
Entrepreneurs Data

Importance of Business Plan to an Entrepreneur: Guide to Implement
Importance of Business Plan to an Entrepreneur – A business plan is an essential road map that entrepreneurs use to navigate the difficult process of starting and expanding a profitable firm. It performs as a strategic instrument for outlining the goals. Also, serve as a financial prediction of a company.
Whether you’re just starting or an experienced entrepreneur looking to sharpen your strategies, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and instructions you need to harness the power of a well-structured business plan.
Importance of a Business Plan to an Entrepreneurs
A strong business plan’s importance cannot be overstated since it provides entrepreneurs with a comprehensive framework for making decisions, attracting investors , securing funding, and navigating the dynamic business world. This article will cover the significance of a business plan. Also, offer practical guidance on how entrepreneurs can utilize it to advance their ventures. Let’s discuss what are the importance of a business plan to an entrepreneur.
A Business Plan Provides a Roadmap for a Business
A business plan may be compared to a road map that directs businesses toward commercial success. It acts as a strategy document that explains the objectives, strategies, and activities necessary to establish and expand a successful company. A business plan offers entrepreneurs a clear path to follow to accomplish their business goals. It is just like a roadmap that aids travelers in navigating new roads and arriving at their destination.
Picture you are going on a road trip to a dream destination. Before setting off, you would carefully plan your route, mark critical milestones, estimate travel time, and consider alternative paths in case of detours. Similarly, a business plan helps entrepreneurs chart their course by defining their vision, identifying target markets, assessing competition, setting financial goals, and mapping out strategies to overcome challenges.
Read – Can Anyone Be an Entrepreneur
Helps Entrepreneurs to Define Their Objectives
A business plan is a valuable tool that helps entrepreneurs in defining their objectives clearly. It offers business owners a well-organized framework for expressing their vision and establishing clear objectives. Entrepreneurs that go through the process of writing a business plan find clarity and concentration in their goals.
Imagine that an entrepreneur wishes to launch a sustainable clothing line. They would specify their goals through the business planning process, such as advancing ethical fashion, minimizing environmental effects, and making a good social impact. The business plan would outline these objectives and establish strategies and action steps to align the business activities with these goals.
Defined objectives in a business plan help entrepreneurs think critically, establish purpose, and guide decision-making. By setting SMART objectives, entrepreneurs can track performance, evaluate strategies, and make necessary adjustments to achieve desired outcomes. For example, an e-commerce business can increase online sales by 50% within a year, allowing regular monitoring, analysis, and adjustments to achieve its target.
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Identifying Their Target Market
When determining the target market for their goods or services, businesses place a lot of weight on their business plans. A business plan aids entrepreneurs in comprehending their potential clients, their demands, and their preferences by doing in-depth market research and analysis. This knowledge is essential for creating efficient marketing plans and modifying the company’s product offerings to satisfy the needs of the target market.
Let’s use the example of an entrepreneur who wants to launch a line of fitness clothes to demonstrate the significance of this. They would do market research as part of the process of writing a business plan to pinpoint their target consumers, such as fitness fanatics, gym visitors, or athletes. The business plan would include insightful information on the target market’s demographics, hobbies, and purchase patterns. With this knowledge, the business owner may carefully coordinate their product offering, price, and marketing messaging to appeal to the determined target demographic.
Entrepreneurs may focus on the appropriate audience, avoid one-size-fits-all techniques, and customize their products, services, and marketing strategies to their consumers’ needs by determining their target market. This aids in comprehending the competitive landscape, spotting gaps, and creating distinctive value propositions that appeal to the target market.
Read – Qualities of a Good Businessman
Helps Entrepreneurs to Assesses Competition
A business plan is a valuable tool that helps entrepreneurs assess their competition and gain a deeper understanding of the market landscape in which they operate. By following a structured approach, a business plan guides entrepreneurs on how to effectively analyze and evaluate their competitors.
A business plan helps entrepreneurs identify their key competitors by conducting research and gathering information about their products or services, pricing strategies, target market, marketing tactics, distribution channels, and customer reviews. This helps entrepreneurs understand their unique selling points and position themselves in the market. Entrepreneurs can compare their strengths and weaknesses to those of their competitors, identifying areas for differentiation. They also analyze market demand and customer preferences to identify gaps or underserved segments, tailoring their products or services to cater to these needs. A business plan guides entrepreneurs in positioning themselves against their competition, developing a unique value proposition that resonates with the target market. This roadmap helps entrepreneurs stay agile and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Importance to Evaluate Feasibility
When assessing the viability of their business idea, entrepreneurs must give the highest priority to their business plans. It acts as a helpful road map for business owners as they determine whether their idea is workable and has the potential to succeed.
Entrepreneurs should undertake in-depth market research and analysis, create financial predictions, perform a SWOT analysis, examine operational factors, and seek professional guidance to determine whether a company strategy is feasible. These steps help determine the feasibility of the business idea, identify potential blind spots, and develop contingency plans. By addressing factors such as resource availability, skills, expertise, infrastructure requirements, and operational processes, entrepreneurs can develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate risks and ensure the venture’s success.
Read – Benefits of Being an Entrepreneur
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Attract Investors
A business plan holds immense importance for entrepreneurs when it comes to attracting investors to support their venture. A well-crafted business plan serves as a persuasive tool that demonstrates the potential of the business and convinces investors to provide financial backing.
To attract investors, entrepreneurs should create a compelling executive summary, detailed business description, market analysis, competitive advantage, financial projections, marketing and sales strategy, management team, risk assessment and mitigation, and clear exit strategy. These elements help investors understand the business’s growth potential, market potential, and competitive advantage.
Helps Entrepreneurs to Secures Their Funding
A business plan is essential for assisting entrepreneurs in obtaining finance for their projects. It acts as a roadmap that details the company’s potential, financial estimates, and growth plans. Entrepreneurs should write a succinct executive summary, thorough business description, market and competitive analysis, financial projections, funding requirements, marketing and sales strategy, management team, risk assessment, and mitigation, and supporting documents to obtain funding through a business plan.
These elements help investors and lenders understand the business’s unique value proposition, target market, revenue potential, and funding requirements. By presenting realistic financial projections, well-supported financial projections, and a well-thought-out marketing and sales strategy, entrepreneurs can secure funding and attract investors and lenders.
Read – Common Myths about Entrepreneurs
Business Plan Guides Entrepreneurs to Resource Allocation
A business plan serves as a valuable tool that guides entrepreneurs in allocating their resources effectively. It provides a clear roadmap for resource allocation by outlining the key areas of the business that require attention and investment.
To effectively allocate resources in a business plan, entrepreneurs should identify resource needs, set priorities, allocate financial resources based on projections and budget, allocate human resources based on skills and expertise, optimize time management, monitor and adjust resource allocation, seek efficiency and optimization, and regularly review and update the plan to reflect changes in resource needs. By doing so, entrepreneurs can optimize their resources and maximize the value derived from available resources. Regularly reviewing and updating the business plan ensures that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.

Importance to Facilitate Decision-Making
A business plan holds great importance for entrepreneurs in facilitating effective decision-making throughout their entrepreneurial journey. It provides a framework that helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions by considering various factors and evaluating potential outcomes.
To effectively use a business plan for decision-making, entrepreneurs should define goals and objectives, gather relevant information, evaluate alternatives, consider financial implications, analyze risks and mitigation strategies, seek input from experts, regularly review and update the plan, and trust intuition and vision. This balances analytical thinking with an entrepreneurial instinct, ensuring long-term sustainability and informed decisions.
Read – Entrepreneur Mindset Books
Identifies Risks and Mitigation Strategies
A business plan plays a vital role in helping entrepreneurs identify risks and develop effective mitigation strategies. By carefully considering potential challenges and uncertainties, entrepreneurs can proactively address them and minimize their impact on the business.
To identify risks and develop mitigation strategies in a business plan, conduct a comprehensive risk assessment, analyze the impact and likelihood of risks, and develop specific strategies. Allocate resources, including financial, personnel, and time, to support the implementation of these strategies. Regularly monitor and update the business plan, seeking external expertise or consulting with industry professionals to gain insights. Communicate the identified risks and mitigation strategies clearly to stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and partners, to demonstrate professionalism and confidence in the business.
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Assists in Team Building
A business plan holds great importance for entrepreneurs in assisting them with team building, as it provides a clear framework for recruiting, developing, and managing their team effectively.
Entrepreneurs can use a business plan to aid in team building by defining roles and responsibilities, establishing recruitment criteria, developing a training and development plan, fostering a collaborative culture, setting performance goals and metrics, regularly evaluating and providing feedback, and fostering leadership and empowerment. These steps help attract and select the right individuals, align with the business plan’s objectives, and promote a supportive environment for innovation and creativity.
Read – Entrepreneurship Books for Students
Business Plan Supports Marketing and Sales Efforts
A business plan holds significant importance in supporting marketing and sales efforts for entrepreneurs. It provides a strategic roadmap for effectively promoting products or services and attracting customers. A business plan helps understand the target market, define the unique selling proposition (USP), develop marketing strategies, allocate budgets, monitor and measure results, and adapt and evolve.
By conducting thorough market research, defining the USP, and focusing on channels and tactics, entrepreneurs can effectively reach and engage their target audience. Regularly updating the business plan to reflect market trends and competitors can help entrepreneurs stay competitive and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Guides Product or Service Development
A business plan is essential for directing entrepreneurs as they create their goods or services. It offers a methodical way to determine consumer demands, specify product characteristics, and create a schedule for product development.
A business plan can guide product or service development by identifying customer needs, defining product or service features, setting development milestones, determining resource requirements, conducting testing and iteration, and integrating marketing and launch strategies. This helps entrepreneurs stay focused, track progress, and ensure the timely completion of activities. The plan should also outline the necessary funding, collaborations, and resources needed for the development process. By incorporating continuous improvement and iterative development, entrepreneurs can create a high-quality offering that meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Read – Green Innovation
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Manage Finances Effectively
A business plan holds great importance for entrepreneurs when it comes to managing finances effectively. It offers a thorough foundation for comprehending the financial facets of the firm and aids business owners in making defensible choices to maximize financial resources.
Entrepreneurs should construct a financial overview, define financial goals and objectives, develop a budget, track financial performance, plan for managing cash flow, and seek expert financial assistance to manage their money efficiently. This helps entrepreneurs forecast future financial needs, allocate resources effectively, and identify potential issues early on. By implementing these strategies, entrepreneurs can ensure the sustainability of their businesses and make informed decisions about their financial future.
Business Plan Measures Progress and Success
A business plan holds significant importance for entrepreneurs in measuring their progress and success. They may compare their accomplishments to it as a standard to see if they are progressing in the correct path.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that are in line with the goals of the business’s plan to successfully measure the growth and success of entrepreneurs. Regularly track and monitor KPIs to assess progress and make informed decisions. Conduct periodic reviews to evaluate progress against the plan, identify areas for adjustments or course corrections, and celebrate milestones and successes. Continuously update and evolve the business plan to reflect evolving goals, strategies, and market conditions.
Read – Difference Between Entrepreneur and Intrapreneur
Business Plan Importance to Enhance Credibility
A business plan plays a crucial role in enhancing the credibility of entrepreneurs and their ventures. It demonstrates to stakeholders, including potential investors, lenders, partners, and even customers, that entrepreneurs have a well-thought-out and strategic approach to their business.
To enhance entrepreneurs’ credibility, a well-presented business plan should present a professional image, conduct thorough market research, highlight the unique selling proposition, provide detailed financial projections, incorporate risk analysis and mitigation strategies, seek third-party validation, and regularly update and refine the plan. This shows credibility and commitment to continuous improvement, demonstrating the business’s ability to adapt and thrive in the ever-changing landscape.
Business Plan Provides a Basis for Partnerships
When forming partnerships, entrepreneurs place a lot of weight on their business plans. It offers a strong platform for prospective partners to comprehend the company. Also, its objectives, and the value it brings.
To successfully attract and establish partnerships, entrepreneurs should clearly define their business, highlight their target customers, market opportunities, and competitive advantages, outline partnership opportunities, develop partnership plans, and use the business plan as a communication tool. This aids potential partners in comprehending the goals and potential of the company as well as the growth potential of the market. Entrepreneurs may successfully convey their vision, ambitions, and potential to potential partners by emphasizing the advantages of collaboration, promoting development and success for both parties.
Read – Imitative Entrepreneurship
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Do Business Expansion
A business plan plays a crucial role for entrepreneurs when it comes to business expansion. It provides a strategic framework and guidance for expanding operations, entering new markets, or launching new products or services.
Entrepreneurs can use a business plan to facilitate expansion by evaluating current performance, defining expansion goals and objectives, conducting market research, developing a strategic expansion plan, assessing financial requirements, monitoring and adjusting the plan as needed, and continuously monitoring and adjusting the plan to ensure success. This approach helps businesses navigate market dynamics, identify strengths and weaknesses, and adapt to unforeseen challenges or opportunities.
Guides Entrepreneurs to Succession Planning
A business plan is of significant importance when it comes to guiding entrepreneurs in succession planning, which involves preparing for the future transition of leadership and ownership within a business.
To effectively use a business plan for succession planning, assess current leadership and ownership, identify potential successors, define succession goals and timeline, develop a succession plan, communicate with stakeholders, and regularly review and update the plan. This process ensures alignment with the long-term vision and aspirations of the business and its stakeholders. Regularly assess the progress of potential successors and provide development opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge.
Importance to Increases Self-Awareness
A business plan is crucial for entrepreneurs because it may help them become more self-aware and better grasp their advantages, disadvantages, and possibilities for growth.
Entrepreneurs should consider their objectives and values, perform a SWOT analysis, create reasonable company goals, ask for criticism and mentoring, constantly evaluate their success, and change to improve their self-awareness. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, entrepreneurs can create a clear vision and align their business plans with their values. By seeking feedback and mentoring, entrepreneurs can develop a stronger self-awareness and improve their business strategies.

An effective business plan is a crucial tool for entrepreneurs . It gives them a path to success. A successful business plan may help entrepreneurs define clear goals. Also, identify their target market, analyze the competition, determine whether their idea is feasible, draw in investors, manage funds, and track their progress. It functions as a manual to assist business owners make wise decisions, manage resources effectively, and adjust to changing conditions.
A solid business plan is crucial for entrepreneurs to navigate the complex commercial world, guiding their companies toward expansion, profitability, and long-term success. It should be evaluated and revised regularly to reflect company demands, serving as a compass for entrepreneurs.
FAQ about the Importance of Business Plans to Entrepreneurs
Why is a business plan important.
Because it gives business owners a clear road map for their venture, a business plan is crucial. It aids in establishing goals, locating target markets, evaluating rivalry, obtaining finance, and coming to wise conclusions. Describing their vision and plans, it functions as a strategic instrument that leads business owners toward success.
When is the Best Time to Write a Business Plan?
Typically, before launching a new firm. It is the ideal time to draft a business plan. Likewise, when a current firm is expected to undergo significant adjustments. Be sure you have a solid strategy in place before approaching investors, looking for finance. Especially, starting a business. Making a business plan, though, is never too late, and you can always change it as your company grows.
What is a Business Plan’s Main Objective?
A business plan’s main objective is to outline an organization’s goals, strategies, and financial predictions. It helps business owners communicate their vision, pinpoint their target market, assess the profitability of their endeavor, entice investors, and allocate their resources effectively. It serves as a compass for monitoring growth and making adjustments as needed.
What are the Typical Challenges of Writing a Business Plan?
Entrepreneurs face hurdles while drafting a business plan, such as limited time and resources, writing skills, market research, financial predictions, and strategic planning. The complexity of the process may be increased by using accurate market data, reasonable estimates, strategic planning, clear writing, and managing other elements of the firm.
Do you REALLY need a business plan?
The top three questions that I get asked most frequently as a professional business plan writer will probably not surprise you:
- What is the purpose of a business plan – why is it really required?
- How is it going to benefit my business if I write a business plan?
- Is a business plan really that important – how can I actually use it?
Keep reading to get my take on what the most essential advantages of preparing a business plan are—and why you may (not) need to prepare one.
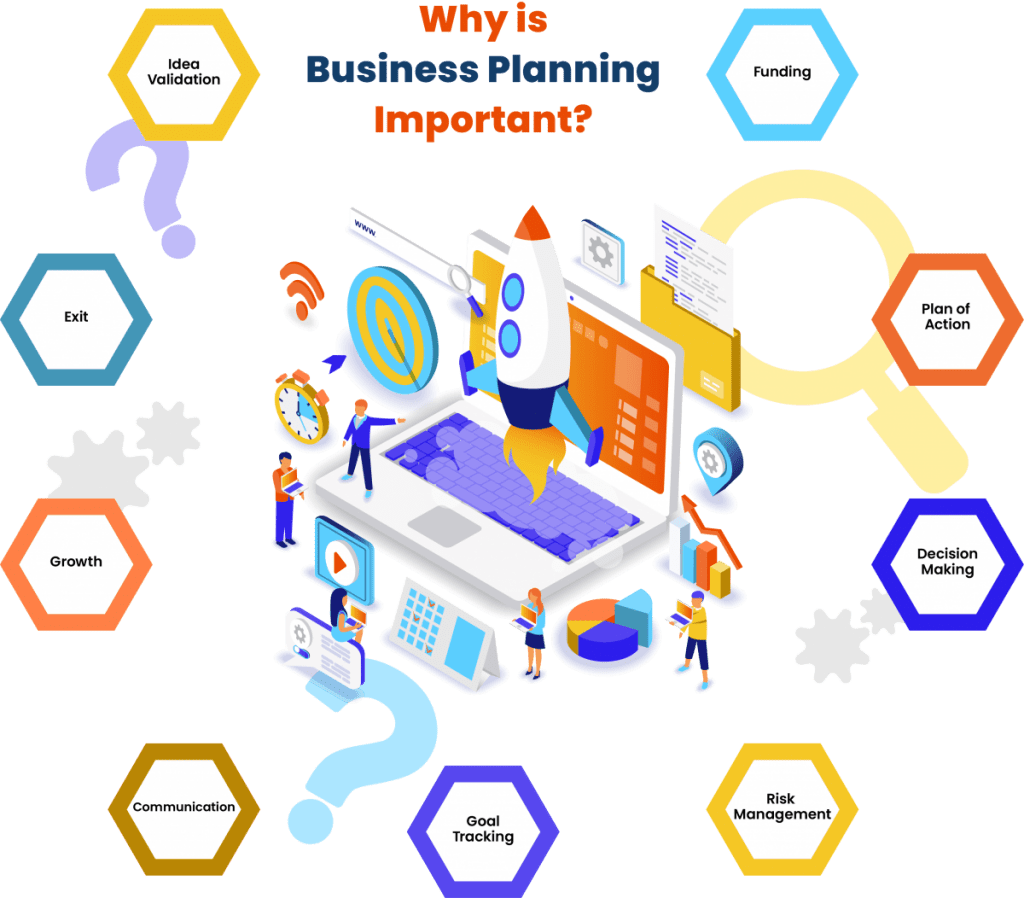
The importance, purpose and benefit of a business plan is in that it enables you to validate a business idea, secure funding, set strategic goals – and then take organized action on those goals by making decisions, managing resources, risk and change, while effectively communicating with stakeholders.
Let’s take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward:
1. Validate Your Business Idea
The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including:
- External: industry, target market of prospective customers, competitive landscape
- Internal: business model, unique selling proposition, operations, marketing, finance
Business planning connects the dots to draw a big picture of the entire business.
And imagine how much time and money you would save if working through a business plan revealed that your business idea is untenable. You would be surprised how often that happens – an idea that once sounded so very promising may easily fall apart after you actually write down all the facts, details and numbers.
While you may be tempted to jump directly into start-up mode, writing a business plan is an essential first step to check the feasibility of a business before investing too much time and money into it. Business plans help to confirm that the idea you are so passionate and convinced about is solid from business point of view.
Take the time to do the necessary research and work through a proper business plan. The more you know, the higher the likelihood that your business will succeed.
2. Set and Track Goals
Successful businesses are dynamic and continuously evolve. And so are good business plans that allow you to:
- Priorities: Regularly set goals, targets (e.g., sales revenues reached), milestones (e.g. number of employees hired), performance indicators and metrics for short, mid and long term
- Accountability: Track your progress toward goals and benchmarks
- Course-correction: make changes to your business as you learn more about your market and what works and what does not
- Mission: Refer to a clear set of values to help steer your business through any times of trouble
Essentially, business plan is a blueprint and an important strategic tool that keeps you focused, motivated and accountable to keep your business on track. When used properly and consulted regularly, it can help you measure and manage what you are working so hard to create – your long-term vision.
As humans, we work better when we have clear goals we can work towards. The everyday business hustle makes it challenging to keep an eye on the strategic priorities. The business planning process serves as a useful reminder.
3. Take Action
A business plan is also a plan of action . At its core, your plan identifies where you are now, where you want your business to go, and how you will get there.
Planning out exactly how you are going to turn your vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between an idea and reality. Success comes not only from having a vision but working towards that vision in a systematic and organized way.
A good business plan clearly outlines specific steps necessary to turn the business objectives into reality. Think of it as a roadmap to success. The strategy and tactics need to be in alignment to make sure that your day-to-day activities lead to the achievement of your business goals.
4. Manage Resources
A business plan also provides insight on how resources required for achieving your business goals will be structured and allocated according to their strategic priority. For example:
Large Spending Decisions
- Assets: When and in what amount will the business commit resources to buy/lease new assets, such as computers or vehicles.
- Human Resources: Objectives for hiring new employees, including not only their pay but how they will help the business grow and flourish.
- Business Space: Information on costs of renting/buying space for offices, retail, manufacturing or other operations, for example when expanding to a new location.
Cash Flow It is essential that a business carefully plans and manages cash flows to ensure that there are optimal levels of cash in the bank at all times and avoid situations where the business could run out of cash and could not afford to pay its bills.
Revenues v. Expenses In addition, your business plan will compare your revenue forecasts to the budgeted costs to make sure that your financials are healthy and the business is set up for success.
5. Make Decisions
Whether you are starting a small business or expanding an existing one, a business plan is an important tool to help guide your decisions:
Sound decisions Gathering information for the business plan boosts your knowledge across many important areas of the business:
- Industry, market, customers and competitors
- Financial projections (e.g., revenue, expenses, assets, cash flow)
- Operations, technology and logistics
- Human resources (management and staff)
- Creating value for your customer through products and services
Decision-making skills The business planning process involves thorough research and critical thinking about many intertwined and complex business issues. As a result, it solidifies the decision-making skills of the business owner and builds a solid foundation for strategic planning , prioritization and sound decision making in your business. The more you understand, the better your decisions will be.
Planning Thorough planning allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time , prepare for anticipate problems before they arise, and ensure that any tactical solutions are in line with the overall strategy and goals.
If you do not take time to plan, you risk becoming overwhelmed by countless options and conflicting directions because you are not unclear about the mission , vision and strategy for your business.
6. Manage Risk
Some level of uncertainty is inherent in every business, but there is a lot you can do to reduce and manage the risk, starting with a business plan to uncover your weak spots.
You will need to take a realistic and pragmatic look at the hard facts and identify:
- Major risks , challenges and obstacles that you can expect on the way – so you can prepare to deal with them.
- Weaknesses in your business idea, business model and strategy – so you can fix them.
- Critical mistakes before they arise – so you can avoid them.
Essentially, the business plan is your safety net . Naturally, business plan cannot entirely eliminate risk, but it can significantly reduce it and prepare you for any challenges you may encounter.
7. Communicate Internally
Attract talent For a business to succeed, attracting talented workers and partners is of vital importance.
A business plan can be used as a communication tool to attract the right talent at all levels, from skilled staff to executive management, to work for your business by explaining the direction and growth potential of the business in a presentable format.
Align performance Sharing your business plan with all team members helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to the long-term vision and strategy.
You need their buy-in from the beginning, because aligning your team with your priorities will increase the efficiency of your business as everyone is working towards a common goal .
If everyone on your team understands that their piece of work matters and how it fits into the big picture, they are more invested in achieving the objectives of the business.
It also makes it easier to track and communicate on your progress.
Share and explain business objectives with your management team, employees and new hires. Make selected portions of your business plan part of your new employee training.
8. Communicate Externally
Alliances If you are interested in partnerships or joint ventures, you may share selected sections of your plan with the potential business partners in order to develop new alliances.
Suppliers A business plan can play a part in attracting reliable suppliers and getting approved for business credit from suppliers. Suppliers who feel confident that your business will succeed (e.g., sales projections) will be much more likely to extend credit.
In addition, suppliers may want to ensure their products are being represented in the right way .
Professional Services Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, including attorneys, accountants, and other professional consultants as needed, to make sure that everyone is on the same page.
Advisors Share the plan with experts and professionals who are in a position to give you valuable advice.
Landlord Some landlords and property managers require businesses to submit a business plan to be considered for a lease to prove that your business will have sufficient cash flows to pay the rent.
Customers The business plan may also function as a prospectus for potential customers, especially when it comes to large corporate accounts and exclusive customer relationships.
9. Secure Funding
If you intend to seek outside financing for your business, you are likely going to need a business plan.
Whether you are seeking debt financing (e.g. loan or credit line) from a lender (e.g., bank or financial institution) or equity capital financing from investors (e.g., venture or angel capital), a business plan can make the difference between whether or not – and how much – someone decides to invest.
Investors and financiers are always looking at the risk of default and the earning potential based on facts and figures. Understandably, anyone who is interested in supporting your business will want to check that you know what you are doing, that their money is in good hands, and that the venture is viable in the long run.
Business plans tend to be the most effective ways of proving that. A presentation may pique their interest , but they will most probably request a well-written document they can study in detail before they will be prepared to make any financial commitment.
That is why a business plan can often be the single most important document you can present to potential investors/financiers that will provide the structure and confidence that they need to make decisions about funding and supporting your company.
Be prepared to have your business plan scrutinized . Investors and financiers will conduct extensive checks and analyses to be certain that what is written in your business plan faithful representation of the truth.
10. Grow and Change
It is a very common misconception that a business plan is a static document that a new business prepares once in the start-up phase and then happily forgets about.
But businesses are not static. And neither are business plans. The business plan for any business will change over time as the company evolves and expands .
In the growth phase, an updated business plan is particularly useful for:
Raising additional capital for expansion
- Seeking financing for new assets , such as equipment or property
- Securing financing to support steady cash flows (e.g., seasonality, market downturns, timing of sale/purchase invoices)
- Forecasting to allocate resources according to strategic priority and operational needs
- Valuation (e.g., mergers & acquisitions, tax issues, transactions related to divorce, inheritance, estate planning)
Keeping the business plan updated gives established businesses better chance of getting the money they need to grow or even keep operating.
Business plan is also an excellent tool for planning an exit as it would include the strategy and timelines for a transfer to new ownership or dissolution of the company.
Also, if you ever make the decision to sell your business or position yourself for a merger or an acquisition , a strong business plan in hand is going to help you to maximize the business valuation.
Valuation is the process of establishing the worth of a business by a valuation expert who will draw on professional experience as well as a business plan that will outline what you have, what it’s worth now and how much will it likely produce in the future.
Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if they clearly understand your business model, your market, your assets and your overall potential to grow and scale .
Related Questions
Business plan purpose: what is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of a business plan is to articulate a strategy for starting a new business or growing an existing one by identifying where the business is going and how it will get there to test the viability of a business idea and maximize the chances of securing funding and achieving business goals and success.
Business Plan Benefits: What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan benefits businesses by serving as a strategic tool outlining the steps and resources required to achieve goals and make business ideas succeed, as well as a communication tool allowing businesses to articulate their strategy to stakeholders that support the business.
Business Plan Importance: Why is business plan important?
The importance of a business plan lies in it being a roadmap that guides the decisions of a business on the road to success, providing clarity on all aspects of its operations. This blueprint outlines the goals of the business and what exactly is needed to achieve them through effective management.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Sep 19, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

10 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024

There’s no question that starting and running a business is hard work. But it’s also incredibly rewarding. And, one of the most important things you can do to increase your chances of success is to have a business plan.
A business plan is a foundational document that is essential for any company, no matter the size or age. From attracting potential investors to keeping your business on track—a business plan helps you achieve important milestones and grow in the right direction.

A business plan isn’t just a document you put together once when starting your business. It’s a living, breathing guide for existing businesses – one that business owners should revisit and update regularly.
Unfortunately, writing a business plan is often a daunting task for potential entrepreneurs. So, do you really need a business plan? Is it really worth the investment of time and resources? Can’t you just wing it and skip the whole planning process?
Good questions. Here’s every reason why you need a business plan.
- 1. Business planning is proven to help you grow 30 percent faster
Writing a business plan isn’t about producing a document that accurately predicts the future of your company. The process of writing your plan is what’s important. Writing your plan and reviewing it regularly gives you a better window into what you need to do to achieve your goals and succeed.
You don’t have to just take our word for it. Studies have proven that companies that plan and review their results regularly grow 30 percent faster. Beyond faster growth, research also shows that companies that plan actually perform better. They’re less likely to become one of those woeful failure statistics, or experience cash flow crises that threaten to close them down.
- 2. Planning is a necessary part of the fundraising process
One of the top reasons to have a business plan is to make it easier to raise money for your business. Without a business plan, it’s difficult to know how much money you need to raise, how you will spend the money once you raise it, and what your budget should be.
Investors want to know that you have a solid plan in place – that your business is headed in the right direction and that there is long-term potential in your venture.
A business plan shows that your business is serious and that there are clearly defined steps on how it aims to become successful. It also demonstrates that you have the necessary competence to make that vision a reality.
Investors, partners, and creditors will want to see detailed financial forecasts for your business that shows how you plan to grow and how you plan on spending their money.
- 3. Having a business plan minimizes your risk
When you’re just starting out, there’s so much you don’t know—about your customers, your competition, and even about operations.
As a business owner, you signed up for some of that uncertainty when you started your business, but there’s a lot you can do to reduce your risk . Creating and reviewing your business plan regularly is a great way to uncover your weak spots—the flaws, gaps, and assumptions you’ve made—and develop contingency plans.
Your business plan will also help you define budgets and revenue goals. And, if you’re not meeting your goals, you can quickly adjust spending plans and create more realistic budgets to keep your business healthy.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- 4. Crafts a roadmap to achieve important milestones
A business plan is like a roadmap for your business. It helps you set, track and reach business milestones.
For your plan to function in this way, your business plan should first outline your company’s short- and long-term goals. You can then fill in the specific steps necessary to reach those goals. This ensures that you measure your progress (or lack thereof) and make necessary adjustments along the way to stay on track while avoiding costly detours.
In fact, one of the top reasons why new businesses fail is due to bad business planning. Combine this with inflexibility and you have a recipe for disaster.
And planning is not just for startups. Established businesses benefit greatly from revisiting their business plan. It keeps them on track, even when the global market rapidly shifts as we’ve seen in recent years.
- 5. A plan helps you figure out if your idea can become a business
To turn your idea into reality, you need to accurately assess the feasibility of your business idea.
You need to verify:
- If there is a market for your product or service
- Who your target audience is
- How you will gain an edge over the current competition
- If your business can run profitably
A business plan forces you to take a step back and look at your business objectively, which makes it far easier to make tough decisions down the road. Additionally, a business plan helps you to identify risks and opportunities early on, providing you with the necessary time to come up with strategies to address them properly.
Finally, a business plan helps you work through the nuts and bolts of how your business will work financially and if it can become sustainable over time.
6. You’ll make big spending decisions with confidence
As your business grows, you’ll have to figure out when to hire new employees, when to expand to a new location, or whether you can afford a major purchase.
These are always major spending decisions, and if you’re regularly reviewing the forecasts you mapped out in your business plan, you’re going to have better information to use to make your decisions.
7. You’re more likely to catch critical cash flow challenges early
The other side of those major spending decisions is understanding and monitoring your business’s cash flow. Your cash flow statement is one of the three key financial statements you’ll put together for your business plan. (The other two are your balance sheet and your income statement (P&L).
Reviewing your cash flow statement regularly as part of your regular business plan review will help you see potential cash flow challenges earlier so you can take action to avoid a cash crisis where you can’t pay your bills.
- 8. Position your brand against the competition
Competitors are one of the factors that you need to take into account when starting a business. Luckily, competitive research is an integral part of writing a business plan. It encourages you to ask questions like:
- What is your competition doing well? What are they doing poorly?
- What can you do to set yourself apart?
- What can you learn from them?
- How can you make your business stand out?
- What key business areas can you outcompete?
- How can you identify your target market?
Finding answers to these questions helps you solidify a strategic market position and identify ways to differentiate yourself. It also proves to potential investors that you’ve done your homework and understand how to compete.
- 9. Determines financial needs and revenue models
A vital part of starting a business is understanding what your expenses will be and how you will generate revenue to cover those expenses. Creating a business plan helps you do just that while also defining ongoing financial needs to keep in mind.
Without a business model, it’s difficult to know whether your business idea will generate revenue. By detailing how you plan to make money, you can effectively assess the viability and scalability of your business.
Understanding this early on can help you avoid unnecessary risks and start with the confidence that your business is set up to succeed.
- 10. Helps you think through your marketing strategy
A business plan is a great way to document your marketing plan. This will ensure that all of your marketing activities are aligned with your overall goals. After all, a business can’t grow without customers and you’ll need a strategy for acquiring those customers.
Your business plan should include information about your target market, your marketing strategy, and your marketing budget. Detail things like how you plan to attract and retain customers, acquire new leads, how the digital marketing funnel will work, etc.
Having a documented marketing plan will help you to automate business operations, stay on track and ensure that you’re making the most of your marketing dollars.
- 11. Clarifies your vision and ensures everyone is on the same page
In order to create a successful business, you need a clear vision and a plan for how you’re going to achieve it. This is all detailed with your mission statement, which defines the purpose of your business, and your personnel plan, which outlines the roles and responsibilities of current and future employees. Together, they establish the long-term vision you have in mind and who will need to be involved to get there.
Additionally, your business plan is a great tool for getting your team in sync. Through consistent plan reviews, you can easily get everyone in your company on the same page and direct your workforce toward tasks that truly move the needle.
- 12. Future-proof your business
A business plan helps you to evaluate your current situation and make realistic projections for the future.
This is an essential step in growing your business, and it’s one that’s often overlooked. When you have a business plan in place, it’s easier to identify opportunities and make informed decisions based on data.
Therefore, it requires you to outline goals, strategies, and tactics to help the organization stay focused on what’s important.
By regularly revisiting your business plan, especially when the global market changes, you’ll be better equipped to handle whatever challenges come your way, and pivot faster.
You’ll also be in a better position to seize opportunities as they arise.
Further Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
- 13. Tracks your progress and measures success
An often overlooked purpose of a business plan is as a tool to define success metrics. A key part of writing your plan involves pulling together a viable financial plan. This includes financial statements such as your profit and loss, cash flow, balance sheet, and sales forecast.
By housing these financial metrics within your business plan, you suddenly have an easy way to relate your strategy to actual performance. You can track progress, measure results, and follow up on how the company is progressing. Without a plan, it’s almost impossible to gauge whether you’re on track or not.
Additionally, by evaluating your successes and failures, you learn what works and what doesn’t and you can make necessary changes to your plan. In short, having a business plan gives you a framework for measuring your success. It also helps with building up a “lessons learned” knowledge database to avoid costly mistakes in the future.
- 14. Your business plan is an asset if you ever want to sell
Down the road, you might decide that you want to sell your business or position yourself for acquisition. Having a solid business plan is going to help you make the case for a higher valuation. Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if it’s easy for them to understand your business model, your target market, and your overall potential to grow and scale.

Free business plan template
Join over 1-million businesses and make planning easy with our simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template.
Download Template
- Writing your business plan
By taking the time to create a business plan, you ensure that your business is heading in the right direction and that you have a roadmap to get there. We hope that this post has shown you just how important and valuable a business plan can be. While it may still seem daunting, the benefits far outweigh the time investment and learning curve for writing one.
Luckily, you can write a plan in as little as 30 minutes. And there are plenty of excellent planning tools and business plan templates out there if you’re looking for more step-by-step guidance. Whatever it takes, write your plan and you’ll quickly see how useful it can be.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- 6. You’ll make big spending decisions with confidence
- 7. You’re more likely to catch critical cash flow challenges early
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How to Run a Productive Monthly Business Plan Review Meeting

11 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline Example to Organize Your Plan

7 Min. Read
5 Consequences of Skipping a Business Plan

8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

The Importance of a Business Plan for Entrepreneurs
Discover the crucial role of a business plan for entrepreneurs. From vision to reality, unleash the power of planning!

The Role of a Business Plan for Entrepreneurs
A business plan serves as a vital tool for entrepreneurs, guiding them from the initial stages of their venture to its successful implementation. It provides a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the vision, goals, and strategies of a business. Understanding what a business plan is and why it is important is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs.

What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a written document that outlines the fundamental aspects of a business. It serves as a blueprint, detailing the mission, vision, target market, products or services, marketing strategies, financial projections, and other essential elements that contribute to the success of a business.
A well-crafted business plan typically includes the following components:
- Executive Summary : Provides an overview of the business, its purpose, and key highlights.
- Company Description : Describes the nature of the business, its structure, and its unique value proposition.
- Market Analysis : Assesses the target market, competition, and industry trends.
- Product or Service Line : Details the offerings and their benefits to customers.
- Marketing and Sales Strategies : Outlines the plans to reach and attract customers.
- Organizational Structure : Defines the roles and responsibilities of team members and their qualifications.
- Financial Projections : Presents the expected financial performance, including revenue, expenses, and profitability.
Why is a Business Plan Important for Entrepreneurs?
A business plan plays a pivotal role in the entrepreneurial journey. Here are key reasons why it is essential:
- Roadmap for Success : A business plan serves as a roadmap, providing a clear path from the initial stages to the long-term goals of the business. It helps entrepreneurs stay focused and make informed decisions, preventing them from getting lost or deviating from their vision.
- Attracting Investors and Lenders : Investors and lenders often require a business plan to assess the viability and potential of a business. A well-prepared plan demonstrates the entrepreneur's commitment, understanding of the market, and potential for profitability, increasing the chances of securing funding.
- Guiding Decision Making : A business plan serves as a decision-making tool, enabling entrepreneurs to evaluate various options and make informed choices. It outlines the strategies and tactics needed to achieve business objectives, ensuring that decisions align with the overall vision and goals.
- Communicating with Stakeholders : A well-written business plan helps entrepreneurs communicate their ideas and plans effectively to team members, stakeholders, and external parties. It aligns everyone involved with the business and facilitates collaboration, fostering a cohesive and productive work environment.
By understanding the importance of a business plan, entrepreneurs can develop a comprehensive and strategic roadmap for their venture. It provides a structured approach for decision making, attracts potential investors, and ensures that the business stays on track towards achieving its goals.
Clarifying Your Vision
Before diving into the details of your business plan, it's essential to clarify your vision and lay a strong foundation for your entrepreneurial journey. This involves defining your business idea and setting clear goals and objectives.
Defining Your Business Idea
To create a successful business plan, you must have a clear understanding of your business idea. Begin by identifying the problem your business aims to solve or the need it fulfills. This could be a product, service, or a unique approach to an existing market.
Take the time to research your target market, competitors, and industry trends. This research will help you refine your business idea, identify gaps in the market, and determine how your offering can stand out. By defining your business idea clearly, you can communicate it effectively in your business plan and attract potential investors or partners.
Setting Clear Goals and Objectives
Once you have a solid understanding of your business idea, it's crucial to establish clear goals and objectives. These goals will guide your business's direction, growth, and decision-making process. Start by setting both short-term and long-term goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals).
Short-term goals may include milestones to achieve within the first year of your business, such as launching a website or acquiring a certain number of customers. Long-term goals could encompass the broader vision for your business, such as achieving a specific market share or expanding into new markets.
In addition to setting goals, it's important to define objectives that outline the steps necessary to reach those goals. Objectives break down your goals into actionable tasks and provide a clear roadmap for implementation. For example, if your goal is to increase sales by 20% in the next year, your objectives might include launching a targeted marketing campaign or expanding distribution channels.
By clearly defining your business idea and setting realistic goals and objectives, you create a strong foundation for your business plan. This clarity will not only guide you in developing the rest of your plan but also demonstrate your vision and commitment to potential investors and stakeholders.
Remember, a well-defined vision and clear goals are integral to the success of your business plan and your overall entrepreneurial journey.
Evaluating Viability and Feasibility
Before diving headfirst into launching a business, it is crucial for entrepreneurs to evaluate the viability and feasibility of their ideas. This process helps determine whether the business has the potential to succeed in the market. Within the business plan, two key components play a vital role in this evaluation: market research and analysis, as well as financial projections and forecasting.
Market Research and Analysis
Market research and analysis are essential steps in assessing the viability of a business idea. Conducting comprehensive market research allows entrepreneurs to gain a deep understanding of the industry, target market, and competitive landscape. It involves gathering and analyzing information related to customer preferences, buying behaviors, market trends, and potential demand for the product or service.
By conducting market research, entrepreneurs can identify gaps in the market, potential opportunities, and areas where their business can differentiate itself from competitors. This information helps in shaping the business strategy, determining pricing strategies, and developing effective marketing plans to reach the target audience. It also allows entrepreneurs to make informed decisions and adjust their business plans accordingly.
Financial Projections and Forecasting
Financial projections and forecasting are vital components of a business plan that help entrepreneurs evaluate the financial feasibility of their venture. By projecting future financial performance, entrepreneurs can assess the viability of their business idea and determine its potential profitability. Financial projections include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, which provide a comprehensive overview of the expected financial outcomes.
To develop accurate financial projections, entrepreneurs need to consider various factors such as revenues, expenses, pricing strategies, production costs, and market demand. By analyzing these factors and making reasonable assumptions, entrepreneurs can estimate their expected sales, costs, and profitability over a specified period. This information is crucial for attracting investors, securing funding, and making sound financial decisions.
Additionally, financial forecasting helps entrepreneurs identify potential risks and challenges that may impact the business's financial performance. By conducting sensitivity analysis and scenario planning, entrepreneurs can explore different outcomes and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks. This demonstrates the entrepreneur's preparedness and ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
It is important to note that financial projections and forecasting should be based on realistic assumptions and thorough research. Seeking guidance from financial experts or utilizing financial modeling tools can help entrepreneurs ensure accuracy and reliability in their projections.
By evaluating the viability and feasibility of their business ideas through market research and financial projections, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions and demonstrate a solid foundation for their business. These steps play a crucial role in shaping the business plan and increasing the chances of success in the competitive marketplace.
Securing Funding and Support
When it comes to turning your business vision into reality, securing funding and support is vital for entrepreneurs. A well-crafted business plan plays a crucial role in attracting investors and lenders while demonstrating your credibility and commitment to the venture.
Attracting Investors and Lenders
One of the primary objectives of a business plan is to attract investors and lenders who can provide the necessary financial support. A comprehensive and compelling business plan acts as a persuasive tool that showcases the potential of your business idea and its profitability.
Investors and lenders carefully evaluate business plans to assess the viability and potential return on investment. It is essential to include key elements in your business plan that appeal to potential funders. These may include:
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of your business plan that highlights the unique selling proposition and the growth potential of your venture.
- Market Analysis: A detailed assessment of the target market, including size, trends, and competition, demonstrating an understanding of the industry landscape.
- Financial Projections: Clear and realistic financial forecasts that outline revenue streams, expenses, and projections for profitability and growth.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: A well-defined plan that outlines how you will reach and attract customers, demonstrating a solid understanding of your target audience and competitive advantage.
- Management Team: Highlight the expertise and experience of your team, showcasing their qualifications to execute the business plan successfully.
By including these elements, you can capture the attention of potential investors and lenders, increasing the likelihood of securing the necessary funding to bring your business idea to life.
Demonstrating Credibility and Commitment
A well-crafted business plan not only attracts financial support but also demonstrates your credibility and commitment to your business venture. Investors and lenders want to see that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and are dedicated to its success.
In your business plan, showcase your expertise, qualifications, and experiences that make you well-suited to lead the venture. This includes highlighting any relevant industry knowledge, previous successful ventures, or unique skills that set you apart from competitors.
Additionally, demonstrating your commitment to the business is crucial. Investors and lenders want to see that you have invested significant time, effort, and resources into developing the business plan. This showcases your dedication and increases their confidence in your ability to execute the plan effectively.
Remember to present your business plan with confidence and professionalism. A well-organized and clearly articulated plan reflects your commitment to professionalism and attention to detail, further enhancing your credibility as an entrepreneur.
By attracting investors and lenders while demonstrating your credibility and commitment, a comprehensive business plan becomes a powerful tool in securing the funding and support necessary to turn your entrepreneurial vision into reality.
Guiding Decision Making and Implementation
A well-crafted business plan serves as a valuable tool for entrepreneurs, providing guidance and direction throughout the journey of turning their vision into reality. In this section, we will explore two key aspects of how a business plan plays a crucial role in guiding decision making and implementation: providing a roadmap for success and tracking progress to make necessary adjustments.
Providing a Roadmap for Success
A business plan acts as a roadmap that outlines the path to success for entrepreneurs. It provides a clear and structured framework for decision making and implementation. By detailing the steps and strategies needed to achieve business goals, a business plan helps entrepreneurs stay focused and on track.
Within the business plan, entrepreneurs define their target market, identify their unique value proposition, and outline their marketing and sales strategies. This comprehensive approach allows entrepreneurs to understand the market dynamics, assess the competition, and develop effective strategies to position their business for success.
Additionally, a business plan helps entrepreneurs anticipate potential challenges and develop contingency plans. By considering various scenarios and outlining strategies to overcome obstacles, entrepreneurs can navigate uncertainties with more confidence and agility. The roadmap provided by a business plan ensures that entrepreneurs are well-prepared to make informed decisions and take the necessary actions to achieve their goals.
Tracking Progress and Making Adjustments
A business plan is not a static document; it evolves along with the business. One of its critical functions is to help entrepreneurs track their progress and make adjustments as needed. By regularly reviewing and comparing actual results against the projected targets outlined in the business plan, entrepreneurs can identify areas where they are excelling and areas that require attention.
Tracking progress allows entrepreneurs to evaluate the effectiveness of their strategies and make informed decisions to optimize their business operations. It enables them to identify trends, patterns, and areas of improvement. For instance, if certain marketing strategies are not generating the desired results, entrepreneurs can refer to their business plan to assess alternative marketing approaches and adjust their tactics accordingly.
Furthermore, the business plan serves as a communication tool when seeking feedback and advice from mentors, advisors, or potential investors. It demonstrates the entrepreneur's commitment to their business and their ability to track and analyze key performance indicators.
By regularly reviewing and updating the business plan, entrepreneurs can align their decisions and actions with the changing dynamics of their business environment. This iterative process ensures that they remain adaptable and responsive to market trends and customer needs.
In summary, a well-crafted business plan not only provides a roadmap for success but also helps entrepreneurs track progress and make necessary adjustments along the way. By having a clear framework in place, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions, stay focused on their goals, and adapt to changes in their business environment. The business plan is a dynamic tool that guides entrepreneurs from the initial stages of their venture to long-term success.
Communicating and Collaborating
A well-crafted business plan not only serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs but also plays a crucial role in aligning team members and stakeholders. Effective communication and collaboration are essential for the success of any business venture. In this section, we will explore two key aspects of communication and collaboration in relation to a business plan: aligning team members and stakeholders, and presenting your business to external parties.
Aligning Team Members and Stakeholders
A business plan acts as a guiding document that helps align team members and stakeholders towards a common vision. By clearly outlining the goals, objectives, and strategies of the business, the plan ensures that everyone involved is on the same page.
When team members have a clear understanding of the business plan, they are better equipped to contribute their skills and expertise towards achieving the stated objectives. This alignment fosters a collaborative environment, where each member is aware of their role and responsibilities in the pursuit of shared goals.
Regular communication and updates are crucial to maintain alignment throughout the implementation of the business plan. Team meetings, progress reports, and feedback sessions allow for continuous collaboration and adjustment as needed. By fostering open lines of communication, entrepreneurs can ensure that team members are engaged, motivated, and working towards the collective success of the business.
Presenting Your Business to External Parties
In addition to aligning internal team members, a business plan is an invaluable tool for presenting your business to external parties. Whether you are seeking funding from investors or entering into partnerships with other organizations, a well-prepared business plan demonstrates your professionalism, credibility, and commitment to success.
When presenting your business to external parties, it is essential to highlight the key elements of your business plan. This includes providing an overview of your business idea, explaining the market opportunity, showcasing your financial projections, and outlining your strategies for success. By effectively communicating these aspects, you can instill confidence in potential investors, lenders, or partners.
It is important to adapt your presentation to the specific needs and interests of your audience. Tailor your communication to address their concerns and emphasize the value proposition of your business. Be prepared to answer questions and provide additional information as needed, ensuring that external parties have a comprehensive understanding of your business and its potential.
Remember to leverage the business plan itself as a visual aid during presentations. Utilize tables and charts to showcase important numerical data, such as financial projections, market analysis, or growth forecasts. These visual representations can enhance the clarity and impact of your communication, making it easier for external parties to grasp the potential of your business.
By effectively aligning team members and stakeholders and presenting your business to external parties, a well-developed business plan becomes a powerful tool for communication and collaboration. It ensures that everyone involved understands the vision, goals, and strategies of the business, fostering a collaborative environment that maximizes the chances of success.
In conclusion, a well-crafted business plan is an essential tool for entrepreneurs looking to turn their vision into reality. It serves as the foundation for market research, financial projections, and securing funding and support. A comprehensive business plan also plays a crucial role in guiding decision making and implementation, providing a roadmap for success while tracking progress and making necessary adjustments.
Effective communication and collaboration are also critical components of a successful business venture. A business plan aligns team members and stakeholders towards shared goals while providing external parties with a clear understanding of the potential of your business.
By following these steps and developing a thorough business plan, entrepreneurs can increase their chances of success in the competitive marketplace. Remember to approach the process with dedication, professionalism, and attention to detail. With a solid foundation in place, you can confidently navigate the challenges of entrepreneurship and achieve your goals.
https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/importance-of-business-plan-for-entrepreneurs
https://www.businessagility.net.au/post/the-top-5-benefits-of-having-a-marketing-plan
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/marketing-plan.asp
Related Blog Post

Business Loan Brokers Master Guide: 5 Great Insights
August 20, 2024
Uncover the secrets to success as a business loan broker! Master the insights that can unleash your potential in this dynamic industry.

How Is a Loan Amortization Schedule Calculated?
Discover the calculation process behind loan amortization schedules. Learn how interest rates and loan terms influence repayment.

What is an Amortization Schedule? How to Calculate It
Demystify the magic of amortization schedules and become a pro at calculating! Discover the key to financial planning and budgeting.

Preparing for a Small Business IRS Audit
Prepare for a small business IRS audit with confidence! Expert tips on documentation, communication, and strategies for success.

How to Prepare for An Audit
Master the art of audit preparation! Gain compliance and confidence with effective documentation and corrective actions.

Revolving Loan Fund Program
August 13, 2024
Unlock capital for your business with a revolving loan fund program. Discover eligibility, benefits, and success stories. Access funds today

Grants for Economic Development
Unlock economic potential with grants for economic development. Learn how to secure funding for community empowerment and growth.

Check Your Eligibility for Applying a Business Loan
Discover if you're eligible for a business loan! Learn the criteria, gather documents, and take the first steps towards funding your dreams.

Small Business Bank Loan Qualification Criteria
Unlock small business bank loan qualification criteria! Discover credit score requirements and financial documentation.

Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
Unlock business loan eligibility criteria. From credit score to collateral, discover what it takes to secure your financial future.

The 4 Most Common Business Loan Requirements
Unlock funding opportunities with the 4 most common business loan requirements. Master credit scores, financial statements, and more!

Loans To Help Business
Unlock the potential of your business with loans! Discover how to fund growth, manage cash flow, and invest in success.

Financing and Capital
Unlock growth potential with financing and capital. Discover alternative options and strategies for maximizing opportunities.

Technology Development Loans Program
Unlock technological growth with development loans! Discover funding options and success stories in our technology development loans program

Economic Development Loan Fund
Discover the Economic Development Loan Fund – fueling innovation, growth, and job opportunities for businesses. Apply now!

Small Business Economic Development (SBED)
Unleash the power of small business economic development (SBED) for growth, jobs, and community impact.

Rural Economic Development Loan and Grant Program
August 12, 2024
Unlock rural economic development with the loan & grant program. Empowering communities for a prosperous future.

Common Mistakes When Applying for Small Business Loans
Avoid these small business loan application mistakes! Don't let lack of preparation or inadequate documentation derail your success.

Avoiding Common Financial Mistakes in Business
Master financial success in business! Avoid common mistakes and achieve long-term growth with essential financial strategies.

9 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Starting A New Business
Avoid these 9 common mistakes when starting a new business! From market research to legal requirements, set yourself up for success.

Construction Company Loans
August 6, 2024
Unlock financial growth with construction company loans. Discover the types, eligibility, pros, and cons for your business success.

What is a Business Debt Consolidation Loan?
Demystifying business debt consolidation loans: Learn how they work and if they're right for your financial needs.

How To Consolidate Business Debt
Master the art of debt consolidation for your business. Discover options, steps, and tips to consolidate business debt effectively.

Minimizing Tax Consequences From Small Business Loans
Minimize tax impacts of small business loans! Discover strategies, loan structures, and tax-efficient options for smart financial planning.

Tax Insights: Monthly Payments on Large Business Loans
Unveiling the tax implications of monthly payments on large business loans. Discover the hidden truth and optimize your financial strategy.

How Could a Business Loan Affect Your Tax Bill?
Discover how a business loan impacts your tax bill. Maximize tax savings with strategic loan utilization.

What You Need to Know About Business Debt Consolidation
Demystifying business debt consolidation: Your ultimate guide to navigating the process and making informed decisions. Get the facts now!

Are Business Loans Taxable?
Untangling the web of business loans and taxable income. Discover if business loans are considered taxable.

Tax Implications of Business Loan
Discover the tax impact of business loans and maximize your bottom line! Uncover deductions, loan forgiveness, and more.

Are Business Loans Tax Deductible
Unlock tax benefits with business loans! Discover if they're tax deductible and maximize your deductions today.

Business and Investment Opportunities
Unlocking new business and investment opportunities. Navigate trends, assess risks, and seize growth potential for success.

Tax Implications of Small Business Loans
Demystify the tax implications of small business loans. Discover how they affect your capital and tax obligations. Expert guidance awaits.

How Business Debt Consolidation Works
Discover the power of business debt consolidation! Lower interest rates and simplify repayment with this strategic financial move.

Write Off Repayment Of A Business Loan
Discover how to maximize benefits by writing off repayment of a business loan. Unlock tax deductions and financial planning strategies.

Business Loans Considered Income?
Demystifying business loans: Are they income? Learn about tax implications and how loans impact your finances. Find out now!

How to Boost Your Small Business Credit Score
July 30, 2024
Boost your small business credit score with expert strategies! Transform your credit for success and unlock new opportunities.

How to Maintain a Good Business Credit Score
Maintain a stellar business credit score with expert tips and strategies. Unlock financial success for your business today!

Complete Guide to Hotel Financing
Unlock the secrets of hotel financing with our complete guide. From debt to equity, master the art of funding your dream hotel.

8 Ways to Build a Good business Credit Score
Unlock financial success with these 8 power moves! Build a stellar business credit score and thrive in the world of business.
How to Improve Your Company Credit Score
Boost your company credit score with expert tips! From reviewing credit reports to building positive credit history.

How to Apply for a Business Loan for Your Restaurant
Unlock your culinary dreams with our ultimate guide to restaurant business loans. Get the funds you need to turn ambition into reality.


What was Third-Round Paycheck Protection Program
Get the inside scoop on the Third-Round Paycheck Protection Program! Discover eligibility criteria, application process, and economic impact

Clean Energy Finance Tools and Resources
Discover clean energy finance tools and resources to fuel sustainability. Unlock funding opportunities for a greener future.

Financing Renewable Energy Projects
Unlocking the funding for renewable energy projects! Discover sustainable financing strategies and successful funding models.

Green Bonds for Financing Renewable Energy
Unlock the power of green bonds for renewable energy financing. Discover how to fuel the transition towards a sustainable future.

Physical Damage Loans
Restore your business after physical damage with ease. Discover the benefits of physical damage loans for quick recovery

Sustainable Agribusiness Financing Program
Discover sustainable agribusiness financing programs for a greener future. Grants, loans, and investments that cultivate sustainability!

Steps for Applying for an SBA Disaster Relief Loan
Master the application steps for SBA disaster relief loans. From eligibility to submission, demystify the process seamlessly.

Guide to Restaurants and Bars Business Loans
August 7, 2024
Unlock the secrets of restaurants & bars business loans. Discover the funding you need to spice up your culinary dreams.

A Physician's Guide to Medical Practice Loans
Unlock the path to prosperity with our comprehensive guide for physicians on medical practice loans. Expert advice for funding your success.

SBA Economic Injury Disaster Loans
July 23, 2024
Discover SBA Economic Injury Disaster Loans - your key to financial security amidst disasters. Get the funding you need today!
.jpg)
6 Best Medical Practice Loans for Physicians
Discover the 6 best medical practice loans for physicians. Unlock funding options to invest in your practice and enhance patient care.

Economic Injury Disaster Loans
Discover the lifeline for businesses: Economic Injury Disaster Loans. Get the funding you need to shield your business from economic setback
.jpg)
How To Get Medical Practice Loans
Discover how to acquire medical practice loans and turn your dreams into a reality. Navigate the loan application process with confidence!

5 Types of Loans to Finance Your Startup Restaurant
Kickstart your restaurant dreams with 5 types of loans! Discover financing options to empower your culinary journey.

7 Lending Options for Agricultural Businesses
Discover 7 effective lending options for agricultural businesses. From traditional bank loans to online lenders.

Global Landscape of Renewable Energy Finance
Unlocking the global landscape of renewable energy finance. Explore funding sources, trends, and innovations to power a sustainable future.

5 Ways to Finance Your Restaurant Business
Discover 5 foolproof ways to finance your restaurant business and make your culinary dreams a reality. Secure funding with confidence!

Business Grants for Women Guide
Unveiling the secrets of business grants for women! Discover how to access funding for your entrepreneurial dreams and achieve empowerment.

Business Tax Credits
Master your tax burden with business tax credits! Discover how to maximize financial advantages and fuel long-term growth.
.jpg)
Physician Loans and Practice Financing
Unlock the path to prosperity with physician loans and practice financing. Navigate the process like a pro!

The Complete Guide to Restaurant Financing and Loans
The complete guide to restaurant financing and loans: Secure the funds you need for your culinary dreams!

Agricultural Credit and Financing Programs
Discover essential agricultural credit and financing programs to secure your farm's future. Explore government-sponsored and private.

How to Apply for a Small Business Disaster Loan
Expert tips on applying for a small business disaster loan. Secure your future with the right guidance for funding success.

Paycheck Protection Program
Demystifying the Paycheck Protection Program: Get the lowdown on eligibility, loan terms, and fund utilization. Stay informed!

Funding the Creative Economy
Unlock the funding potential of the creative economy! Discover government grants, private investments, crowdfunding, and more.

What are Tax Write-Offs and How Do They Work?
Discover the magic of business tax write-offs! Maximize deductions, navigate tax laws, and boost your bottom line.

Nontraditional Financing Sources
Unlock the future of funding with nontraditional financing sources. Explore crowdfunding, peer-to-peer lending, and venture capital.

New Funding and Business Models
Navigate the future of funding and business models with innovation. Explore strategies for growth and adaptation.

Professional Services Firms Business Loans
Unleash the potential of professional services firms with business loans. Boost growth, enhance services, and manage finances effectively.

10 Nontraditional Financing Options for Small Businesses
Discover 10 fresh financing solutions for small businesses! From crowdfunding to microloans, think outside the box for financial success.

Credits and Deductions for Businesses
Unlock the power of credits and deductions for businesses! Propel your financial success with strategic tax benefits.

Cultural and Creative Industries
Unleash the power of cultural and creative industries in driving innovation. Explore economic, social impact and technological advancements.

Professional Services Loans | Architecture Funding
Secure architecture funding with professional services loans. From eligibility criteria to loan management.

Types of Business Insurance
Safeguard your business with the right insurance! Discover the types of business insurance to protect your success.

11 Non-Bank Small Business Financing Options
Discover 11 non-bank small business financing options to fuel your entrepreneurial dreams. Unlock funding without the hassle of traditional.

Types of Commercial Real Estate Loans
Discover a range of commercial real estate loan options! From traditional mortgages to creative financing solutions.

Financing a Professional Services Business
Unlock financial success for your professional services business with tailored financing solutions. Fuel your ambitions today!

Small Business Bookkeeping (2024 Guide)
Master small business bookkeeping with ease! Discover essential practices, tax compliance, and financial insights. Unlock success today!

Alternative Funding Options: 6 Non-Traditional Ways
Discover 6 non-conventional ways to secure funding. From crowdfunding to bartering, explore alternative funding options today!

9 Financial Health Ratios for Your Business
Master the 9 business ratios to power up your financial health. Gain insights on liquidity, profitability, efficiency, and leverage!

MSME Financing Programs
Unleash the potential of MSME financing programs. Access capital, expand your business and fuel economic growth. Explore success stories now

Economic Factors Affecting Small Business Lending
Unveiling the economic factors shaping small business lending. Explore interest rates, regulations, and alternative options.

Commercial Real Estate Lending Trends
Discover the latest commercial real estate lending trends! From technology's impact to alternative options, stay ahead of the game.

Indicators of a Company's Financial Health
Unveil the secrets to a company's financial health! Discover crucial indicators and analysis tools for informed decision-making.

How to Develop a Strategic Financial Plan for Your Business
Unlock business success with a strategic financial plan! Learn how to develop and implement effective strategies for profitability.

What is the Best Measure of a Company's Financial Health?
Unlock the secret to financial success! Discover the best measure of a company's financial health and make informed decisions.

The Value of Strategic Financial Planning
Unlock financial success with strategic planning! Maximize wealth, conquer debt, and secure your future.

Top Trends in Commercial Lending: A Look at the Future
Unlock the future of commercial lending with top trends! Explore technology, regulations, customer-centricity, and risk management.
Effects of Small Loans on Bank and Small Business Growth
Unveil the impact of small loans on bank and small business growth. Discover the benefits and future trends in this insightful analysis.

6 Indicators Your Company Has Good Financial Health
Is your company financially fit? Discover the 6 signs of good financial health and set the stage for success.

An Introduction to Government Loans
Discover the keys to financial success with an introduction to government loans. Unlock your potential today!

Small Business Wage Subsidy
Unlock financial stability with the small business wage subsidy. Discover eligibility, benefits, and effective fund management strategies.

The Role of Business Loans in Economic Recovery
Discover the vital role of business loans in economic recovery! Explore loan options, benefits and government initiatives for fueling growth

What is Strategic Financial Planning?
Unlock the secrets of strategic financial planning! Learn how to set goals, execute strategies, and secure your financial future.

How Much Can I Borrow for a Business Loan
Unlock your business potential with the ultimate guide on borrowing for your business. Discover how much you can borrow for a business loan.

What is the Cost of Invoice Discounting?
Unveil the cost of invoice discounting! Dive into factors, hidden fees, and make informed decisions for your financial future.

Financial Planning Tips for Entrepreneurs
Unlock financial success as an entrepreneur with essential tips for effective financial planning. Maximize your wealth to secure your future

The Ins and Outs of Credit Card Factoring
Navigate credit card factoring with ease! Discover the ins and outs of this business financing solution for growth and success.

How Can Fintech Help Small Businesses Succeed?
Discover how fintech revolutionizes small businesses, empowering growth and success through streamlined operations.
.png)
Sign up for our newsletter for product updates, new blog posts, and the chance to be featured in our Small Business Spotlight!

The importance of a business plan

Business plans are like road maps: it’s possible to travel without one, but that will only increase the odds of getting lost along the way.
Owners with a business plan see growth 30% faster than those without one, and 71% of the fast-growing companies have business plans . Before we get into the thick of it, let’s define and go over what a business plan actually is.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a 15-20 page document that outlines how you will achieve your business objectives and includes information about your product, marketing strategies, and finances. You should create one when you’re starting a new business and keep updating it as your business grows.
Rather than putting yourself in a position where you may have to stop and ask for directions or even circle back and start over, small business owners often use business plans to help guide them. That’s because they help them see the bigger picture, plan ahead, make important decisions, and improve the overall likelihood of success.
Why is a business plan important?
A well-written business plan is an important tool because it gives entrepreneurs and small business owners, as well as their employees, the ability to lay out their goals and track their progress as their business begins to grow. Business planning should be the first thing done when starting a new business. Business plans are also important for attracting investors so they can determine if your business is on the right path and worth putting money into.
Business plans typically include detailed information that can help improve your business’s chances of success, like:
- A market analysis : gathering information about factors and conditions that affect your industry
- Competitive analysis : evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors
- Customer segmentation : divide your customers into different groups based on specific characteristics to improve your marketing
- Marketing: using your research to advertise your business
- Logistics and operations plans : planning and executing the most efficient production process
- Cash flow projection : being prepared for how much money is going into and out of your business
- An overall path to long-term growth
What is the purpose of a business plan?
A business plan is like a map for small business owners, showing them where to go and how to get there. Its main purposes are to help you avoid risks, keep everyone on the same page, plan finances, check if your business idea is good, make operations smoother, and adapt to changes. It's a way for small business owners to plan, communicate, and stay on track toward their goals.
10 reasons why you need a business plan
I know what you’re thinking: “Do I really need a business plan? It sounds like a lot of work, plus I heard they’re outdated and I like figuring things out as I go...”.
The answer is: yes, you really do need a business plan! As entrepreneur Kevin J. Donaldson said, “Going into business without a business plan is like going on a mountain trek without a map or GPS support—you’ll eventually get lost and starve! Though it may sound tedious and time-consuming, business plans are critical to starting your business and setting yourself up for success.
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business.
1. To help you with critical decisions
The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and crisis management. Sitting down and considering all the ramifications of any given decision is a luxury that small businesses can’t always afford. That’s where a business plan comes in.
Building a business plan allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time.
Creating a robust business plan is a forcing function—you have to sit down and think about major components of your business before you get started, like your marketing strategy and what products you’ll sell. You answer many tough questions before they arise. And thinking deeply about your core strategies can also help you understand how those decisions will impact your broader strategy.
Send invoices, estimates, and other docs:
- via links or PDFs
- automatically, via Wave
*While subscribed to Wave’s Pro Plan, get 2.9% + $0 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0 (Amex) per transaction for the first 10 transactions of each month of your subscription, then 2.9% + $0.60 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0.60 (Amex) per transaction. Discover processing is only available to US customers. See full terms and conditions for the US and Canada . See Wave’s Terms of Service for more information.
Send invoices, get paid, track expenses, pay your team, and balance your books with our financial management software.
2. To iron out the kinks
Putting together a business plan requires entrepreneurs to ask themselves a lot of hard questions and take the time to come up with well-researched and insightful answers. Even if the document itself were to disappear as soon as it’s completed, the practice of writing it helps to articulate your vision in realistic terms and better determine if there are any gaps in your strategy.
3. To avoid the big mistakes
Only about half of small businesses are still around to celebrate their fifth birthday . While there are many reasons why small businesses fail, many of the most common are purposefully addressed in business plans.
According to data from CB Insights , some of the most common reasons businesses fail include:
- No market need : No one wants what you’re selling.
- Lack of capital : Cash flow issues or businesses simply run out of money.
- Inadequate team : This underscores the importance of hiring the right people to help you run your business.
- Stiff competition : It’s tough to generate a steady profit when you have a lot of competitors in your space.
- Pricing : Some entrepreneurs price their products or services too high or too low—both scenarios can be a recipe for disaster.
The exercise of creating a business plan can help you avoid these major mistakes. Whether it’s cash flow forecasts or a product-market fit analysis , every piece of a business plan can help spot some of those potentially critical mistakes before they arise. For example, don’t be afraid to scrap an idea you really loved if it turns out there’s no market need. Be honest with yourself!
Get a jumpstart on your business plan by creating your own cash flow projection .
4. To prove the viability of the business
Many businesses are created out of passion, and while passion can be a great motivator, it’s not a great proof point.
Planning out exactly how you’re going to turn that vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between concept and reality. Business plans can help you confirm that your grand idea makes sound business sense.

A critical component of your business plan is the market research section. Market research can offer deep insight into your customers, your competitors, and your chosen industry. Not only can it enlighten entrepreneurs who are starting up a new business, but it can also better inform existing businesses on activities like marketing, advertising, and releasing new products or services.
Want to prove there’s a market gap? Here’s how you can get started with market research.
5. To set better objectives and benchmarks
Without a business plan, objectives often become arbitrary, without much rhyme or reason behind them. Having a business plan can help make those benchmarks more intentional and consequential. They can also help keep you accountable to your long-term vision and strategy, and gain insights into how your strategy is (or isn’t) coming together over time.
6. To communicate objectives and benchmarks
Whether you’re managing a team of 100 or a team of two, you can’t always be there to make every decision yourself. Think of the business plan like a substitute teacher, ready to answer questions any time there’s an absence. Let your staff know that when in doubt, they can always consult the business plan to understand the next steps in the event that they can’t get an answer from you directly.
Sharing your business plan with team members also helps ensure that all members are aligned with what you’re doing, why, and share the same understanding of long-term objectives.
7. To provide a guide for service providers
Small businesses typically employ contractors , freelancers, and other professionals to help them with tasks like accounting , marketing, legal assistance, and as consultants. Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, while ensuring everyone is on the same page.
8. To secure financing
Did you know you’re 2.5x more likely to get funded if you have a business plan?If you’re planning on pitching to venture capitalists, borrowing from a bank, or are considering selling your company in the future, you’re likely going to need a business plan. After all, anyone that’s interested in putting money into your company is going to want to know it’s in good hands and that it’s viable in the long run. Business plans are the most effective ways of proving that and are typically a requirement for anyone seeking outside financing.
Learn what you need to get a small business loan.
9. To better understand the broader landscape
No business is an island, and while you might have a strong handle on everything happening under your own roof, it’s equally important to understand the market terrain as well. Writing a business plan can go a long way in helping you better understand your competition and the market you’re operating in more broadly, illuminate consumer trends and preferences, potential disruptions and other insights that aren’t always plainly visible.
10. To reduce risk
Entrepreneurship is a risky business, but that risk becomes significantly more manageable once tested against a well-crafted business plan. Drawing up revenue and expense projections, devising logistics and operational plans, and understanding the market and competitive landscape can all help reduce the risk factor from an inherently precarious way to make a living. Having a business plan allows you to leave less up to chance, make better decisions, and enjoy the clearest possible view of the future of your company.
Business plan FAQs
How does having a business plan help small business owners make better decisions.
Having a business plan supports small business owners in making smarter decisions by providing a structured framework to assess all parts of their businesses. It helps you foresee potential challenges, identify opportunities, and set clear objectives. Business plans help you make decisions across the board, including market strategies, financial management, resource allocation, and growth planning.
What industry-specific issues can business plans help tackle?
Business plans can address industry-specific challenges like regulatory compliance, technological advancements, market trends, and competitive landscape. For instance, in highly regulated industries like healthcare or finance, a comprehensive business plan can outline compliance measures and risk management strategies.
How can small business owners use their business plans to pitch investors or apply for loans?
In addition to attracting investors and securing financing, small business owners can leverage their business plans during pitches or loan applications by focusing on key elements that resonate with potential stakeholders. This includes highlighting market analysis, competitive advantages, revenue projections, and scalability plans. Presenting a well-researched and data-driven business plan demonstrates credibility and makes investors or lenders feel confident about your business’s potential health and growth.
Understanding the importance of a business plan
Now that you have a solid grasp on the “why” behind business plans, you can confidently move forward with creating your own.
Remember that a business plan will grow and evolve along with your business, so it’s an important part of your whole journey—not just the beginning.
Related Posts
Now that you’ve read up on the purpose of a business plan, check out our guide to help you get started.
The information and tips shared on this blog are meant to be used as learning and personal development tools as you launch, run and grow your business. While a good place to start, these articles should not take the place of personalized advice from professionals. As our lawyers would say: “All content on Wave’s blog is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal or financial advice.” Additionally, Wave is the legal copyright holder of all materials on the blog, and others cannot re-use or publish it without our written consent.

A business journal from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania
Knowledge at Wharton Podcast
How entrepreneurs can create effective business plans, march 2, 2010 • 16 min listen.
When an entrepreneur has identified a potential business opportunity, the next step is developing a business plan for the new venture. What exactly should the new plan contain? How can the entrepreneur ensure it has the substance to find interest among would-be investors? In this installment of a series of podcasts for the Wharton-CERT Business Plan Competition, Wharton management professor Ian MacMillan explains that business plans must contain several crucial elements: They must articulate a market need; identify products or services to fill that need; assess the resources required to produce those products or services; address the risks involved in the venture; and estimate the potential revenues and profits.

An edited transcript of the interview appears below:
Knowledge at Wharton: Professor MacMillan, thank you for speaking with us about the necessity of entrepreneurs writing business plans. To start with a basic question, what exactly is a business plan?
Ian MacMillan: A business plan to me is a 25-page, maximum 30-page, document, which is a description, analysis and evaluation of a venture that you want to get funded by somebody. It provides critical information to the reader — usually an investor — about you, the entrepreneur, about the market that you are going to enter, about the product that you want to enter with, your strategy for entry, what the prospects are financially, and what the risks are to anybody who invests in the project.
Knowledge at Wharton: Could you explain some of these elements in a little more detail and describe how entrepreneurs can develop an effective business plan?
MacMillan: Let me start by saying that you probably want to avoid developing a detailed business plan unless you have done some initial work. Basically what happens is that by doing a little bit of work, you earn the right to do more work. The first thing I would do before you start a business plan is think about a concept statement. A concept statement is about three to five pages that you put together and share with potential customers or investors just to see if they think it’s worth the energy and effort of doing more detailed work.
The concept statement has a few pieces to it. You are going to have a description of the market need that has to be fulfilled; a description of the products or services that you think are going to fulfill that need; a description of the key resources that you think are going to be needed to provide that product or service; a specification of what resources are currently available; an articulation of what you think the risks are; and then a sort of rough and ready estimate of what you think the profits and profitability will be.
The idea is to put together this concept document and begin to share it around with people who are going to have to support your venture if you take it forward. This allows you to rethink as a result of feedback that you get. You might get word back from the various stakeholders — like potential customers or distributors — that this really wasn’t such a good idea after all. That saves you the energy and effort of putting together a big business plan.
Knowledge at Wharton: Assuming the concept statement works out and you want to move towards the business plan, what else would you need? And where can you find the information? Some information can be hard to locate, especially about your competitors.
MacMillan: It’s really important to go out and speak to your potential customers. You need to find the people who you think will buy your product and talk to them about what dissatisfies them with their current offerings. You should get a sense from them about who is providing the alternative at the moment. Remember, the world has gone for maybe 100,000 years without your idea — and people are getting by; they’re not dying. Something out there is servicing their need. So what is the closest competitive alternative to what you want to offer?
That is what you need to find out — and that involves talking and listening. And for all the enthusiasm you have for your venture or your idea, you really need to listen to people who are eventually going to write a check for it.
Before you go on to write a business plan, you have to do some more work. If the concept statement looks good, then the next step is to do a 15- to 20-page feasibility analysis. This means we are now going to take this idea to the next level. We’ve learned from potential customers and distributors. We’ve learned who the major competitors are. We’ve shaped the idea more clearly, and now we’re digging deeper.
The next challenge you face is to say, well, if you start this business, what evidence do you have that the market actually wants it? Who do you think would write a check for your product? You need to articulate what makes your product or your service feasible. What has to be done in order to make this thing real? You need a description of how you intend to enter the market, a description of who the major competitors are, a preliminary plan — a very rough plan — which specifies what you think your revenues and profits are going to be, and an estimate of what you think the required investment will be. And only then, once you have articulated that, and once again shared it with your stakeholder community, will you perhaps be able to go and write a business plan.
Knowledge at Wharton: Once you have done your feasibility analysis and assuming you get the go ahead from your stakeholders, what is the next step?
MacMillan: The idea of the business plan is to convince the stakeholders. First, what we need to do in a business plan is show that we understand the needs — the unmet needs — of potential customers. Second, we need to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the current most competitive offering out there. Third, we need to understand the skills and capabilities that you and your team have as entrepreneurs. Next we need to understand what the investors need to get out of their investment, because they have to put their money in and they need to have some kind of sense of what they are going to get in terms of returns. In addition, the investment needs to be competitive with alternative investments that the investors might make.
The most important idea in the business plan is to articulate and satisfy the different perspectives of various stakeholders. This process sets in motion some basic requirements in the business plan — to tee up right from the start — evidence that the customer will accept it. Probably a third of the ventures out there that fail are because some person came up with the right product that they thought the world would love and then found out that the customers couldn’t care less. What you want to try to do in a business plan is convince the reader that there are customers out there who will in fact buy the product — not because it’s a great product, but because they want it and they are willing to pay for it.
Moreover, you need to convince the reader that you have some kind of proprietary position that you can defend. You also need to convince your readers that you have an experienced and motivated management team and that you have the experience and the management capabilities to pull it off. You need to convince potential investors that they are going to get a better return than they could get elsewhere, so you need to estimate the net present value of this venture. You need to show that the risk they are taking will be accompanied by appropriate returns for that risk. If we look at the contents of a typical business plan, you need to be able to articulate all these issues in some 25 to 30 pages. People get tired if they have to read too much.
Now let’s look at the various components of the business plan document:
First, you need an executive summary that grabs the attention of the potential investor. This should be done in no more than two pages. The executive summary is meant to convince the potential investor to read further and say, “Wow! This is why I should read more about this business plan.”
Next, you need a market analysis. What is the market? How fast is it growing? How big is it? Who are the major players? In addition, you need a strategy section. It should address questions such as, “How are you going to get into this market? And how are you going to win in that marketplace against current competition?”
After that, you need a marketing plan. How are we going to segment the market? Which parts of the market are we going to attack? How are we going to get the attention of that market and attract it to our product or service?
You also need an operations plan that answers the question, “How are we going to make it happen?” And you need an organization plan, which shows who the people are who will take part in the venture.
You need to list the key events that will take place as the plan unfolds. What are the major things that are going to happen? If your plan happens to be about a physical product, are you going to have a prototype or a model? If it happens to be a software product, are you going to have a piece of software developed — a prototypical piece of software? What are the key milestones by which investors can judge what progress you are making in the investment? Remember that you will not get all your money up front. You will get your funds allocated contingent on your ability to achieve key milestones. So you may as well indicate what those milestones are.
You should also include a hard-nosed assessment of the key risks. For example, what are the market risks? What are the product risks? What are the financial risks? What are the competitive risks? To the extent that you are upfront and honest about it, you will convince your potential investors that you have done your homework. You need to also be able to indicate how you will mitigate these risks — because if you can’t mitigate them, investors are not going to put money into your venture.
After that, what you get down to is a financial plan where you basically do a five-year forecast of what you think the finances are going to be — maybe with quarterly data or projections for the first two years and annual for the next three years.
You need a pro forma profit and loss statement. You need a pro forma balance sheet if you have assets in the balance sheet. You need to have a pro forma cash flow. Your cash flow is important, because it is the cash flow that kills. You may have great profits on your books but you may run out of money — so you need a pro forma cash flow statement. And you need a financing plan that explains, as the project unfolds, what tranches of financing you will need and how will you go about raising that money.
Finally you need a financial evaluation that tells investors, if you make this investment, what is its value going to be to you as an investor. That is basically the structure of the plan.
Knowledge at Wharton: Let’s say you have written a business plan and presented it to your investors. How closely do you have to be tied to the plan? Does it mean that once you are executing against the plan, you should reject new opportunities you find because they are not part of your plan? Or should you build in some flexibility that allows you to explore emerging opportunities?
MacMillan: Is this an opportunity for me to speak about discovery-driven planning?
Knowledge at Wharton: Of course.
MacMillan: Okay. The thing about most entrepreneurial ventures is that your outcome is uncertain — because what you are doing is very new. It is very, very hard to predict what the actual outcome is going to be. One of the most fundamental flaws is that in the face of unfolding uncertainty, you single-mindedly and bloody-mindedly pursue the original objective.
The reality is that the true opportunity will emerge over time. What venture capitalists do is they will put a small amount of money into the project, allow the entrepreneur to enter that market space and then — contingent on performance and contingent on what apparent traction you can get in that market space — completely re-plan to find out what the true opportunity really is. It is insanity to insist that people actually meet their plan as it was originally written.
This doesn’t mean you compromise your objectives. The idea is that I want to keep on trying to meet my objectives, but how I meet them must change as the plan unfolds. That’s basically what led to all the work that Wharton has done in the last few years on discovery driven planning. It’s a way of thinking about planning that says, “I’m going to make small investments. If I’m wrong early, I can fail fast, fail cheap and move on. But as I find out what the true opportunity is, I can aggressively invest in what this opportunity is.”
Knowledge at Wharton: Could you give an example of a company that has used this discovery-driven planning process to take its business to the next level?
MacMillan: One company that has done the most in this area is Air Products. What they have been able to do is use discovery-driven planning to unfold completely different businesses from the ones that they were in. Air Products makes things like carbon dioxide and oxygen and nitrogen. It is a very old-line company. Using discovery-driven planning, they have been able to move aggressively into, for instance, the service sector. Once they recognized that they were able to deliver reliably and predictably in the face of uncertain demand, they developed a set of skills that allowed them to enter the service business where the return on investment and return on assets are far higher than putting a huge plant in place.
Knowledge at Wharton: Professor MacMillan, thanks so much.
More From Knowledge at Wharton

How AI Analytics Spurs Innovation at Newly Public Firms

Why Are Retailers Making a Hard U-Turn on Self-checkout?
Why skilled immigration can lead to economic prosperity, looking for more insights.
Sign up to stay informed about our latest article releases.
Please turn on JavaScript in your browser
It appears your web browser is not using JavaScript. Without it, some pages won't work properly. Please adjust the settings in your browser to make sure JavaScript is turned on.
Nine reasons why you need a business plan
Building a great business plan helps you plan, strategize and succeed. Presented by Chase for Business .

Making the decision to create a new business is an exciting yet stressful experience. Starting a business involves many tasks and obstacles, so it’s important to focus before you take action. A solid business plan can provide direction, help you attract investors and ensure you maintain momentum.
No matter what industry you plan on going into, a business plan is the first step for any successful enterprise. Building your business plan helps you figure out where you want your business to go and identify the necessary steps to get you there. This is a key document for your company to both guide your actions and track your progress.
What is the purpose of a business plan?
Think of a business plan like a roadmap. It enables you to solve problems and make key business decisions, such as marketing and competitive analysis, customer and market analysis and logistics and operations plans.
It can also help you organize your thoughts and goals, as well as give you a better idea of how your company will work. Good planning is often the difference between success and failure.
Here are nine reasons your company needs a business plan.
1. Prove your idea is viable
Through the process of writing a business plan, you can assess whether your company will be successful. Understanding market dynamics, as well as competitors, will help determine if your idea is viable.
This is also the time to develop financial projections for your business plan, like estimated startup costs, a profit and loss forecast, a break-even analysis and a cash flow statement . By taking time to investigate the viability of your idea, you can build goals and strategies to support your path to success.
A proper business plan proves to all interested parties—including potential investors, customers, employees, partners and most importantly yourself — that you are serious about your business.
2. Set important goals
As a business owner, the bulk of your time will mostly likely be spent managing day-to-day tasks. As a result, it might be hard to find time after you launch your business to set goals and milestones. Writing a business plan allows you to lay out significant goals for yourself ahead of time for three or even five years down the road. Create both short- and long-term business goals.
3. Reduce potential risks
Prevent your business from falling victim to unexpected dangers by researching before you break ground. A business plan opens your eyes to potential risks that your business could face. Don’t be afraid to ask yourself the hard questions that may need research and analysis to answer. This is also good practice in how your business would actually manage issues when they arise. Incorporate a contingency plan that identifies risks and how you would respond to them effectively.
The most common reasons businesses fail include:
- Lack of capital
- Lack of market impact or need
- Unresearched pricing (too high or low)
- Explosive growth that drains all your capital
- Stiff competition
Lack of capital is the most prevalent reason why businesses fail. To best alleviate this problem, take time to determine how your business will generate revenue. Build a comprehensive model to help mitigate future risks and long-term pain points. This can be turned into a tool to manage growth and expansion.
4. Secure investments
Whether you’re planning to apply for an SBA loan , build a relationship with angel investors or seek venture capital funding, you need more than just an elevator pitch to get funding. All credible investors will want to review your business plan. Although investors will focus on the financial aspects of the plan, they will also want to see if you’ve spent time researching your industry, developed a viable product or service and created a strong marketing strategy.
While building your business plan, think about how much raised capital you need to get your idea off the ground. Determine exactly how much funding you’ll need and what you will use it for. This is essential for raising and employing capital.
5. Allot resources and plan purchases
You will have many investments to make at the launch of your business, such as product and services development, new technology, hiring, operations, sales and marketing. Resource planning is an important part of your business plan. It gives you an idea of how much you’ll need to spend on resources and it ensures your business will manage those resources effectively.
A business plan provides clarity about necessary assets and investment for each item. A good business plan can also determine when it is feasible to expand to a larger store or workspace.
In your plan, include research on new products and services, where you can buy reliable equipment and what technologies you may need. Allocate capital and plan how you’ll fund major purchases, such as with a Chase small business checking account or business credit card .
6. Build your team
From seasoned executives to skilled labor, a compelling business plan can help you attract top-tier talent, ideally inspiring management and employees long after hiring. Business plans include an overview of your executive team as well as the different roles you need filled immediately and further down the line.
Small businesses often employ specialized consultants, contractors and freelancers for individual tasks such as marketing, accounting and legal assistance. Sharing a business plan helps the larger team work collectively in the same direction.
This will also come into play when you begin working with any new partners. As a new business, a potential partner may ask to see your business plan. Building partnerships takes time and money, and with a solid business plan you have the opportunity to attract and work with the type of partners your new business needs.
7. Share your vision
When you start a business, it's easy to assume you'll be available to guide your team. A business plan helps your team and investors understand your vision for the company. Your plan will outline your goals and can help your team make decisions or take action on your behalf. Share your business plan with employees to align your full staff toward a collective goal or objective for the company. Consider employee and stakeholder ownership as a compelling and motivating force.
8. Develop a marketing strategy
A marketing strategy details how you will reach your customers and build brand awareness. The clearer your brand positioning is to investors, customers, partners and employees, the more successful your business will be.
Important questions to consider as you build your marketing strategy include:
- What industry segments are we pursuing?
- What is the value proposition of the products or services we plan to offer?
- Who are our customers?
- How will we retain our customers and keep them engaged with our products or services and marketing?
- What is our advertising budget?
- What price will we charge?
- What is the overall look and feel of our brand? What are our brand guidelines?
- Will we need to hire marketing experts to help us create our brand?
- Who are our competitors? What marketing strategies have worked (or not worked) for them?
With a thoughtful marketing strategy integrated into your business plan, your company goals are significantly more in reach.
9. Focus your energy
Your business plan determines which areas of your business to focus on while also avoiding possible distractions. It provides a roadmap for critical tradeoffs and resource allocation.
As a business owner, you will feel the urge to solve all of your internal and customers’ problems, but it is important to maintain focus. Keep your priorities at the top of your mind as you set off to build your company.
As a small business owner, writing a business plan should be one of your first priorities. Read our checklist for starting a business, and learn how to take your business from a plan to reality. When you’re ready to get started, talk with a Chase business banker to open a Chase business checking or savings account today.
For Informational/Educational Purposes Only: The views expressed in this article may differ from other employees and departments of JPMorgan Chase & Co. Views and strategies described may not be appropriate for everyone and are not intended as specific advice/recommendation for any individual. You should carefully consider your needs and objectives before making any decisions and consult the appropriate professional(s). Outlooks and past performance are not guarantees of future results.
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. Member FDIC. Equal Opportunity Lender, ©2023 JPMorgan Chase & Co
What to read next
Manage your business how to navigate rising health care costs.

Many business owners are feeling the pinch of higher health care costs. Find out how you and your employees can get the most out of your plan.
MANAGE YOUR BUSINESS Small business owners remain vigilant about cybersecurity threats

The Chase Business Leaders Outlook survey reveals how small business owners are adopting new technology while remaining vigilant about cybersecurity threats.
MANAGE YOUR BUSINESS How to spot imposter fraud

Advances in technology are making it more difficult to detect an imposter scam. Here’s what you need to know to help protect yourself and your business.
START YOUR BUSINESS What is a DUNS number, and how do you get one?

Boost your business credibility with this nine-digit number.
Your Article Library
Business plan: 6 major uses of a business plan by an entrepreneur.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6 Major Uses of a Business Plan by An Entrepreneur !
A business plan can be used by an entrepreneur for a variety of objectives. It is primarily used to get funding but there can be a number of other uses too.

Image Courtesy : wikihow.com/images/9/9d/Become-an-Entrepreneur-Step-6-Version-2.jpg
Some major applications of the business plan are discussed here.
1. Equity Funding :
A venture capitalist or an angel investor will very rarely commit an investment to a start-up without perusing its business plan. The venture capitalist will primarily use the business plan to gauge risks and forecast growth prospects. The investor will never restrict analysis of the business to just the business plan but it will always remain an important reference point.
2. Bank Finance :
A banker obviously concentrates on the ability of the business to repay the debt and on the availability of collateral or other securities. Banks look for at least some specific issues to be addressed in the business plan. For example, a bank needs projected balance sheets and profit and loss accounts for the first five years.
3. Alliances :
An entrepreneurial firm may need to form alliances with other firms to reach new markets, develop new products, or create common facilities. Other firms may want to know more about the business before committing to any long-term arrangement. Sometimes, a business plan can help convince a well-established retailer or distributor to commit to the start-up.
4. Recruitment:
A good business needs support from experienced top-level employees. A business plan will help them understand what they are getting into. Of course, showing the business plan to the rank and file is not necessary.
5. Explain the Business :
A business plan helps in planning. While writing the business plan, it is likely that the entrepreneur was able to detect many shortcomings in the original business idea and these shortcomings could be overcome by thinking through and plugging the gaps.
Later, this plan can serve as a guide or manual to help in business and strategy formulation.
6. Miscellaneous Uses :
Very often, an entrepreneur seeks moral support from friends and family. A business plan can be a good way of presenting your business to your father, mother, wife, and colleagues. By going through it, they will have a better appreciation of what you are setting out to do.
Related Articles:
- Business Plans: Five Versions of Business Plans for an Entrepreneur to Choose From
- Making a Business Plan: 6 Major Problems faced in making the Marketing Plan Work
Business Planning
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- United Kingdom
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
This Is the Goal-Setting Method Shohei Ohtani Learned in High School That Helped Get Him to the World Series The MLB superstar's success did not come as a surprise to him. He had a plan.
By David James Oct 25, 2024
Key Takeaways
- Back in high school, Shohei Ohtani created very specific list of goals.
- He credits using the Harada Method to achieve them.
- Ohtani and his Los Angeles Dodgers face the New York Yankees in the 2024 World Series.
The 2024 World Series is Major League Baseball's dream come true: two franchises in the biggest TV markets featuring two of the most famous players in the game.
One of those athletes is Shohei Ohtani , widely considered the best player in the league — and perhaps in the history of the game. When not injured, the 30-year-old superstar pitcher throws 100-mph fastballs. And on the other side of the plate, as a batter, he leads the league in home runs and is the only person in baseball to have 50 home runs and 50 stolen bases in one year.
On the eve of Game 1, fitness coach Dan Founder took to Threads to break down the Harada Method, a system of setting and achieving goals that Ohtani learned from his high school coach Takashi Harada and utilized to accomplish so much in sports. Here's how Founder broke it down:
Post by @danfounder View on Threads
"Here Shohei Ohtani's list of goals , which is insane to look at in hindsight," Founder wrote.
- Age 18: Join a MLB team
- Age 19: Master English and reach AAA
- Age 20: Called up to the majors, make 1.5 billion JPY (~13 million USD)
- Age 21: Starting rotation, 16 wins
- Age 22: Win the Cy Young award
- Age 23: Member of Japan WBC team
- Age 24: Throw a no-hitter and 25 wins
- Age 25: Throw fastest pitch in the world 175 kph (~108mph)
- Age 26: Win the World Series and get married
- Age 27: Member of Japan WBC team & MVP
- Age 28: 1st son is born
- Age 29: Throw 2nd no-hitter
- Age 30: Get most wins by a Japanese pitcher ( in 1 MLB season? )
- Age 31: 1st daughter is born
- Age 32: Win 2nd World Series
- Age 33: 2nd son is born
- Age 34: Win 3rd World Series
- Age 35: Member of Japan WBC team
- Age 36: Break the strike out record?
- Age 37: 1st son starts baseball
- Age 38: Stats drop, start to think about retirement
- Age 39: Decide to retire at end of next season
- Age 40: Throw no-hitter in my very last game
- Age 41: Return to Japan
- Age 42: Introduce the American system to Japan?
Founder then broke down the framework of the Harada Method to show how Ohtani has achieved so much of this lofty list and more.
Step 1: Grade yourself on self-reliance
Using the following 33 categories, rate yourself on a scale of one to ten of how these words describe you, with one being "not accurate" and ten being "the most accurate."
- Accountable
- Highly skilled
- Imaginative
- Independent
- Inspired – love to work
- Inquisitive
- Knowledgeable
- Responsible
- Self-managed
- Strong-willed
- Trustworthy
Step 2: Create your long-term goal
"This is your north star where your actions will be directed towards," explains Founder. "It will organize your goals, purposes, self-analysis, and action plan."
Step 3: Analyze obstacles
Once you determine the biggest hurdles between you and success, "you then create countermeasures to solve those obstacles before they happen," says Founder. "This helps you plan tasks and routines to achieve the goal when the going gets rough."
Related: Want to Inspire Your Team for Success? Check Out These 11 Quotes From World Series Champs.
Step 4: Create an Open 64 chart
This is a chart made up of eight nine-box grids, 72 boxes total. At the center of each nine-box grid, you put a big goal that will serve as a pillar of your overall achievement and surround that with eight small tasks that will help you achieve that big goal. In the end you will have 64 mini-tasks and routines that support getting to your long-term goals.

So for example, if one of your goals is being in great physical shape, you'd list eight tasks needed to get there — setting a workout schedule, committing to healthy eating, getting a health club membership, and the like.
Step 5: Create a checklist of routines
"It's not enough to set a goal," says Founder. "You must set a system of traits that will make the goal an inevitability. Have a list you check daily to ensure you're taking the actions needed to make your vision a reality."
Step 6: Keep a daily performance journal
"The journal is broken down into tasks to be completed and reflections on one's performance at the end of the day," writes Founder. "The journal builds self-awareness while keeping you aligned with your target."
Related: Alex Rodriguez's 4 Major League Keys to Success
Step 7: Enlist help
Founder ends by saying that the final step is to connect with a coach and a supportive community. "We cannot achieve things on our own," he says. "Find a coach who can help you achieve success faster and stay accountable. Find people around you who can support and assist you on the way to achieving your goal."
Entrepreneur Staff
Staff writer
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- U.S. Diners Are Feeding the $1 Trillion Restaurant Industry Like Never Before. Here's Why — and What They're Hungry for, According to Resy's CEO.
- Lock SearchGPT is About to Change How Customers Find Your Business. Are You Ready?
- AI Startups Received $2.9 Billion in Funding Last Quarter. These 3 U.S. Companies Received a Lot of It — And You've Probably Never Heard of Them.
- Lock Gen Xers Earning Up to $100,000 a Year Won't Retire Like Boomers Did. They're Embracing This Strategy Instead.
- 'We Are Not Red or Blue — We Are Golden': McDonald's Tells Employees It's Non-Political After Trump Visit
- Lock In Her Late 30s, She Pursued Another Creative Side Hustle — Then Turned It Into a Multimillion-Dollar Business
Most Popular Red Arrow
You have one month left to buy a house, according to barbara corcoran. here's why..
"If you are planning on waiting a year and seeing where interest rates go, you are out of your mind," Corcoran said.
These 3 Side Hustles Make the Most Money While Working Fewer Hours, According to a New Survey
The survey also found that having a side hustle doubled as a path to becoming more employable.
The McRib Is Back, But Only at Select McDonald's — Here's Where to Find It
This scarcity is nothing new. In 2022, McDonald's announced a "Farewell Tour" for the McRib, suggesting that it might be the last time customers could get their hands on it.
This New Restaurant Is Banking on One Dish — Because It's the Only Entrée on the Menu
The new hotspot is gaining buzz on social media for its innovative yet super simple concept.
Adobe Says Creators 'Need to Embrace' AI — It's Now Built Into Photoshop and Can't Be Turned Off
Adobe announced the new AI tools last week.
Stop Chasing Algorithms — Here's How Creators Can Take Control of Their Content and Monetize on Their Own Terms
Social media platforms promise creators visibility, but the real challenge lies in relying on algorithms for income.
Successfully copied link

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Related: First Steps: Writing the Executive Summary of Your Business Plan. 3. Business description. You can fill anywhere from a few paragraphs to a few pages when writing your business ...
Use a business plan to keep track of dates and deadlines in one place. This is valuable even for the one-person business and vital for teams. You'll be better at delegating. The business plan is ...
Importance of Entrepreneurs to Assists in Team Building. A business plan holds great importance for entrepreneurs in assisting them with team building, as it provides a clear framework for recruiting, developing, and managing their team effectively. Entrepreneurs can use a business plan to aid in team building by defining roles and ...
In business, you do not want to wing it. You want a plan -- a document that lays out the path of your company for the next three to five years so you can see the route to your goals and know ...
Let's take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward: 1. Validate Your Business Idea. The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including: External: industry, target market of prospective ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Rice University's Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51, 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2.
Build a strategy. 4. Crafts a roadmap to achieve important milestones. A business plan is like a roadmap for your business. It helps you set, track and reach business milestones. For your plan to function in this way, your business plan should first outline your company's short- and long-term goals.
Startups. The classic business plan writer is an entrepreneur seeking funds to help start a new venture. Many, many great companies had their starts on paper, in the form of a plan that was used ...
A business plan serves as a vital tool for entrepreneurs, guiding them from the initial stages of their venture to its successful implementation. It provides a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the vision, goals, and strategies of a business. Understanding what a business plan is and why it is important is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs.
13. To share your business plans with coworkers and family. When you open a business, you will likely get a lot of questions about what you do from previous coworkers and family members. Drafting a business plan can help you answer these questions, sharing your goals and plans with them.
Here are 5 reasons why you need a business plan: 1. It will help you steer your business as you start and grow. Think of a business plan as a GPS to get your business going. A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan like a GPS for how to structure, run, and grow ...
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business. 1. To help you with critical decisions. The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and ...
MacMillan: The idea of the business plan is to convince the stakeholders. First, what we need to do in a business plan is show that we understand the needs — the unmet needs — of potential ...
Temper your enthusiasm. If your plan indicates that the business idea isn't sound, by all means look for errors. But don't make the mistake of skewing your plan to fit an idea that isn't sound ...
Writing a business plan allows you to lay out significant goals for yourself ahead of time for three or even five years down the road. Create both short- and long-term business goals. 3. Reduce potential risks. Prevent your business from falling victim to unexpected dangers by researching before you break ground.
A business plan helps in planning. While writing the business plan, it is likely that the entrepreneur was able to detect many shortcomings in the original business idea and these shortcomings could be overcome by thinking through and plugging the gaps. Later, this plan can serve as a guide or manual to help in business and strategy formulation. 6.
Being realistic is important because it lends credibility to your presentation. Always assume things will take 15 percent longer than you anticipated. Therefore, 20 weeks is now 23 weeks. 6. Be ...
Schools Fall Short on Teaching Financial Literacy — Here's 3 Ways Parents Can Raise Future Entrepreneurs Entrepreneurship is not just for adults. Teaching kids the basics of business and finance ...
Related: TV Shows All Entrepreneurs Should Be Watching Financial and Business Service Ideas 1. Accounting and Tax Services. Experience, training or licensing may be needed. At some point, most ...
Step 7: Enlist help Founder ends by saying that the final step is to connect with a coach and a supportive community. "We cannot achieve things on our own," he says.