keywords: Include relevant terms to improve discoverability in databases.
- Avoid References: Abstracts should be standalone and not rely on citations.
- Maintain Objectivity: Present findings neutrally without exaggeration.
Examples of Research Paper Abstracts
Example 1: scientific research.
Title: The Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Anxiety Levels Among College Students Abstract: This study examines the impact of aerobic exercise on anxiety levels among college students. A total of 150 participants were randomly assigned to either an exercise or a control group. Participants in the exercise group engaged in 30-minute aerobic sessions thrice weekly for eight weeks. Anxiety levels were measured using the Beck Anxiety Inventory before and after the intervention. Results indicated a significant reduction in anxiety scores among the exercise group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). These findings suggest that aerobic exercise may serve as an effective intervention for anxiety management.
Example 2: Social Sciences Research
Title: The Role of Social Media in Shaping Political Opinions Among Young Adults Abstract: This research investigates the influence of social media platforms on the political opinions of young adults aged 18–30. Using a mixed-methods approach, we conducted surveys (n = 500) and in-depth interviews (n = 20) to explore participants’ exposure to political content online. Findings revealed that 62% of respondents reported significant shifts in their political views due to social media interactions. Qualitative analysis highlighted the role of algorithm-driven content in reinforcing political biases. The study underscores the importance of critical digital literacy in mitigating the impact of social media on political polarization.
Example 3: Engineering Research
Title: Optimization of Solar Panel Efficiency Through Material Engineering Abstract: This paper explores advanced material engineering techniques to enhance solar panel efficiency. Experimental tests were conducted on polymer-based coatings to improve light absorption and minimize reflection. Results showed that panels with modified coatings exhibited a 12% increase in energy output compared to standard models. The findings demonstrate the potential of material innovation in advancing renewable energy technology.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Exceeding Word Limits: Adhere to the specified length guidelines.
- Including Unnecessary Details: Avoid adding minor or irrelevant information.
- Using Technical Jargon: Keep language accessible to a broad audience.
- Neglecting Results: Ensure the abstract highlights significant findings.
- Failing to Revise: Proofread carefully to eliminate errors and improve readability.
An abstract is a critical component of a research paper, summarizing its content in a concise and accessible way. Whether you are submitting your work to a journal, conference, or academic institution, following a clear structure and emphasizing clarity and precision will enhance the impact of your abstract. By adhering to best practices and learning from well-crafted examples, you can effectively communicate the essence of your research to a wider audience.
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.).
- Swales, J. M., & Feak, C. B. (2012). Academic Writing for Graduate Students . University of Michigan Press.
- Day, R. A., & Gastel, B. (2016). How to Write and Publish a Scientific Paper . Cambridge University Press.
- Glasman-Deal, H. (2020). Science Research Writing for Non-Native Speakers of English . Imperial College Press.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Tables in Research Paper – Types, Creating Guide...

How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step...

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Figures in Research Paper – Examples and Guide
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

How To Write A Research Paper Abstract | Steps And Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at September 23rd, 2024 , Revised On October 24, 2024
An abstract is written to pique a reader’s interest and if necessary, motivate them to leave the comfort of their home and get the full article or paper.
In simpler words, an abstract is a well-structured summary of your academic work, such as an article, research paper , thesis or dissertation. It outlines the most important aspects of your work and is about 300-500 words. Although the structure may vary from discipline to discipline, it is still a necessary part of academic writing.
Abstract Research Paper Definition
A research paper abstract is the face of the research paper. This means that it is what creates the first impression of the paper. It is the summary of the research paper and communicates the content quality and relevance. They exist with one vital purpose, and that is to sell your research. A reader quickly scrutinises and scans the abstract to gain an idea of your research, the problem statement addressed, the methodologies used and the results gained from it.
An abstract most commonly has the following parts:
- Introduction
Types of Abstracts In Research Paper
One of the main purposes of an abstract is to describe your paper. It can either be informative, descriptive, structured or unstructured. Let’s develop a common understanding of how research paper abstracts are written based on content and writing style.
Structured Abstract
Structured abstracts are mostly written in journals and have a separate paragraph for each section. Each part is organised and has distinct headings such as introduction/background, objective, design, methodologies, material, results and conclusion.
Unstructured Abstract
An unstructured abstract is mostly used in social sciences and humanities disciplines and does not have separate paragraphs for each section. It consists of one whole paragraph that serves as the face of the research paper.
Descriptive Abstract
A descriptive abstract only outlines the crucial details of the researcher’s publication. They are mostly short, consisting of 75-105 words. They briefly explain the background, mission statement, purpose and objective but omit the research methodologies, results and conclusions.
Informative Abstract
This abstract can be both structured and unstructured and provides detailed information on the research paper. This means that it is an extensive paragraph on each aspect of research and provides accurate data on each section, especially results.

How to Make Abstract In Research Paper
The abstract part of the research paper summarises the main points of the article. Whether you are applying for research grants, writing a thesis or dissertation or studying a research problem , it is necessary to know how to make a good abstract for a research paper. Here are some of the details on how to write a research paper abstract.
General Topic In Study
This section serves as the introduction to the research paper. It answers the questions of what is being studied or what problem statement is being addressed here. The hypothesis and purpose are highlighted within this section, setting the context for the rest of the research paper.
It is recommended to never go into detailed information as this part only offers initial information regarding the research. Also, this part is always written in the present or past tense, and never in the future as the research has been completed.
Our study’s main objective was to assess the photoprotective capability of chocolate consumption, by contrasting a simple dark chocolate with a specifically made chocolate with preserved high flavanol. According to the study’s hypothesis, eating chocolate induced with HF can provide nutritional defence against skin damage by the sun.
Research/Analytical Methods
Next, it is important to write the research methods used in the research. Either qualitative or quantitative methods, every aspect of them should be mentioned to give the reader a good idea of what scale, survey and sample was used within the research. Some questions that need to be answered in this paragraph are:
- What was the research setting?
- What was the sample size, and how were the participants sampled?
- What was the research method used?
- What was the primary outcome of the initial test?
- What questions or treatments were administered to the participants?
A double-blinded in vivo study was carried out, where 30 healthy adults participated in it. It included 8 males and 22 females between the age of 10 years to 43 years. Fifteen subjects each were given either an HF or LF chocolate and were divided based on their skin phototypes.
Results/ Arguments
This section can be both in present and past tense and must include the main findings of the study. It should be detailed and lengthy, giving all relevant results. These are the following questions this section of the abstract research paper must answer:
- What did the study yield?
- What were the results in comparison to the hypothesis ?
- What were the predictions and were the outcomes similar to it?
In conclusion, our research revealed that eating chocolate high in flavanol shields humans from damaging UV rays, mainly because of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The research indicates that HF chocolate lessens the acute inflammatory response to UV rays, by regulating the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide.
Discussions
Finally, you should discuss the conclusions and the author’s thoughts on the research. Whether the hypothesis proved to be right or not is mostly discussed here, along with the limitations or complications encountered during the research. It is necessary to mention this as a reader must be aware of the credibility and generalisability of the research.
Our research concludes by showing that cocoa flavanols have the potential to be a safe natural method of shielding skin from UV damage.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Research Paper Abstract Example
Here is an abstract example for research papers to help you understand how abstracts are written:
Does the lockdown have a role in stopping COVID-19?
Every day the coronavirus is spreading, with deaths and fatalities increasing day by day. This has led to a nationwide lockdown all over the world. Our study aims to study the effect of lockdown days on the spread of coronavirus in countries. COVID-19 data from 49 countries was gathered from www.worldometer.com. As of May 5, 2020, there were 1440776 approved active cases of COVID-19 from the countries included in this study. Data on COVID-19 days and lockdown days was obtained from the websites of the official institutions of these 49 countries. Moreover, the correlation test was used to analyse the associations between total COVID-19 cases and the lockdown days. The lockdown days were seen to be correlated to the COVID-19 pandemic. The social-isolation phenomenon; the lockdown has been seen to prevent COVID-19 and the spread of this deadly virus. There are several concerns about the ability of the national healthcare system to effectively manage COVID-19 patients. To slow down the spread of this virus, it is necessary to take the strictest of actions. Even though Italy and Spain have the highest death rates because of COVID-19, there has been a sudden drop in the rates because of the strict measures taken by the government.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should i write an abstract.
You should write an abstract when you are completing a thesis or dissertation, submitting a research design or applying for research grants. You can also write an abstract if you are writing a book
What are things to avoid while writing an abstract?
You should avoid using passive sentences and future tenses. Avoid detailed descriptions as an abstract is supposed to be just a summary. Complex jargon and complicated long sentences should also be avoided as they take away the reader’s interest. Lastly, always address your problem statement in a good way.
Should I cite sources in an abstract?
You should try to focus on showcasing your original work, rather than cite other work. Try to make your work as comprehensive and understanding so that your work is highlighted better.
You May Also Like
Struggling to find relevant and up-to-date topics for your dissertation? Here is all you need to know if unsure about how to choose dissertation topic.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
Find how to write research questions with the mentioned steps required for a perfect research question. Choose an interesting topic and begin your research.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works

Magnum Proofreading Services
Writing an Abstract for a Research Paper: Guidelines, Examples, and Templates
There are six steps to writing a standard abstract. (1) Begin with a broad statement about your topic. Then, (2) state the problem or knowledge gap related to this topic that your study explores. After that, (3) describe what specific aspect of this problem you investigated, and (4) briefly explain how you went about doing this. After that, (5) describe the most meaningful outcome(s) of your study. Finally, (6) close your abstract by explaining the broad implication(s) of your findings.
In this article, I present step-by-step guidelines for writing an abstract for an academic paper. These guidelines are fo llowed by an example of a full abstract that follows these guidelines and a few fill-in-the-blank templates that you can use to write your own abstract.
Guidelines for Writing an Abstract
The basic structure of an abstract is illustrated below.
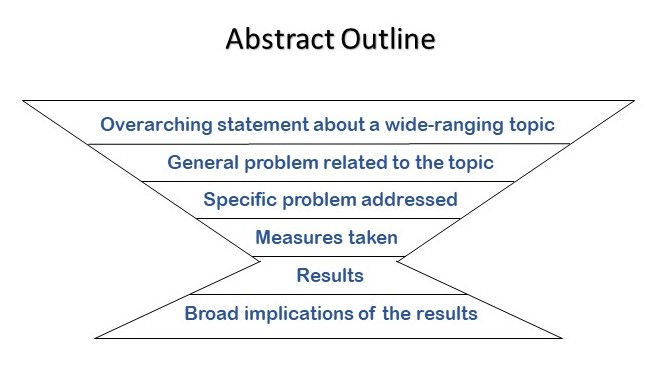
A standard abstract starts with a very general statement and becomes more specific with each sentence that follows until once again making a broad statement about the study’s implications at the end. Altogether, a standard abstract has six functions, which are described in detail below.
Start by making a broad statement about your topic.
The first sentence of your abstract should briefly describe a problem that is of interest to your readers. When writing this first sentence, you should think about who comprises your target audience and use terms that will appeal to this audience. If your opening sentence is too broad, it might lose the attention of potential readers because they will not know if your study is relevant to them.
Too broad : Maintaining an ideal workplace environment has a positive effect on employees.
The sentence above is so broad that it will not grab the reader’s attention. While it gives the reader some idea of the area of study, it doesn’t provide any details about the author’s topic within their research area. This can be fixed by inserting some keywords related to the topic (these are underlined in the revised example below).
Improved : Keeping the workplace environment at an ideal temperature positively affects the overall health of employees.
The revised sentence is much better, as it expresses two points about the research topic—namely, (i) what aspect of workplace environment was studied, (ii) what aspect of employees was observed. The mention of these aspects of the research will draw the attention of readers who are interested in them.
Describe the general problem that your paper addresses.
After describing your topic in the first sentence, you can then explain what aspect of this topic has motivated your research. Often, authors use this part of the abstract to describe the research gap that they identified and aimed to fill. These types of sentences are often characterized by the use of words such as “however,” “although,” “despite,” and so on.
However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking.
The above example is typical of a sentence describing the problem that a study intends to tackle. The author has noticed that there is a gap in the research, and they briefly explain this gap here.
Although it has been established that quantity and quality of sleep can affect different types of task performance and personal health, the interactions between sleep habits and workplace behaviors have received very little attention.
The example above illustrates a case in which the author has accomplished two tasks with one sentence. The first part of the sentence (up until the comma) mentions the general topic that the research fits into, while the second part (after the comma) describes the general problem that the research addresses.
Express the specific problem investigated in your paper.
After describing the general problem that motivated your research, the next sentence should express the specific aspect of the problem that you investigated. Sentences of this type are often indicated by the use of phrases like “the purpose of this research is to,” “this paper is intended to,” or “this work aims to.”
Uninformative : However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking. The present article aimed to provide new insights into the relationship between workplace bullying and absenteeism .
The second sentence in the above example is a mere rewording of the first sentence. As such, it adds nothing to the abstract. The second sentence should be more specific than the preceding one.
Improved : However, a comprehensive understanding of how different workplace bullying experiences are associated with absenteeism is currently lacking. The present article aimed to define various subtypes of workplace bullying and determine which subtypes tend to lead to absenteeism .
The second sentence of this passage is much more informative than in the previous example. This sentence lets the reader know exactly what they can expect from the full research article.
Explain how you attempted to resolve your study’s specific problem.
In this part of your abstract, you should attempt to describe your study’s methodology in one or two sentences. As such, you must be sure to include only the most important information about your method. At the same time, you must also be careful not to be too vague.
Too vague : We conducted multiple tests to examine changes in various factors related to well-being.
This description of the methodology is too vague. Instead of merely mentioning “tests” and “factors,” the author should note which specific tests were run and which factors were assessed.
Improved : Using data from BHIP completers, we conducted multiple one-way multivariate analyses of variance and follow-up univariate t-tests to examine changes in physical and mental health, stress, energy levels, social satisfaction, self-efficacy, and quality of life.
This sentence is very well-written. It packs a lot of specific information about the method into a single sentence. Also, it does not describe more details than are needed for an abstract.
Briefly tell the reader what you found by carrying out your study.
This is the most important part of the abstract—the other sentences in the abstract are there to explain why this one is relevant. When writing this sentence, imagine that someone has asked you, “What did you find in your research?” and that you need to answer them in one or two sentences.
Too vague : Consistently poor sleepers had more health risks and medical conditions than consistently optimal sleepers.
This sentence is okay, but it would be helpful to let the reader know which health risks and medical conditions were related to poor sleeping habits.
Improved : Consistently poor sleepers were more likely than consistently optimal sleepers to suffer from chronic abdominal pain, and they were at a higher risk for diabetes and heart disease.
This sentence is better, as the specific health conditions are named.
Finally, describe the major implication(s) of your study.
Most abstracts end with a short sentence that explains the main takeaway(s) that you want your audience to gain from reading your paper. Often, this sentence is addressed to people in power (e.g., employers, policymakers), and it recommends a course of action that such people should take based on the results.
Too broad : Employers may wish to make use of strategies that increase employee health.
This sentence is too broad to be useful. It does not give employers a starting point to implement a change.
Improved : Employers may wish to incorporate sleep education initiatives as part of their overall health and wellness strategies.
This sentence is better than the original, as it provides employers with a starting point—specifically, it invites employers to look up information on sleep education programs.
Abstract Example
The abstract produced here is from a paper published in Electronic Commerce Research and Applications . I have made slight alterations to the abstract so that this example fits the guidelines given in this article.
(1) Gamification can strengthen enjoyment and productivity in the workplace. (2) Despite this, research on gamification in the work context is still limited. (3) In this study, we investigated the effect of gamification on the workplace enjoyment and productivity of employees by comparing employees with leadership responsibilities to those without leadership responsibilities. (4) Work-related tasks were gamified using the habit-tracking game Habitica, and data from 114 employees were gathered using an online survey. (5) The results illustrated that employees without leadership responsibilities used work gamification as a trigger for self-motivation, whereas employees with leadership responsibilities used it to improve their health. (6) Work gamification positively affected work enjoyment for both types of employees and positively affected productivity for employees with leadership responsibilities. (7) Our results underline the importance of taking work-related variables into account when researching work gamification.
In Sentence (1), the author makes a broad statement about their topic. Notice how the nouns used (“gamification,” “enjoyment,” “productivity”) are quite general while still indicating the focus of the paper. The author uses Sentence (2) to very briefly state the problem that the research will address.
In Sentence (3), the author explains what specific aspects of the problem mentioned in Sentence (2) will be explored in the present work. Notice that the mention of leadership responsibilities makes Sentence (3) more specific than Sentence (2). Sentence (4) gets even more specific, naming the specific tools used to gather data and the number of participants.
Sentences (5) and (6) are similar, with each sentence describing one of the study’s main findings. Then, suddenly, the scope of the abstract becomes quite broad again in Sentence (7), which mentions “work-related variables” instead of a specific variable and “researching” instead of a specific kind of research.
Abstract Templates
Copy and paste any of the paragraphs below into a word processor. Then insert the appropriate information to produce an abstract for your research paper.
Template #1
Researchers have established that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . However, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The goal of this paper is to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . The achieve this goal, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . We found that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
Template #2
It is well-understood that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . Despite this, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The current research aims to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . To accomplish this, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . It was discovered that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
Template #3
Extensive research indicates that [Make a broad statement about your area of research.] . Nevertheless, [Describe the knowledge gap that your paper addresses.] . The present work is intended to [Describe the purpose of your paper.] . To this end, we [Briefly explain your methodology.] . The results revealed that [Indicate the main finding(s) of your study; you may need two sentences to do this.] . [Provide a broad implication of your results.] .
- How to Write an Abstract
Related Posts
How to Write a Research Paper in English: A Guide for Non-native Speakers
How to Write an Abstract Quickly
Using the Present Tense and Past Tense When Writing an Abstract
1 commentaire
Well explained! I have given you a credit

How to Write an Abstract in Research Papers (with Examples)

An abstract in research papers is a keyword-rich summary usually not exceeding 200-350 words. It can be considered the “face” of research papers because it creates an initial impression on the readers. While searching databases (such as PubMed) for research papers, a title is usually the first selection criterion for readers. If the title matches their search criteria, then the readers read the abstract, which sets the tone of the paper. Titles and abstracts are often the only freely available parts of research papers on journal websites. The pdf versions of full articles need to be purchased. Journal reviewers are often provided with only the title and abstract before they agree to review the complete paper. [ 1]
Abstracts in research papers provide readers with a quick insight into what the paper is about to help them decide whether they want to read it further or not. Abstracts are the main selling points of articles and therefore should be carefully drafted, accurately highlighting the important aspects. [ 2]
This article will help you identify the important components and provide tips on how to write an abstract in research papers effectively
What is an Abstract?
An abstract in research papers can be defined as a synopsis of the paper. It should be clear, direct, self-contained, specific, unbiased, and concise. These summaries are published along with the complete research paper and are also submitted to conferences for consideration for presentation.
Abstracts are of four types and journals can follow any of these formats: [ 2]
- Structured
- Unstructured
- Descriptive
- Informative
Structured abstracts are used by most journals because they are more organized and have clear sections, usually including introduction/background; objective; design, settings, and participants (or materials and methods); outcomes and measures; results; and conclusion. These headings may differ based on the journal or the type of paper. Clinical trial abstracts should include the essential items mentioned in the CONSORT (Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials) guidelines.

Figure 1. Structured abstract example [3]
Unstructured abstracts are common in social science, humanities, and physical science journals. They usually have one paragraph and no specific structure or subheadings. These abstracts are commonly used for research papers that don’t report original work and therefore have a more flexible and narrative style.

Figure 2. Unstructured abstract example [3]
Descriptive abstracts are short (75–150 words) and provide an outline with only the most important points of research papers. They are used for shorter articles such as case reports, reviews, and opinions where space is at a premium, and rarely for original investigations. These abstracts don’t present the results but mainly list the topics covered.
Here’s a sample abstract . [ 4]
“Design of a Radio-Based System for Distribution Automation”
A new survey by the Maryland Public Utilities Commission suggests that utilities have not effectively explained to consumers the benefits of smart meters. The two-year study of 86,000 consumers concludes that the long-term benefits of smart meters will not be realized until consumers understand the benefits of shifting some of their power usage to off-peak hours in response to the data they receive from their meters. The study presents recommendations for utilities and municipal governments to improve customer understanding of how to use the smart meters effectively.
Keywords: smart meters, distribution systems, load, customer attitudes, power consumption, utilities
Informative abstracts (structured or unstructured) give a complete detailed summary, including the main results, of the research paper and may or may not have subsections.

Figure 3. Informative abstract example [5]
Purpose of Abstracts in Research
Abstracts in research have two main purposes—selection and indexing. [ 6,7]
- Selection : Abstracts allow interested readers to quickly decide the relevance of a paper to gauge if they should read it completely.
- Indexing : Most academic journal databases accessed through libraries enable you to search abstracts, allowing for quick retrieval of relevant articles and avoiding unnecessary search results. Therefore, abstracts must necessarily include the keywords that researchers may use to search for articles.
Thus, a well-written, keyword-rich abstract can p ique readers’ interest and curiosity and help them decide whether they want to read the complete paper. It can also direct readers to articles of potential clinical and research interest during an online search.

Contents of Abstracts in Research
Abstracts in research papers summarize the main points of an article and are broadly categorized into four or five sections. Here are some details on how to write an abstract .
Introduction/Background and/or Objectives
This section should provide the following information:
- What is already known about the subject?
- What is not known about the subject or what does the study aim to investigate?
The hypothesis or research question and objectives should be mentioned here. The Background sets the context for the rest of the paper and its length should be short so that the word count could be saved for the Results or other information directly pertaining to the study. The objective should be written in present or past simple tense.
Examples:
The antidepressant efficacy of desvenlafaxine (DV) has been established in 8-week, randomized controlled trials. The present study examined the continued efficacy of DV across 6 months of maintenance treatment . [ 1]
Objective: To describe gastric and breast cancer risk estimates for individuals with CDH1 variants.
Design, Setting, and Participants (or Materials and Methods)
This section should provide information on the processes used and should be written in past simple tense because the process is already completed.
A few important questions to be answered include:
- What was the research design and setting?
- What was the sample size and how were the participants sampled?
- What treatments did the participants receive?
- What were the data collection and data analysis dates?
- What was the primary outcome measure?
Hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated for each cancer type and used to calculate cumulative risks and risks per decade of life up to age 80 years.

This section, written in either present or past simple tense, should be the longest and should describe the main findings of the study. Here’s an example of how descriptive the sentences should be:
Avoid: Response rates differed significantly between diabetic and nondiabetic patients.
Better: The response rate was higher in nondiabetic than in diabetic patients (49% vs 30%, respectively; P<0.01).
This section should include the following information:
- Total number of patients (included, excluded [exclusion criteria])
- Primary and secondary outcomes, expressed in words, and supported by numerical data
- Data on adverse outcomes
Example: [ 8]
In total, 10.9% of students were reported to have favorable study skills. The minimum score was found for preparation for examination domain. Also, a significantly positive correlation was observed between students’ study skills and their Grade Point Average (GPA) of previous term (P=0.001, r=0.269) and satisfaction with study skills (P=0.001, r=0.493).
Conclusions
Here, authors should mention the importance of their findings and also the practical and theoretical implications, which would benefit readers referring to this paper for their own research. Present simple tense should be used here.
Examples: [ 1,8]
The 9.3% prevalence of bipolar spectrum disorders in students at an arts university is substantially higher than general population estimates. These findings strengthen the oft-expressed hypothesis linking creativity with affective psychopathology.
The findings indicated that students’ study skills need to be improved. Given the significant relationship between study skills and GPA, as an index of academic achievement, and satisfaction, it is necessary to promote the students’ study skills. These skills are suggested to be reinforced, with more emphasis on weaker domains.

When to Write an Abstract
In addition to knowing how to write an abstract , you should also know when to write an abstract . It’s best to write abstracts once the paper is completed because this would make it easier for authors to extract relevant parts from every section.
Abstracts are usually required for: [ 7]
- submitting articles to journals
- applying for research grants
- writing book proposals
- completing and submitting dissertations
- submitting proposals for conference papers
Mostly, the author of the entire work writes the abstract (the first author, in works with multiple authors). However, there are professional abstracting services that hire writers to draft abstracts of other people’s work.
How to Write an Abstract (Step-by-Step Process)
Here are some key steps on how to write an abstract in research papers: [ 9]
- Write the abstract after you’ve finished writing your paper.
- Select the major objectives/hypotheses and conclusions from your Introduction and Conclusion sections.
- Select key sentences from your Methods section.
- Identify the major results from the Results section.
- Paraphrase or re-write the sentences selected in steps 2, 3, and 4 in your own words into one or two paragraphs in the following sequence: Introduction/Objective, Methods, Results, and Conclusions. The headings may differ among journals, but the content remains the same.
- Ensure that this draft does not contain: a. new information that is not present in the paper b. undefined abbreviations c. a discussion of previous literature or reference citations d. unnecessary details about the methods used
- Remove all extra information and connect your sentences to ensure that the information flows well, preferably in the following order: purpose; basic study design, methodology and techniques used; major findings; summary of your interpretations, conclusions, and implications. Use section headings for structured abstracts.
- Ensure consistency between the information presented in the abstract and the paper.
- Check to see if the final abstract meets the guidelines of the target journal (word limit, type of abstract, recommended subheadings, etc.) and if all the required information has been included.
Choosing Keywords for Abstracts
Keywords [ 2] are the important and repeatedly used words and phrases in research papers and can help indexers and search engines find papers relevant to your requirements. Easy retrieval would help in reaching a wider audience and eventually gain more citations. In the fields of medicine and health, keywords should preferably be chosen from the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) list of the US National Library of Medicine because they are used for indexing. These keywords need to be different from the words in the main title (automatically used for indexing) but can be variants of the terms/phrases used in the title, abstract, and the main text. Keywords should represent the content of your manuscript and be specific to your subject area.
Basic tips for authors [ 10,11]
- Read through your paper and highlight key terms or phrases that are most relevant and frequently used in your field, to ensure familiarity.
- Several journals provide instructions about the length (eg, 3 words in a keyword) and maximum number of keywords allowed and other related rules. Create a list of keywords based on these instructions and include specific phrases containing 2 to 4 words. A longer string of words would yield generic results irrelevant to your field.
- Use abbreviations, acronyms, and initializations if these would be more familiar.
- Search with your keywords to ensure the results fit with your article and assess how helpful they would be to readers.
- Narrow down your keywords to about five to ten, to ensure accuracy.
- Finalize your list based on the maximum number allowed.
Few examples: [ 12]
Important Tips for Writing an Abstract
Here are a few tips on how to write an abstract to ensure that your abstract is complete, concise, and accurate. [ 1,2]
- Write the abstract last.
- Follow journal-specific formatting guidelines or Instructions to Authors strictly to ensure acceptance for publication.
- Proofread the final draft meticulously to avoid grammatical or typographical errors.
- Ensure that the terms or data mentioned in the abstract are consistent with the main text.
- Include appropriate keywords at the end.
Do not include:
- New information
- Text citations to references
- Citations to tables and figures
- Generic statements
- Abbreviations unless necessary, like a trial or study name

Key Takeaways
Here’s a quick snapshot of all the important aspects of how to write an abstract . [2]
- An abstract in research is a summary of the paper and describes only the main aspects. Typically, abstracts are about 200-350 words long.
- Abstracts are of four types—structured, unstructured, descriptive, and informative.
- Abstracts should be simple, clear, concise, independent, and unbiased (present both favorable and adverse outcomes).
- They should adhere to the prescribed journal format, including word limits, section headings, number of keywords, fonts used, etc.
- The terminology should be consistent with the main text.
- Although the section heading names may differ for journals, every abstract should include a background and objective, analysis methods, primary results, and conclusions.
- Nonstandard abbreviations, references, and URLs shouldn’t be included.
- Only relevant and specific keywords should be used to ensure focused searches and higher citation frequency.
- Abstracts should be written last after completing the main paper.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Do all journals have different guidelines for abstracts?
A1. Yes, all journals have their own specific guidelines for writing abstracts; a few examples are given in the following table. [ 6,13,14,15]
Q2. What are the common mistakes to avoid when writing an abstract?
A2. Listed below are a few mistakes that authors may make inadvertently while writing abstracts.
- Copying sentences from the paper verbatim
An abstract is a summary, which should be created by paraphrasing your own work or writing in your own words. Extracting sentences from every section and combining them into one paragraph cannot be considered summarizing.
- Not adhering to the formatting guidelines
Journals have special instructions for writing abstracts, such as word limits and section headings. These should be followed strictly to avoid rejections.
- Not including the right amount of details in every section
Both too little and too much information could discourage readers. For instance, if the Background has very little information, the readers may not get sufficient context to appreciate your research. Similarly, incomplete information in the Methods and a text-heavy Results section without supporting numerical data may affect the credibility of your research.
- Including citations, standard abbreviations, and detailed measurements
Typically, abstracts shouldn’t include these elements—citations, URLs, and abbreviations. Only nonstandard abbreviations are allowed or those that would be more familiar to readers than the expansions.
- Including new information
Abstracts should strictly include only the same information mentioned in the main text. Any new information should first be added to the text and then to the abstract only if necessary or if permitted by the word limit.
- Not including keywords
Keywords are essential for indexing and searching and should be included to increase the frequency of retrieval and citation.
Q3. What is the difference between abstracts in research papers and conference abstracts? [16]
A3. The table summarizes the main differences between research and conference abstracts.
Thus, abstracts are essential “trailers” that can market your research to a wide audience. The better and more complete the abstract the more are the chances of your paper being read and cited. By following our checklist and ensuring that all key elements are included, you can create a well-structured abstract that summarizes your paper accurately.
References
- Andrade C. How to write a good abstract for a scientific paper or conference presentation. Indian J Psychiatry . 2011; 53(2):172-175. Accessed June 14, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3136027/
- Tullu MS. Writing the title and abstract for a research paper: Being concise, precise, and meticulous is the key. 2019; 13(Suppl 1): S12-S17. Accessed June 14, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6398294/
- Zawia J. Writing an Academic Paper? Get to know Abstracts vs. Structured Abstracts. Medium. Published October 16, 2023. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://medium.com/@jamala.zawia/writing-an-academic-paper-get-to-know-abstracts-vs-structured-abstracts-11ed86888367
- Markel M and Selber S. Technical Communication, 12 th edition. 2018; pp. 482. Bedford/St Martin’s.
- Abstracts. Arkansas State University. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://www.astate.edu/a/global-initiatives/online/a-state-online-services/online-writing-center/resources/How%20to%20Write%20an%20Abstract1.pdf
- AMA Manual of Style. 11 th edition. Oxford University Press.
- Writing an Abstract. The University of Melbourne. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://services.unimelb.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/471274/Writing_an_Abstract_Update_051112.pdf
- 10 Good Abstract Examples that will Kickstart Your Brain. Kibin Essay Writing Blog. Published April 5, 2017. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://www.kibin.com/essay-writing-blog/10-good-abstract-examples/
- A 10-step guide to make your research paper abstract more effective. Editage Insights. Published October 16, 2013. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://www.editage.com/insights/a-10-step-guide-to-make-your-research-paper-abstract-more-effective
- Using keywords to write your title and abstract. Taylor & Francis Author Services. Accessed June 15, 2024. https://authorservices.taylorandfrancis.com/publishing-your-research/writing-your-paper/using-keywords-to-write-title-and-abstract/
- How to choose and use keywords in research papers. Paperpal by Editage blog. Published March 10, 2023. Accessed June 17, 2024. https://paperpal.com/blog/researcher-resources/phd-pointers/how-to-choose-and-use-keywords-in-research-papers
- Title, abstract and keywords. Springer. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://www.springer.com/it/authors-editors/authorandreviewertutorials/writing-a-journal-manuscript/title-abstract-and-keywords/10285522
- Abstract and keywords guide. APA Style, 7 th edition. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/abstract-keywords-guide.pdf
- Abstract guidelines. American Society for Microbiology. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://asm.org/events/asm-microbe/present/abstract-guidelines
- Guidelines for conference abstracts. The Lancet. Accessed June 16, 2024. https://www.thelancet.com/pb/assets/raw/Lancet/pdfs/Abstract_Guidelines_2013.pdf
- Is a conference abstract the same as a paper abstract? Global Conference Alliance, Inc. Accessed June 18, 2024. https://globalconference.ca/is-a-conference-abstract-the-same-as-a-paper-abstract/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What are Journal Guidelines on Using Generative AI Tools
- How to Write a High-Quality Conference Paper
How to Write Dissertation Acknowledgements?
- How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?
Top 7 AI Tools for Research 2024
You may also like, how to write a thematic literature review, chicago style citation guide: understanding the chicago manual..., what is the purpose of an abstract why..., what are citation styles which citation style to..., what are the types of literature reviews , abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples .
Academic & Employability Skills
Subscribe to academic & employability skills.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Writing an abstract - a six point checklist (with samples)
Posted in: abstract , dissertations

The abstract is a vital part of any research paper. It is the shop front for your work, and the first stop for your reader. It should provide a clear and succinct summary of your study, and encourage your readers to read more. An effective abstract, therefore should answer the following questions:
- Why did you do this study or project?
- What did you do and how?
- What did you find?
- What do your findings mean?
So here's our run down of the key elements of a well-written abstract.
- Size - A succinct and well written abstract should be between approximately 100- 250 words.
- Background - An effective abstract usually includes some scene-setting information which might include what is already known about the subject, related to the paper in question (a few short sentences).
- Purpose - The abstract should also set out the purpose of your research, in other words, what is not known about the subject and hence what the study intended to examine (or what the paper seeks to present).
- Methods - The methods section should contain enough information to enable the reader to understand what was done, and how. It should include brief details of the research design, sample size, duration of study, and so on.
- Results - The results section is the most important part of the abstract. This is because readers who skim an abstract do so to learn about the findings of the study. The results section should therefore contain as much detail about the findings as the journal word count permits.
- Conclusion - This section should contain the most important take-home message of the study, expressed in a few precisely worded sentences. Usually, the finding highlighted here relates to the primary outcomes of the study. However, other important or unexpected findings should also be mentioned. It is also customary, but not essential, to express an opinion about the theoretical or practical implications of the findings, or the importance of their findings for the field. Thus, the conclusions may contain three elements:
- The primary take-home message.
- Any additional findings of importance.
- Implications for future studies.

Example Abstract 2: Engineering Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone.

Abstract from: Dalstra, M., Huiskes, R. and Van Erning, L., 1995. Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone. Journal of biomechanical engineering, 117(3), pp.272-278.
And finally... A word on abstract types and styles
Abstract types can differ according to subject discipline. You need to determine therefore which type of abstract you should include with your paper. Here are two of the most common types with examples.
Informative Abstract
The majority of abstracts are informative. While they still do not critique or evaluate a work, they do more than describe it. A good informative abstract acts as a surrogate for the work itself. That is, the researcher presents and explains all the main arguments and the important results and evidence in the paper. An informative abstract includes the information that can be found in a descriptive abstract [purpose, methods, scope] but it also includes the results and conclusions of the research and the recommendations of the author. The length varies according to discipline, but an informative abstract is usually no more than 300 words in length.
Descriptive Abstract A descriptive abstract indicates the type of information found in the work. It makes no judgements about the work, nor does it provide results or conclusions of the research. It does incorporate key words found in the text and may include the purpose, methods, and scope of the research. Essentially, the descriptive abstract only describes the work being summarised. Some researchers consider it an outline of the work, rather than a summary. Descriptive abstracts are usually very short, 100 words or less.
Adapted from Andrade C. How to write a good abstract for a scientific paper or conference presentation. Indian J Psychiatry. 2011 Apr;53(2):172-5. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.82558. PMID: 21772657; PMCID: PMC3136027 .
Have you seen?
Share this:.
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Click here to cancel reply.
- Email * (we won't publish this)
Write a response
Critical Writing
How you can be a better critical writer: going beyond description Have you ever handed in a piece of writing – an essay or report, for example – and got comments back from your tutor saying that it needs to...

Navigating the dissertation process: my tips for final years
Imagine for a moment... After months of hard work and research on a topic you're passionate about, the time has finally come to click the 'Submit' button on your dissertation. You've just completed your longest project to date as part...

8 ways to beat procrastination
Whether you’re writing an assignment or revising for exams, getting started can be hard. Fortunately, there’s lots you can do to turn procrastination into action.

- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 3. The Abstract
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Resources
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
An abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of 300 words or less, the major aspects of the entire paper in a prescribed sequence that includes: 1) the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated; 2) the basic design of the study; 3) major findings or trends found as a result of your analysis; and, 4) a brief summary of your interpretations and conclusions.
Writing an Abstract. The Writing Center. Clarion University, 2009; Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper. The Writing Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison; Koltay, Tibor. Abstracts and Abstracting: A Genre and Set of Skills for the Twenty-first Century . Oxford, UK: Chandos Publishing, 2010;
Importance of a Good Abstract
Sometimes your professor will ask you to include an abstract, or general summary of your work, with your research paper. The abstract allows you to elaborate upon each major aspect of the paper and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Therefore, enough key information [e.g., summary results, observations, trends, etc.] must be included to make the abstract useful to someone who may want to examine your work.
How do you know when you have enough information in your abstract? A basic rule-of-thumb is to imagine that you are another researcher doing a similar study. Then ask yourself: if your abstract was the only part of the paper you could access, would you be happy with the amount of information presented there? Does it tell the whole story about your study? If the answer is "no" then the abstract likely needs to be revised.
Farkas, David K. “A Scheme for Understanding and Writing Summaries.” Technical Communication 67 (August 2020): 45-60; How to Write a Research Abstract. Office of Undergraduate Research. University of Kentucky; Staiger, David L. “What Today’s Students Need to Know about Writing Abstracts.” International Journal of Business Communication January 3 (1966): 29-33; Swales, John M. and Christine B. Feak. Abstracts and the Writing of Abstracts . Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2009.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types of Abstracts
To begin, you need to determine which type of abstract you should include with your paper. There are four general types.
Critical Abstract A critical abstract provides, in addition to describing main findings and information, a judgment or comment about the study’s validity, reliability, or completeness. The researcher evaluates the paper and often compares it with other works on the same subject. Critical abstracts are generally 400-500 words in length due to the additional interpretive commentary. These types of abstracts are used infrequently.
Descriptive Abstract A descriptive abstract indicates the type of information found in the work. It makes no judgments about the work, nor does it provide results or conclusions of the research. It does incorporate key words found in the text and may include the purpose, methods, and scope of the research. Essentially, the descriptive abstract only describes the work being summarized. Some researchers consider it an outline of the work, rather than a summary. Descriptive abstracts are usually very short, 100 words or less. Informative Abstract The majority of abstracts are informative. While they still do not critique or evaluate a work, they do more than describe it. A good informative abstract acts as a surrogate for the work itself. That is, the researcher presents and explains all the main arguments and the important results and evidence in the paper. An informative abstract includes the information that can be found in a descriptive abstract [purpose, methods, scope] but it also includes the results and conclusions of the research and the recommendations of the author. The length varies according to discipline, but an informative abstract is usually no more than 300 words in length.
Highlight Abstract A highlight abstract is specifically written to attract the reader’s attention to the study. No pretense is made of there being either a balanced or complete picture of the paper and, in fact, incomplete and leading remarks may be used to spark the reader’s interest. In that a highlight abstract cannot stand independent of its associated article, it is not a true abstract and, therefore, rarely used in academic writing.
II. Writing Style
Use the active voice when possible , but note that much of your abstract may require passive sentence constructions. Regardless, write your abstract using concise, but complete, sentences. Get to the point quickly and always use the past tense because you are reporting on a study that has been completed.
Abstracts should be formatted as a single paragraph in a block format and with no paragraph indentations. In most cases, the abstract page immediately follows the title page. Do not number the page. Rules set forth in writing manual vary but, in general, you should center the word "Abstract" at the top of the page with double spacing between the heading and the abstract. The final sentences of an abstract concisely summarize your study’s conclusions, implications, or applications to practice and, if appropriate, can be followed by a statement about the need for additional research revealed from the findings.
Composing Your Abstract
Although it is the first section of your paper, the abstract should be written last since it will summarize the contents of your entire paper. A good strategy to begin composing your abstract is to take whole sentences or key phrases from each section of the paper and put them in a sequence that summarizes the contents. Then revise or add phrases or words to make the narrative flow clearly and smoothly. A useful strategy is to avoid using conjunctions [ e.g. and, but, if] that connect long clauses or sentences and, instead, write short, concise sentences . Note that statistical findings should be reported parenthetically [i.e., written in parentheses].
Before handing in your final paper, check to make sure that the information in the abstract completely agrees with what you have written in the paper. Think of the abstract as a sequential set of complete sentences describing the most crucial information using the fewest necessary words. The abstract SHOULD NOT contain:
- A catchy introductory phrase, provocative quote, or other device to grab the reader's attention,
- Lengthy background or contextual information,
- Redundant phrases, unnecessary adverbs and adjectives, and repetitive information;
- Acronyms or abbreviations,
- References to other literature [say something like, "current research shows that..." or "studies have indicated..."],
- Using ellipticals [i.e., ending with "..."] or incomplete sentences,
- Jargon or terms that may be confusing to the reader,
- Citations to other works, and
- Any sort of image, illustration, figure, or table, or references to them.
Abstract. Writing Center. University of Kansas; Abstract. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Abstracts. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Borko, Harold and Seymour Chatman. "Criteria for Acceptable Abstracts: A Survey of Abstracters' Instructions." American Documentation 14 (April 1963): 149-160; Abstracts. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Hartley, James and Lucy Betts. "Common Weaknesses in Traditional Abstracts in the Social Sciences." Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology 60 (October 2009): 2010-2018; Koltay, Tibor. Abstracts and Abstracting: A Genre and Set of Skills for the Twenty-first Century. Oxford, UK: Chandos Publishing, 2010; Procter, Margaret. The Abstract. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Riordan, Laura. “Mastering the Art of Abstracts.” The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association 115 (January 2015 ): 41-47; Writing Report Abstracts. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing Abstracts. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Koltay, Tibor. Abstracts and Abstracting: A Genre and Set of Skills for the Twenty-First Century . Oxford, UK: 2010; Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper. The Writing Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison.
Writing Tip
Never Cite Just the Abstract!
Citing to just a journal article's abstract does not confirm for the reader that you have conducted a thorough or reliable review of the literature. If the full-text is not available, go to the USC Libraries main page and enter the title of the article [NOT the title of the journal]. If the Libraries have a subscription to the journal, the article should appear with a link to the full-text or to the journal publisher page where you can get the article. If the article does not appear, try searching Google Scholar using the link on the USC Libraries main page [scroll down under the heading Quick Links]. If you still can't find the article after doing this, contact a librarian or you can request it from our free i nterlibrary loan and document delivery service .
- << Previous: Research Process Video Series
- Next: Executive Summary >>
- Last Updated: Dec 13, 2024 2:07 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to…
Two Types of Abstracts The informative abstract is a brief description of a document's contents. It usually summarizes the major sections and points of a paper. If you are writing an informative abstract of a scientific or technical paper, it typically summarizes the introduction, methods, results, and discussion sections.
An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a thesis, dissertation or research paper). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about. Although the structure may vary slightly depending on your discipline, your abstract should describe the purpose of your ...
Research Paper Abstract. An abstract is a brief summary of a research paper that typically ranges from 150 to 300 words. It succinctly describes the key components of the study, including its objectives, methods, findings, and implications. Key Characteristics of an Abstract: Concise: Provides a complete overview within a limited word count.
Abstract Research Paper Definition. A research paper abstract is the face of the research paper. This means that it is what creates the first impression of the paper. It is the summary of the research paper and communicates the content quality and relevance. They exist with one vital purpose, and that is to sell your research.
There are six steps to writing a standard abstract. (1) Begin with a broad statement about your topic. Then, (2) state the problem or knowledge gap related to this topic that your study explores. After that, (3) describe what specific aspect of this problem you investigated, and (4) briefly explain how you went about doing this. After that, (5) describe the most meaningful outcome(s) of your ...
It provides an overview of the paper and helps readers decide whether to read the full text. Limit your abstract to 250 words. 1. Abstract Content . The abstract addresses the following (usually 1-2 sentences per topic): • key aspects of the literature review • problem under investigation or research question(s) • clearly stated ...
An abstract in research papers is a keyword-rich summary usually not exceeding 200-350 words. It can be considered the "face" of research papers because it creates an initial impression on the readers. While searching databases (such as PubMed) for research papers, a title is usually the first selection criterion for readers.
The abstract is a vital part of any research paper. It is the shop front for your work, and the first stop for your reader. ... That is, the researcher presents and explains all the main arguments and the important results and evidence in the paper. An informative abstract includes the information that can be found in a descriptive abstract ...
An abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of 300 words or less, the major aspects of the entire paper in a prescribed sequence that includes: 1) the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated; 2) the basic design of the study; 3) major findings or trends found as a result of your analysis; and, 4) a brief summary of your interpretations and conclusions.