- CBSE Notes For Class 10
- Class 10 Social Science Geography
- Chapter 1 Resources And Development

CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development
Chapter 1 of Class 10 Geography introduces you to resources and their classification. Furthermore, going into the depth of the chapter, you will learn about the development of resources and resource planning in India. You will learn about land resources and the classification of different types of soils found in India. In the end, the chapter discusses Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation. All these topics are discussed in detail in “CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources and Development“. Go through these CBSE Class 10 Social Science notes and make your studies more effective. You can also download these notes in PDF.
- Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources
- Chapter 3 Water Resources
- Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources
- Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
- Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources and Development
Everything in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs and is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable is termed a ‘ Resource ’. Human beings themselves are essential components of resources. They transform material available in the environment into resources and use them.
Classification of Resources
Resources can be classified in the following ways:
(a) On the basis of origin – biotic and abiotic
(b) On the basis of exhaustibility – renewable and non-renewable
(c) On the basis of ownership – individual, community, national and international
(d) On the basis of the status of development – potential, developed stock and reserves
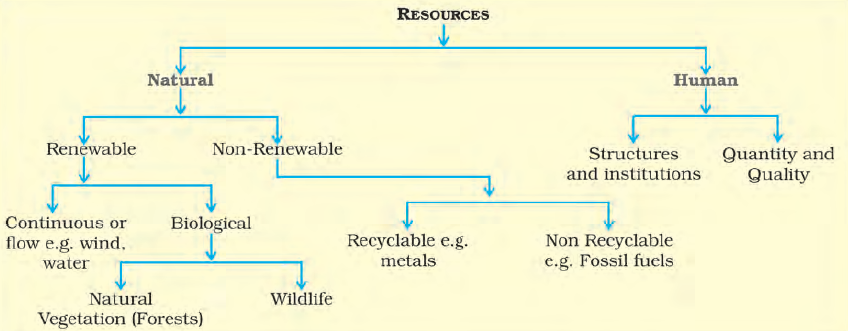
(a) On the Basis of Origin – Biotic and Abiotic
Biotic Resources are obtained from the biosphere and have life.
Eg: Human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc.
Abiotic Resources: All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources.
Eg: rocks and metals.
(b) On the Basis of Exhaustibility – Renewable and Non-Renewable
The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as Renewable or Replenishable Resources . The renewable resource may further be divided into continuous or flow.
Eg: Solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc.
Non-Renewable Resources occur over a very long geological time. These resources take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources, like metals, are recyclable and some, like fossil fuels, cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use.
Eg: Minerals and fossil fuels.
(c) On the Basis of Ownership – Individual, Community, National and International
Individual Resources are owned privately by individuals. In villages, people own lands, whereas in urban areas, people own plots, houses and other properties.
Eg: Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc.
Community Owned Resources are accessible to all the members of the community.
Eg: Grazing grounds, burial grounds, public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds etc.
National Resources are owned by a nation or country. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast are termed territorial water, and resources therein belong to the nation.
Eg: Roads, canals, railways etc.
International Resources are regulated by international institutions. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
(d) On the Basis of the Status of Development – Potential, Developed Stock and Reserves
Potential Resources are the resources which are found in a region but have not been utilised.
Eg: Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far, these have not been developed properly.
Developed Resources: Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and the level of their feasibility.
Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access are called stocks .
Eg: Hydrogen can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have advanced technology to use it.
Reserves are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing technical ‘know-how’, but their use has not been started. These can be used to meet future requirements.
Eg: Water in the dams, forests etc. is a reserve which can be used in the future.
Development of Resources
Resources have been used by human beings indiscriminately and this has led to the following major problems.
- Depletion of resources to satisfy the greed of a few individuals.
- Accumulation of resources in a few hands, which, in turn, divided the society into two segments i.e., rich and poor.
- It has led to global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
Resource planning is essential for the sustainable existence of all forms of life. Sustainable Economic Development means “development should take place without damaging the environment, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of future generations.”
Resource Planning
In India, there are some regions which can be considered self-sufficient in terms of the availability of resources and there are some regions which have an acute shortage of some vital resources. This calls for balanced resource planning at the national, state, regional and local levels.
Resource Planning in India
Resource planning is a complex process which involves:
(i) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
(ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set-up for implementing resource development plans.
(iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes. India has made concerted efforts towards achieving the goals of resource planning right from the First Five Year Plan launched after Independence.
To overcome irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources, resource conservation at various levels is important.
Land Resources
Land is a natural resource of utmost importance. It supports natural vegetation, wildlife, human life, economic activities, transport and communication systems. India has land under a variety of relief features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains and islands as shown below:
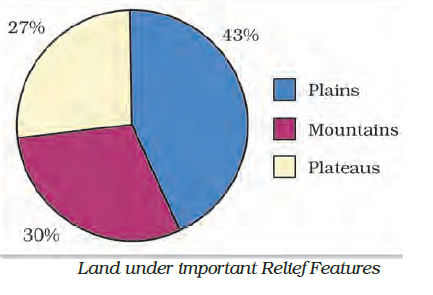
Land Utilisation
Land resources are used for the following purposes:
- Land not available for cultivation
a) Barren and wasteland
b) Land put to non-agricultural uses
- Fallow lands
- Other uncultivated lands (excluding fallow land)
- Net sown area
Land Use Pattern in India
The use of land is determined
- Physical factors: such as topography, climate, soil types
- Human factors: such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions etc.
The data below represents the land use pattern in India.
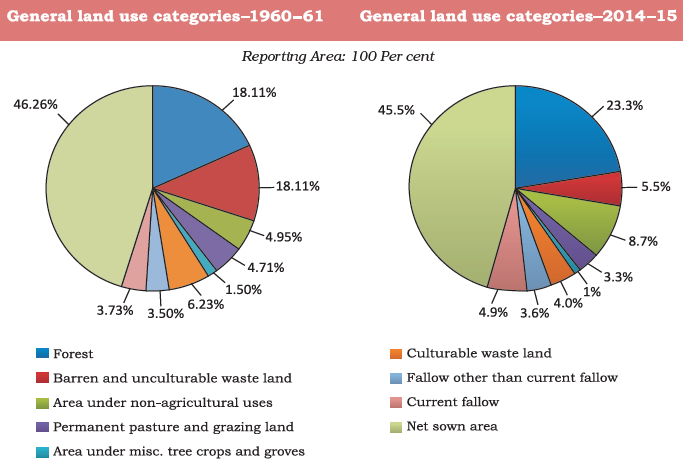
Waste land is the land put to other non-agricultural uses which include rocky, arid and desert areas, roads, railways, industry etc. Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it, has resulted in land degradation.
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
Human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, mining and quarrying have contributed significantly to land degradation. Mining sites leave deep scars and traces of overburdening the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country.
Some of the ways through which we can solve the problems of land degradation are:
- Afforestation and proper management of grazing.
- Planting of shelter belts of plants.
- Stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes.
- Proper management of wastelands.
- Control of mining activities.
- Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment.
Soil as a Resource
Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. It is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms on the earth.
- It takes millions of years to form soil up to a few cms in depth. Various forces of nature, such as changes in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers, etc., contribute to the formation of soil.
- Parent rock or bedrock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil.
- Chemical and organic changes which take place in the soil play an important role.
- Soil also consists of organic (humus) and inorganic materials.
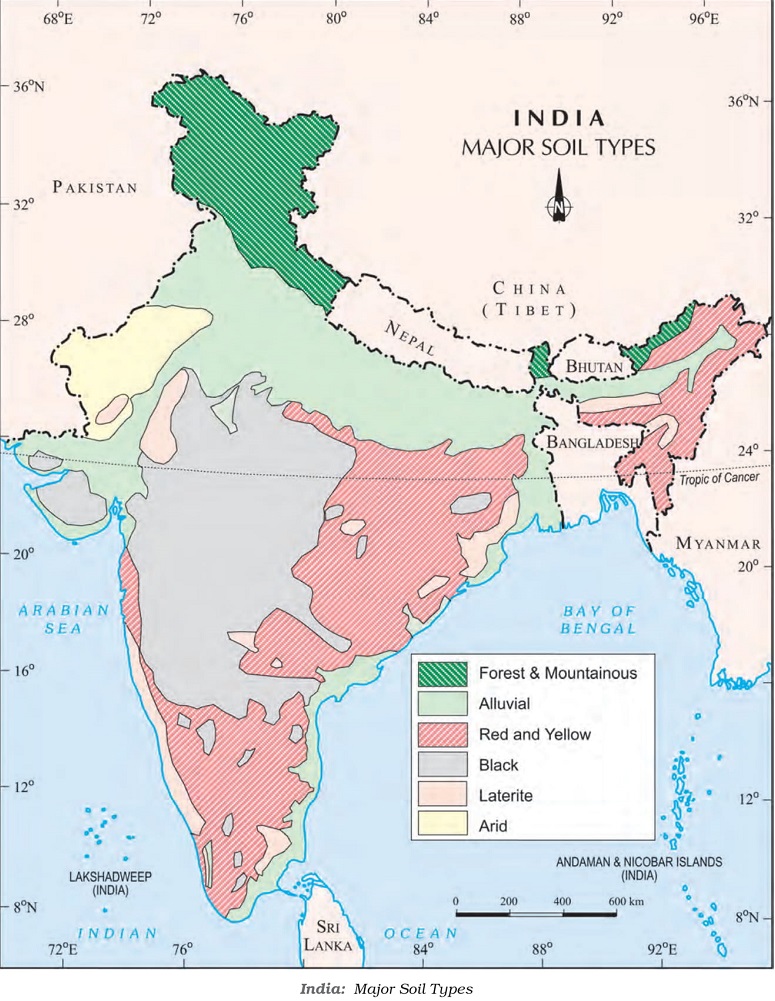
Classification of Soils
On the basis of the factors responsible for soil formation, colour, thickness, texture, age, and chemical and physical properties, the soils of India are classified into different types, as mentioned below.
Alluvial Soils
- The entire northern plains are made of alluvial soil.
- The Alluvial Soil is deposited by 3 important Himalayan river systems – the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
- It is also found in Rajasthan, Gujarat and eastern coastal plains, particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri rivers.
- The alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay. As we move inland towards the river valleys, soil particles appear to be bigger in size whereas in the upper side of the river valley, the soils are coarse.
- Based on age, Alluvial soils can be classified as:
- Old Alluvial (Bangar): The Bangar soil has a higher concentration of kanker nodules than the Khadar.
- New Alluvial (Khadar): It has more fine particles and is more fertile than the Bangar.
- Alluvial soils are very fertile. These soils contain an adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime, which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops.

- This soil is black in colour and is also known as regur soil . Climatic conditions, along with the parent rock material are the important factors for the formation of black soil.
- The soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil.
- This type of soil is typical of the Deccan trap (Basalt) region spread over the northwest Deccan plateau and is made up of lava flows.
- The soil covers the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh and extends in the southeast direction along the Godavari and the Krishna valleys.
- The black soils are made up of extremely fine i.e. clayey material and are well-known for their capacity to hold moisture.
- Black soil is nutrients rich and contains calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime.
- The soil is sticky when wet and difficult to work on unless tilled immediately after the first shower or during the pre-monsoon period.

Red and Yellow Soils
- This type of soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau.
- These soils develop a reddish colour due to the diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks. It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form.
- Found in parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, southern parts of the middle Ganga plain and along the Piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.

Laterite Soil
- The laterite soil develops under tropical and subtropical climates with the alternate wet and dry season.
- This soil is the result of intense leaching due to heavy rain.
- Lateritic soils are acidic (pH<6.0) in nature and generally deficient in plant nutrients. This type of soil is found mostly in Southern states, Western Ghats region of Maharashtra, Odisha, some parts of West Bengal and the northeast regions.
- The soil supports deciduous and evergreen forests but humus poor.
- This soil is very useful for growing tea and coffee.

- Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
- This soil is generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas, the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
- Arid soil lacks humus and moisture.
- The lower horizons of the soil are occupied by Kankar because of the increasing calcium content downwards. The Kankar layer formations in the bottom horizons restrict the infiltration of water.

Forest Soils
- These soils are found in the hilly and mountainous areas.
- The soil texture is loamy and silty on the valley sides and coarse-grained on the upper slopes.
- In the snow-covered areas of the Himalayas, these soils experience denudation and are acidic with low humus content. The soil is fertile on the river terraces and alluvial fans.
The map below shows the different types of soils found in India.
Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation
The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion. The soil erosion is caused due to human activities like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc. Also, there are some natural forces like wind, glacier and water which lead to soil erosion. Soil erosion is also caused due to defective methods of farming.
The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. The land becomes unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land . When water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope and the topsoil is washed away, it is known as sheet erosion . The wind blows loose soil off flat or sloping land, known as wind erosion .
Different Ways for Soil Conservation
- Ploughing along the contour lines decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is called Contour Ploughing .
- Terrace cultivation restricts erosion. This type of agriculture practice is done in the Western and Central Himalayas.
- When a large field is divided into strips and strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. Then, this breaks up the force of the wind. This method is known as Strip Cropping .
- Planting lines of trees to create shelter helps in the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in western India. Rows of such trees are called Shelter Belts .
Keep learning and stay tuned for more updates on CBSE and NCERT. Download BYJU’S App and subscribe to the YouTube channel to access interactive Maths and Science videos.
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
Why are resources important.
Without resources none of our needs would be satisfied. All raw materials are obtained from resources.
What are the types of resources?
Resources can be categorised into natural, human and human-made resources.
Why is soil considered a resource?
Soil is a form of environmental asset and provides several benefits for all species of life.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Thanks for geography notes

Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
- 15th January 2024
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development help students to score good marks in the exams. These NCERT Solutions are prepared by expert teachers and based on the latest pattern and edition of NCERT book. Here we have provided answers to all the questions in a very easy language.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development Questions and Answers
Question 1. Multiple choice questions
(i) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation (b) Deforestation (c) Over irrigation (d) Overgrazing
Answer: (c) Over irrigation
(ii) In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practised?
(a) Punjab (b) Plains of Uttar Pradesh (c) Haryana (d) Uttarakhand
Answer: (d) Uttarakhand
(iii) In which of the following states is black soil found?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir (b) Gujarat (c) Rajasthan (d) Jharkhand
Answer: (b) Gujarat
Question 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
(ii) What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
(iii) What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Answer: (i) Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are states having black soil. Cotton is mainly grown in black soil.
(ii) Alluvial Soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast.
Three features of alluvial soil:
- Alluvial soil is rich in nutrients like potash and lime, making it highly fertile.
- Alluvial soil has a fine texture, owing to the fine silt deposited by river waters. The fine particles allow the soil to retain moisture effectively.
- The fertility and texture of Alluvial soil make it ideal for agriculture. They are ideal for growing sugarcane, wheat and paddy.
(iii) In hilly areas, soil erosion can be controlled by ploughing across contour-lines, making use of terrace farming techniques and using strips of grasses to check soil erosion by wind and water.
Question 3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
(ii) How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Answer: (I) The land use pattern in India involves diverse uses, including agriculture, forestry, mining, construction, and other activities. Since 1960-61, the land under forest in India has not increased significantly due to several factors:
- The growing population has led to increased demand for food, resulting in the conversion of forest land to agricultural land.
- Rapid urbanization and industrialization have required more land, often at the expense of forest areas.
- Over the years, forests have been overexploited for timber, fuelwood, and other resources, leading to deforestation.
- While there have been policies aimed at increasing forest cover, their implementation has often been ineffective or insufficient.
(ii) Technical and economic development has led to more consumption of resources on account of various factors such as:
- Technological advancements have enabled mass production in industries, increasing the consumption of natural resources like minerals, fossil fuels, and water.
- Economic development has fueled urbanization, leading to the construction of more buildings, roads, and infrastructure, thereby consuming large amounts of materials like cement, steel, and energy.
- Technological advancements in transportation have resulted in more vehicles and travel, increasing the consumption of fossil fuels.
More study materials for CBSE Class 10
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment

NCERT Solutions for Class 10th: Ch 1 Resources and Development Geography
Ncert solutions for class 10th: ch 1 resources and development geography social studies (s.st), contact form.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
- NCERT Solutions
- Social Science Contemporary India
- Chapter 1 Resources And Development

NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Resources and Development Class 10 - FREE PDF Download
Vedantu's Class 10 Geography NCERT Solutions are your life raft! Aligned with the latest CBSE Class 10 Social Science syllabus , the Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 offers a comprehensive guide to understanding this pivotal era. Dive deep into sustainable development, resource planning, land resources, and more, explaining clearly and breaking down complex terms, making geography accessible and engaging.

Conquer your exams with a solid grasp of Chapter 1 content, boost your historical knowledge, and develop critical thinking skills. Download your FREE PDF for resources and development class 10 today and embark on a successful journey.
Glance on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
Uncover the different types of resources – natural, human, and man-made – and understand how we classify them based on their availability (renewable vs. non-renewable) with class 10th geography chapter 1.
Learn how resource utilisation is linked to a country's economic and social progress.
Explore the concept of sustainable development and its importance for the resources and development class 10 questions and answers.
Gain insights into the challenges of resource depletion and environmental degradation.
Discover strategies for responsible resource management and conservation practices and can also refer to class 10 geography chapter 1 question answer PDF download.
See how resource availability from the Resources and Development class 10 PDF is impacted by land degradation, soil erosion, and deforestation.
Analyse case studies to understand the interconnectedness of resources and development from Geography Chapter 1, class 10.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development
1. Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation
(b) Deforestation
(c) Over irrigation
(d) Overgrazing
Ans: (c) Over irrigation
(ii) In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practiced?
(a) Punjab
(b) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
(c) Haryana
(d) Uttarakhand
Ans: (d) Uttarakhand
(iii) In which of the following states black soil is predominantly found?
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Jharkhand
Ans: (b) Maharashtra
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
Ans: Maharashtra: This state is known for its black cotton soil, particularly suitable for growing cotton.
Madhya Pradesh: Similar to Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh also has black soil regions where cotton is a major crop.
Andhra Pradesh: Cotton cultivation thrives in Andhra Pradesh's black soil areas. While cotton is prominent, other crops like tobacco can also be grown in this type of soil.
(ii) What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Ans: The type of soil found in the river deltas of the eastern coast of India is alluvial soil. Here are three main features of alluvial soil:
High fertility: Alluvial soil is rich in nutrients like potash, phosphoric acid, and lime due to the constant deposition of sediments from rivers. This makes it highly fertile and ideal for agriculture.
Light and well-drained: Alluvial soil is generally loose and sandy in texture, allowing for good drainage and aeration. This is beneficial for plant root growth and prevents waterlogging.
Varied composition: The exact composition of alluvial soil can vary depending on the source river and the distance from the delta.
(iii) What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Ans: Land Management Practices:
Contour ploughing and planting
Cover cropping
Drainage ditches
Rotational grazing
Bioengineering
Education and Awareness:
3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Explain land use patterns in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
Ans: India's land use reflects a balancing act. Over 50% is dedicated to agriculture, with forests covering about 22% (below the recommended 33%).
Urbanization and infrastructure needs are also rising.
Limited forest cover increase since the 1960s stems from competing needs for land, encroachment, deforestation, and slow forest regrowth.
Sustainable practices like agroforestry and stricter environmental regulations are key to achieving a more balanced and sustainable land use pattern in India.
(ii) How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Ans: Technical and economic advancements have become double-edged swords for resource consumption.
Improved technology allows for greater production, requiring more materials.
New industries and products constantly emerge, each demanding resources.
As economies grow, living standards rise, leading to increased consumption of goods and services.
While technology might unlock new resources, it can also accelerate their exploitation.
To ensure a sustainable future, we need to find a balance between development and responsible resource management through methods like renewable energy and promoting conservation.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
Benefits of ncert solutions for geography class 10 chapter 1.
A few advantages you will get by opting for the class 10 geography chapter 1 question answers are:
Gain a clear understanding of different resource types (natural, human, man-made) and their classification with geography class 10 chapter 1 question answers.
Enhance your exam skills with diverse question formats aligned with the CBSE curriculum for Geography class 10, chapter 1.
Break down complex concepts with easy-to-follow explanations, ensuring a solid grasp of the material for Geography Chapter 1 class 10.
Develop critical thinking skills by analysing real-world examples like land degradation and deforestation by referring to resources and development class 10 PDF.
Learn responsible resource management and conservation strategies with resources and development class 10 questions and answers.
Download your FREE PDF of NCERT Solutions for class 10th Geography Chapter 1 today and become a champion of sustainable development!
In addition to these NCERT Solutions, the official website provides Class 10 Resources and Development Revision Notes and Class 10 Resources and Development Important Questions . Utilise both resources for effective practice and a deeper understanding of the chapter.
Mastering resources and development is key to a sustainable future. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography (Chapter 1) empowers you. Make informed choices about resource use, advocate for sustainable practices, and become an active citizen. This knowledge goes beyond exams – use it to understand current events, explore solutions, and contribute to a more sustainable world. Access class 10 geography chapter 1 question answer PDF download and keep learning!
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography- Other Chapter-wise Links for FREE PDF
Dive into our FREE PDF links offering chapter-wise NCERT solutions prepared by Vedantu Experts, to help you understand and master the social concepts.
Related Important Links for Class 10 Geography
Faqs on ncert solutions for class 10 geography chapter 1 resources and development.
1. Why do we Need resources and development class 10 PDF?
Class 10 Social Science Resources and Development Solutions are important because they help students understand the chapter in detail and prepare for their final exams. The chapter covers topics such as resource planning in India, identification and inventory of resources, evolving a planning structure, and appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans. The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science give students a further advantage to answer different questions that may come in their exams from various topics. These solutions provide clear and understandable answers in an engaging and easy-to-learn manner. Students can download these solutions for free from Vedantu website.
2. How can Vedantu Help You understand Geography Chapter 1 class 10?
Vedantu can help you in understanding Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Ch 1 by providing NCERT Solutions for the chapter. These solutions are crafted by subject matter experts and are available for free download on Vedantu's website. The solutions are provided in a simple language that is easily understandable and helps students understand the chapter in detail. Vedantu also provides chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science, including History, Geography, Political Science and Economics, which can help students prepare for their exams and score good marks. Students can download these solutions in PDF format from Vedantu's website or app and revise the complete syllabus to score more marks.
3. What about geography class 10, chapter 1 from Contemporary India?
Chapter 1 of Class 10 Contemporary India is about Resources and Development. This chapter introduces students to resources and their classification. It covers topics such as resource planning in India, identification and inventory of resources, evolving a planning structure, and appropriate technology, skill, and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans. The chapter also discusses the three stages of resource planning in India, which are identification and inventory of resources, evolving a planned structure, and matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans. Students can find NCERT Solutions and notes for this chapter on our Vedantu website.
4. How can you categorise resources based on ownership from Geography class 10 chapter 1 question answers?
On the basis of ownership, resources can be classified as (1) Individual or Community-owned resources and (2) Natural or International resources. Individual resources are the resources that are privately owned by individuals whereas community-owned resources are those that belong to the entire community and are accessible to all the members. All the resources such as minerals, water resources, forests, etc. found in a nation and up to 12 nautical miles from the coastline belong to the nation. Oceanic resources beyond 200 nm are regulated by international institutions.
5. What are the obstacles to the development of resources as discussed in class 10 geography chapter 1 question answers?
Resources are vital for our survival, sustenance and development, and well-being. Human beings have used the resources indiscriminately over the course of history. There are various problems that need to be overcome to ensure optimum development of resources. These include depletion of resources, resources accumulation in a few hands, and indiscriminate exploitation of resources. Consequently, the climatic conditions across the world have deteriorated.
6. Does resource availability ensure a region's development from resources and development class 10?
Resources are crucial for our survival and the development of quality of life but the availability of resources does not automatically translate into the development of the region. There are regions that are rich in resources but are not entirely developed. Availability of resources is important. But what is equally important is the availability of necessary technology and institutions to ensure that resources are used in an optimum, efficient, and judicious way.
7. Where can I find solutions to class 10 Geography Chapter 1?
Vedantu is one of the websites on which you can trust. The Vedantu website will help you to tackle all your doubts and concerns related to important questions or solutions smartly. The solutions are provided in PDF format and are accessible even on the go. These materials are also available on the Vedantu app. All the material is free of cost. The answers are crafted to satisfy every demand of the question and allow you to find for yourself the best way of presenting the answer and score an extra mark in the final battle.
8. What are some key topics covered in the NCERT resources and development class 10 questions and answers?
Classification of resources (natural, human-made, renewable, non-renewable)
The importance of resource development for a nation's economic and social progress
The concept of sustainable development and its principles
Challenges of resource depletion and environmental degradation
Strategies for responsible resource management and conservation practices.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Free PDF Download
Ncert solutions for class 10 geography chapter 1 – resources and development.
The subject geography is not as easy as it looks. Also, the students take the subject very lightly. But, the students forget the fact that it is one of the most scoring subjects of Social Science. Our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 will guide you with the content of the chapter. Also, it will assist students in understanding the topics of the Chapter.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 aims to help students understand the Chapter in an easy way. Also, our expert makes them using their expert knowledge and experience. Download the Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Download NCERT Solutions for other subjects here.
Download NCERT Solution for Class 7 Chapter-wise here.
Download NCERT Solutions for other chapters of Geography here.
CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 – Resources and Development NCERT Solutions
First of all, let’s discuss resources. Resources refer to all those things present in the environment to satisfy our need is Resources. Also, the Chapter tells how we use these resources for development.

Sub-topics covered under NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
1.1 Types of Resources- The topic discusses the various types of resources which mention below:
1.1.1 On the basis of Origin
- Biotic Resources-like flora and fauna.
- Abiotic Resources- like rocks and metals.
1.1.2 On the basis of Exhaustibility
- Renewable Resources- Like solar and wind energy, water, etc.
- Non-Renewable Resources- Like CNG, petroleum, coal, etc.
1.1.3 On the basis of Ownership
- Individual Resources- Owned by an individual.
- Community Owned Resources- Owned by the community such as burial ground, Village ponds, etc.
- National Resources- The resources within the country.
- International Resources- Those resources which are outside the Exclusive Economic Zone of the country.
1.1.4 On the basis of Status of Development
- Potential Resources- The resources which are present in an area but cannot be utilized.
- Developed Resources- There quantity and quality has been resolute for utilization.
- Stock- Refers to those resources which cannot be used due to lack of suitable technology.
1.2 Development of Resources-
This topic deals with the way by which we can find a sustainable way of using resources. Also, the ways by which we can stop misuse or overuse of resources.
1.3 Resource Planning- This topic discusses the plan which we can make for using resources. Also, how a country like India (rich in resources) can utilize this plan.
1.4 Resource Planning in India- This topic deals with a complex process that involves identification, evolving and matching of resources. Also, how a country like India can make and execute such a plan successfully.
1.4.1 Conservation of Resources- Discusses the ways by which irrational and over-utilization of resources can be checked.
1.5 Land Resources- Talks about the land which is the most useful and important resource. Also, the ways to use this finite resource are carefully planned.
1.6 Land Utilization- ways in which we can use forest, cultivation, fallow Lands, etc.
1.7 Land Use Pattern in India- Discuss the various land use pattern like agriculture, forest, barren, non-agricultural, etc.
1.8 Land Degradation and Conservation- Discusses the ways of ruining of land. On the other hand, discuss the ways to preserve the land.
1.9 Soil as a Resource- This topic deals with soil which is the key natural renewable resource. Above all, it supports all human life on earth. Furthermore, the topic covers various factors which affect the soil.
1.10 Classification of Soil-
This topic further divides into several subtopics which describe the various types of soils mentioned below:
- Alluvial Soil
- Reds and yellow Soil
- Laterite Soil
- Forest Soils
1.11 Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation- This topic discusses the ways by which the topmost layer get degraded. And in the second part discuss the ways of conserving this soil.
You can download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 by clicking on the download button below

Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
Toppr provides free study materials, 1000+ hours of free video lectures, live doubts solving, and more. For online assistance and live doubt clearance, mock test, adaptive learning, simple and easy solutions download the Toppr app for Android and iOS app or signup for free.
Solved Questions For You:
Question 1. The means for the movement of goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations can be termed as which of the following?
Question 2: Which of the following networks of pipeline bring mineral oil to the refinery of Barauni and petrochemical complex of Haldia?
Question 3: Which of the following mode of transport is fuel-efficient and environment-friendly?
Question 4: Which of the following is a means of mass communication?
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 6 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 1 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 4 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Free PDF Download
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


COMMENTS
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development contains answers to all exercise questions of created by the subject matter experts at BYJU'S to help students ace the CBSE exams confidently.
Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development Assignment. Get printable school Assignments for Class 10 Geography.
This document contains a geography assignment on resources and development with questions covering various topics: 1. One mark questions define key terms like contour ploughing, waste land, and sustainable development and ask students to identify specific resources, soils, and national planning documents.
Chapter 1 of Class 10 Geography introduces you to resources and their classification. Furthermore, going into the depth of the chapter, you will learn about the development of resources and resource planning in India.
CBSE Class 10 Geography - Resources and Development (1) - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development help students to score good marks in the exams. These NCERT Solutions are prepared by expert teachers and based on the latest pattern and edition of NCERT book. Here we have provided answers to all the questions in a very easy language. Question 1.
(i) Land resources in India are primarily divided into agricultural land, forest land, land meant for pasture and grazing, and waste land. Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas, and land used for other non-agricultural purposes such as housing, roads and industry.
You can now download the Class 10 Geography Ch 1 Questions and Answers PDF here. This NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography contains answers of all questions asked in Chapter 1 in textbook, Contemporary India II .
Glance on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development. Uncover the different types of resources – natural, human, and man-made – and understand how we classify them based on their availability (renewable vs. non-renewable) with class 10th geography chapter 1.
Our NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 will guide you with the content of the chapter. Also, it will assist students in understanding the topics of the Chapter. The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 aims to help students understand the Chapter in an easy way.