
- Submissions
- Announcements
- Lesson Plans

What Is Power?

Angela L.E. Walmsley and Michael C. Brown, Concordia University Wisconsin
For many teachers of introductory statistics, power is a concept that is often not used. In many cases, it’s avoided altogether. In fact, many Advanced Placement (AP) teachers stay away from the topic when they teach tests of significance, according to Floyd Bullard in “Power in Tests of Significance.” However, power is an important concept to understand as a consumer of research, no matter what field or profession a student may enter as an adult. Hence, discussion of power should be included in an introductory course.
To discuss and understand power, one must be clear on the concepts of Type I and Type II errors. Doug Rush provides a refresher on Type I and Type II errors (including power and effect size) in the Spring 2015 issue of the Statistics Teacher Network , but, briefly, a Type I Error is rejecting the null hypothesis in favor of a false alternative hypothesis, and a Type II Error is failing to reject a false null hypothesis in favor of a true alternative hypothesis. The probability of a Type I error is typically known as Alpha, while the probability of a Type II error is typically known as Beta.
Now on to power. Many learners need to be exposed to a variety of perspectives on the definition of power. Bullard describes multiple ways to interpret power correctly:
- Power is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is false.
- Power is the probability of making a correct decision (to reject the null hypothesis) when the null hypothesis is false.
- Power is the probability that a test of significance will pick up on an effect that is present.
- Power is the probability that a test of significance will detect a deviation from the null hypothesis, should such a deviation exist.
- Power is the probability of avoiding a Type II error.
Simply put, power is the probability of not making a Type II error, according to Neil Weiss in Introductory Statistics .
Mathematically, power is 1 – beta. The power of a hypothesis test is between 0 and 1; if the power is close to 1, the hypothesis test is very good at detecting a false null hypothesis. Beta is commonly set at 0.2, but may be set by the researchers to be smaller.
Consequently, power may be as low as 0.8, but may be higher. Powers lower than 0.8, while not impossible, would typically be considered too low for most areas of research.
Bullard also states there are the following four primary factors affecting power:
- Significance level (or alpha)
- Sample size
- Variability, or variance, in the measured response variable
- Magnitude of the effect of the variable
Power is increased when a researcher increases sample size, as well as when a researcher increases effect sizes and significance levels. There are other variables that also influence power, including variance ( σ2 ), but we’ll limit our conversation to the relationships among power, sample size, effect size, and alpha for this discussion.
In reality, a researcher wants both Type I and Type II errors to be small. In terms of significance level and power, Weiss says this means we want a small significance level (close to 0) and a large power (close to 1).
Having stated a little bit about the concept of power, the authors have found it is most important for students to understand the importance of power as related to sample size when analyzing a study or research article versus actually calculating power. We have found students generally understand the concepts of sampling, study design, and basic statistical tests, but sometimes struggle with the importance of power and necessary sample size. Therefore, the chart in Figure 1 is a tool that can be useful when introducing the concept of power to an audience learning statistics or needing to further its understanding of research methodology.
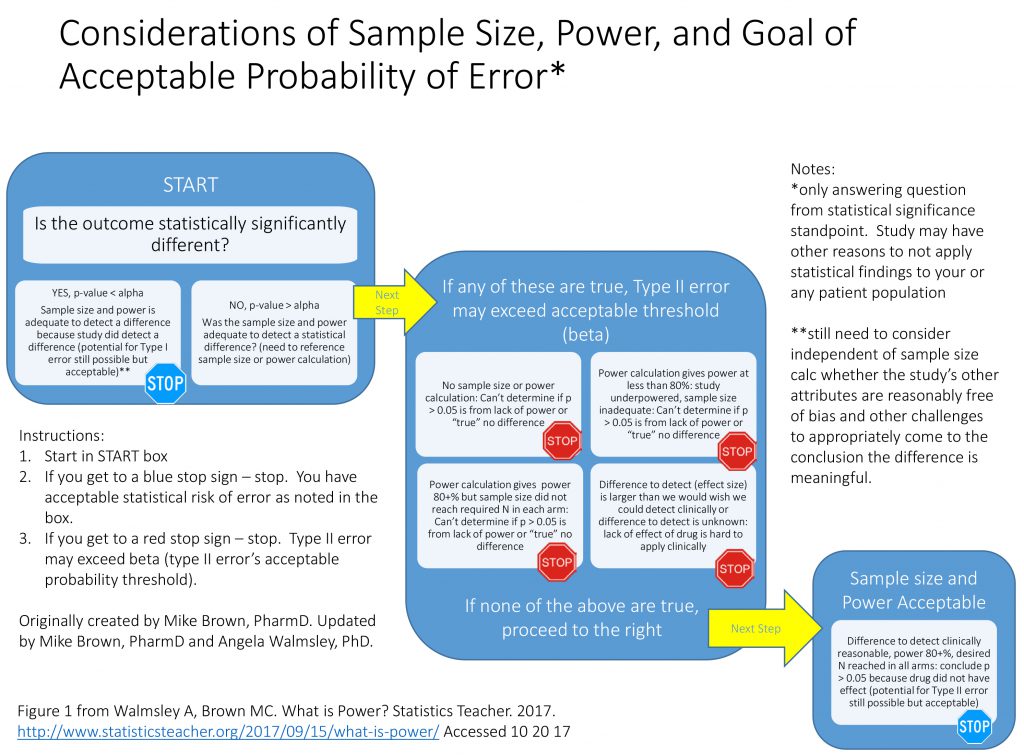
Figure 1 A tool that can be useful when introducing the concept of power to an audience learning statistics or needing to further its understanding of research methodology
This concept is important for teachers to develop in their own understanding of statistics, as well. This tool can help a student critically analyze whether the research study or article they are reading and interpreting has acceptable power and sample size to minimize error. Rather than concentrate on only the p -value result, which has so often traditionally been the focus, this chart (and the examples below) help students understand how to look at power, sample size, and effect size in conjunction with p -value when analyzing results of a study. We encourage the use of this chart in helping your students understand and interpret results as they study various research studies or methodologies.
Examples for Application of the Chart
Imagine six fictitious example studies that each examine whether a new app called StatMaster can help students learn statistical concepts better than traditional methods. Each of the six studies were run with high-school students, comparing the morning AP Statistics class (35 students) that incorporated the StatMaster app to the afternoon AP Statistics class (35 students) that did not use the StatMaster app. The outcome of each of these studies was the comparison of mean test scores between the morning and afternoon classes at the end of the semester.
Statistical information and the fictitious results are shown for each study (A–F) in Figure 2, with the key information shown in bold italics. Although these six examples are of the same study design, do not compare the made-up results across studies. They are six independent pretend examples to illustrate the chart’s application.
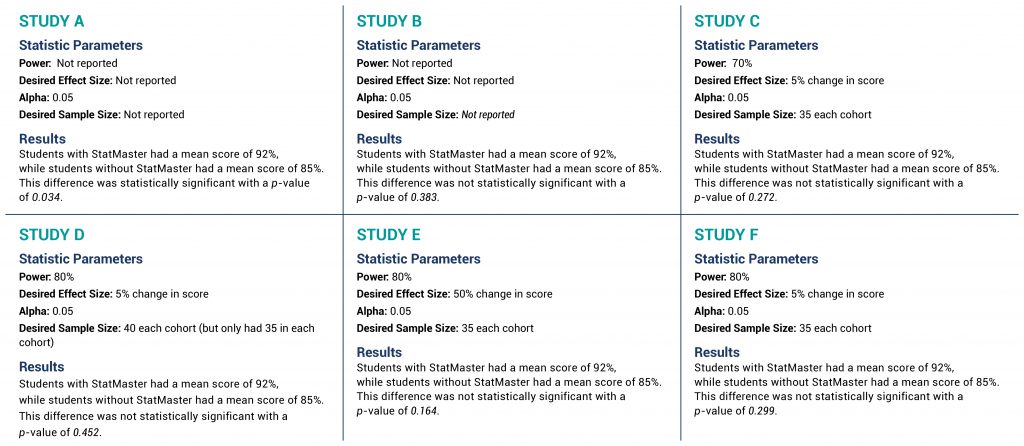
Figure 2 Six fictitious example studies that each examine whether a new app called StatMaster can help students learn statistical concepts better than traditional methods (click to view larger)
In Study A , the key element is the p -value of 0.034. Since this is less than alpha of 0.05, the results are statistically significant and we can stop at the blue stop sign in the START box. While the study is still at risk of making a Type I error, this result does not leave open the possibility of a Type II error. Said another way, the power is adequate to detect a difference because they did detect a difference that was statistically significant. It does not matter that there is no power or sample size calculation when the p -value is less than alpha.
In Study B , the summaries are the same except for the p -value of 0.383. Since this is greater than the alpha of 0.05, we move in the chart to the large middle box to check for the presence or absence of acceptable Type II error. In this case, the criteria of the upper left box are met (that there is no sample size or power calculation) and therefore the lack of a statistically significant difference may be due to inadequate power (or a true lack of difference, but we cannot exclude inadequate power). We hit the upper left red STOP. Since inadequate power—or excessive risk of Type II error—is a possibility, drawing a conclusion as to the effectiveness of StatMaster is not statistically possible.
In Study C , again the p -value is greater than alpha, taking us back to the second main box. Unlike Study B, the presence of a desired power and sample size calculation allows us to avoid the red STOP in the upper left quadrant, but the power of 70% leaves us hitting the criteria of the upper right red STOP. With a power of 70%, our threshold of potential Type II error is 30% (1-0.7), which is above the traditionally acceptable 20%. The ability to draw a statistical conclusion regarding StatMaster is hampered by the potential of unacceptably high risk of Type II error.
In Study D , the p -value continues to be greater than alpha, but—unlike Study B and Study C—Study D has an appropriate power set at 80%. That is a good thing. The challenge becomes the desired sample size to meet this 80% power. Study D says it needs 40 subjects in each class to be confident of 80% power, but the study only has 35 subjects, so we hit the red STOP in the lower left quadrant. Because the desired sample size was not met, the actual power is less than 80%, leaving us effectively in the same situation as Study C—at risk of excessive Type II error beyond 20%.
In Study E , the challenges are more complex. With a p -value greater than alpha, we once again move to the middle large box to examine the potential of excessive or indeterminate Type II error. In this case, power (80%), alpha (0.05), and sample size (35 in each cohort) are all adequate. The effect size, however, is set at 50%.
While a 50% change in score would be of interest, it has two problems. First, it is likely that previous course offerings provide some estimate of performance in the absence of StatMaster, and—presuming it is even remotely close to the mean of 85% seen in Study E—a 50% increase would not be mathematically possible, making this an impractical effect size. Second, a sample size will provide adequate power to detect an effect size that is at least as big as the desired effect size or bigger, but not smaller . Reviewing the equation earlier in this manuscript provides the mathematical evidence of this concept.
So, while an effect size of 50% would be impressive—in the absence of a statistically significant outcome—Study E would not be certain to have adequate power to detect a smaller effect size, even though a smaller effect size might be of interest. Therefore, we are left at the red STOP sign in the lower right corner.
Note that, unlike the other red STOP signs, this example requires subjective judgment and is less objective than the other three paths to potentially exceeding acceptable Type II error. As noted earlier, this is a complex and challenging scenario to interpret, but is quite plausible (even common), and therefore included for consideration.
Our final example is Study F, in which we can progress to the box describing sample size and power as acceptable. The power (80%), desired effect size (5% change), and alpha (0.05) are all appropriate and the desired sample size (35 in each cohort) was met, leading us to the statistical conclusion that the absence of a statistically significant finding demonstrates no difference exists. Recognize that the potential for Type II error still exists, but it is no greater than 1 – power—or in this case 20% (1 – 0.8)—which is why it is deemed acceptable.
In conclusion, we encourage teachers to introduce the concept of power and its importance in evaluating statistical research. We are hopeful that both the sample scenarios and the flowchart are useful for both teachers and students as they explore the concept of power and how it relates to effect size, sample size, and significance level in general.

Recent Posts
- NCTM Defines Key Issues in Mathematics Education with New Position Statements
- Association Between Gender and Sport Watching Preference?
- Editors’ Note: Fall 2024
- Statistics, Data Science Education: Key for Future of High School Mathematics
- ASA/NCTM Joint Committee Members Share Favorite Resources
Previous Issues
- December 2024
- November 2023
- October 2022
- October 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- September 2019
- January 2019
- October 2017
- September 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
Statistics Teacher (ST) is an online journal published by the American Statistical Association (ASA) – National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) Joint Committee on Curriculum in Statistics and Probability for Grades K-12. ST supports the teaching and learning of statistics through education articles, lesson plans, announcements, professional development opportunities, technology, assessment, and classroom resources. Authors should use this form to submit articles or lesson plans.
Linen Theme by The Theme Foundry
Copyright © 2024 American Statistical Association. All rights reserved.
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
25.2 - power functions, example 25-2 section .

Let's take a look at another example that involves calculating the power of a hypothesis test.
Let \(X\) denote the IQ of a randomly selected adult American. Assume, a bit unrealistically, that \(X\) is normally distributed with unknown mean \(\mu\) and standard deviation 16. Take a random sample of \(n=16\) students, so that, after setting the probability of committing a Type I error at \(\alpha=0.05\), we can test the null hypothesis \(H_0:\mu=100\) against the alternative hypothesis that \(H_A:\mu>100\).
What is the power of the hypothesis test if the true population mean were \(\mu=108\)?
Setting \(\alpha\), the probability of committing a Type I error, to 0.05, implies that we should reject the null hypothesis when the test statistic \(Z\ge 1.645\), or equivalently, when the observed sample mean is 106.58 or greater:
because we transform the test statistic \(Z\) to the sample mean by way of:
\(Z=\dfrac{\bar{X}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\qquad \Rightarrow \bar{X}=\mu+Z\dfrac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}} \qquad \bar{X}=100+1.645\left(\dfrac{16}{\sqrt{16}}\right)=106.58\)
Now, that implies that the power, that is, the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, when \(\mu=108\) is 0.6406 as calculated here (recalling that \(Phi(z)\) is standard notation for the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal random variable):
\( \text{Power}=P(\bar{X}\ge 106.58\text{ when } \mu=108) = P\left(Z\ge \dfrac{106.58-108}{\frac{16}{\sqrt{16}}}\right) \\ = P(Z\ge -0.36)=1-P(Z<-0.36)=1-\Phi(-0.36)=1-0.3594=0.6406 \)
and illustrated here:
In summary, we have determined that we have (only) a 64.06% chance of rejecting the null hypothesis \(H_0:\mu=100\) in favor of the alternative hypothesis \(H_A:\mu>100\) if the true unknown population mean is in reality \(\mu=108\).
What is the power of the hypothesis test if the true population mean were \(\mu=112\)?
Because we are setting \(\alpha\), the probability of committing a Type I error, to 0.05, we again reject the null hypothesis when the test statistic \(Z\ge 1.645\), or equivalently, when the observed sample mean is 106.58 or greater. That means that the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, when \(\mu=112\) is 0.9131 as calculated here:
\( \text{Power}=P(\bar{X}\ge 106.58\text{ when }\mu=112)=P\left(Z\ge \frac{106.58-112}{\frac{16}{\sqrt{16}}}\right) \\ = P(Z\ge -1.36)=1-P(Z<-1.36)=1-\Phi(-1.36)=1-0.0869=0.9131 \)
In summary, we have determined that we now have a 91.31% chance of rejecting the null hypothesis \(H_0:\mu=100\) in favor of the alternative hypothesis \(H_A:\mu>100\) if the true unknown population mean is in reality \(\mu=112\). Hmm.... it should make sense that the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis is larger for values of the mean, such as 112, that are far away from the assumed mean under the null hypothesis.
What is the power of the hypothesis test if the true population mean were \(\mu=116\)?
Again, because we are setting \(\alpha\), the probability of committing a Type I error, to 0.05, we reject the null hypothesis when the test statistic \(Z\ge 1.645\), or equivalently, when the observed sample mean is 106.58 or greater. That means that the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, when \(\mu=116\) is 0.9909 as calculated here:
\(\text{Power}=P(\bar{X}\ge 106.58\text{ when }\mu=116) =P\left(Z\ge \dfrac{106.58-116}{\frac{16}{\sqrt{16}}}\right) = P(Z\ge -2.36)=1-P(Z<-2.36)= 1-\Phi(-2.36)=1-0.0091=0.9909 \)
In summary, we have determined that, in this case, we have a 99.09% chance of rejecting the null hypothesis \(H_0:\mu=100\) in favor of the alternative hypothesis \(H_A:\mu>100\) if the true unknown population mean is in reality \(\mu=116\). The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis is the largest yet of those we calculated, because the mean, 116, is the farthest away from the assumed mean under the null hypothesis.
Are you growing weary of this? Let's summarize a few things we've learned from engaging in this exercise:
- First and foremost, my instructor can be tedious at times..... errrr, I mean, first and foremost, the power of a hypothesis test depends on the value of the parameter being investigated. In the above, example, the power of the hypothesis test depends on the value of the mean \(\mu\).
- As the actual mean \(\mu\) moves further away from the value of the mean \(\mu=100\) under the null hypothesis, the power of the hypothesis test increases.
It's that first point that leads us to what is called the power function of the hypothesis test . If you go back and take a look, you'll see that in each case our calculation of the power involved a step that looks like this:
\(\text{Power } =1 - \Phi (z) \) where \(z = \frac{106.58 - \mu}{16 / \sqrt{16}} \)
That is, if we use the standard notation \(K(\mu)\) to denote the power function, as it depends on \(\mu\), we have:
\(K(\mu) = 1- \Phi \left( \frac{106.58 - \mu}{16 / \sqrt{16}} \right) \)
So, the reality is your instructor could have been a whole lot more tedious by calculating the power for every possible value of \(\mu\) under the alternative hypothesis! What we can do instead is create a plot of the power function, with the mean \(\mu\) on the horizontal axis and the power \(K(\mu)\) on the vertical axis. Doing so, we get a plot in this case that looks like this:
Now, what can we learn from this plot? Well:
We can see that \(\alpha\) (the probability of a Type I error), \(\beta\) (the probability of a Type II error), and \(K(\mu)\) are all represented on a power function plot, as illustrated here:
We can see that the probability of a Type I error is \(\alpha=K(100)=0.05\), that is, the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true is 0.05.
We can see the power of a test \(K(\mu)\), as well as the probability of a Type II error \(\beta(\mu)\), for each possible value of \(\mu\).
We can see that \(\beta(\mu)=1-K(\mu)\) and vice versa, that is, \(K(\mu)=1-\beta(\mu)\).
And we can see graphically that, indeed, as the actual mean \(\mu\) moves further away from the null mean \(\mu=100\), the power of the hypothesis test increases.
Now, what would do you suppose would happen to the power of our hypothesis test if we were to change our willingness to commit a Type I error? Would the power for a given value of \(\mu\) increase, decrease, or remain unchanged? Suppose, for example, that we wanted to set \(\alpha=0.01\) instead of \(\alpha=0.05\)? Let's return to our example to explore this question.
Example 25-2 (continued) Section

Let \(X\) denote the IQ of a randomly selected adult American. Assume, a bit unrealistically, that \(X\) is normally distributed with unknown mean \(\mu\) and standard deviation 16. Take a random sample of \(n=16\) students, so that, after setting the probability of committing a Type I error at \(\alpha=0.01\), we can test the null hypothesis \(H_0:\mu=100\) against the alternative hypothesis that \(H_A:\mu>100\).
Setting \(\alpha\), the probability of committing a Type I error, to 0.01, implies that we should reject the null hypothesis when the test statistic \(Z\ge 2.326\), or equivalently, when the observed sample mean is 109.304 or greater:
\(\bar{x} = \mu + z \left( \frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}} \right) =100 + 2.326\left( \frac{16}{\sqrt{16}} \right)=109.304 \)
That means that the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, when \(\mu=108\) is 0.3722 as calculated here:
So, the power when \(\mu=108\) and \(\alpha=0.01\) is smaller (0.3722) than the power when \(\mu=108\) and \(\alpha=0.05\) (0.6406)! Perhaps we can see this graphically:
By the way, we could again alternatively look at the glass as being half-empty. In that case, the probability of a Type II error when \(\mu=108\) and \(\alpha=0.01\) is \(1-0.3722=0.6278\). In this case, the probability of a Type II error is greater than the probability of a Type II error when \(\mu=108\) and \(\alpha=0.05\).
All of this can be seen graphically by plotting the two power functions, one where \(\alpha=0.01\) and the other where \(\alpha=0.05\), simultaneously. Doing so, we get a plot that looks like this:
This last example illustrates that, providing the sample size \(n\) remains unchanged, a decrease in \(\alpha\) causes an increase in \(\beta\) , and at least theoretically, if not practically, a decrease in \(\beta\) causes an increase in \(\alpha\). It turns out that the only way that \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) can be decreased simultaneously is by increasing the sample size \(n\).
Teach yourself statistics
Power of a Hypothesis Test
The probability of not committing a Type II error is called the power of a hypothesis test.
Effect Size
To compute the power of the test, one offers an alternative view about the "true" value of the population parameter, assuming that the null hypothesis is false. The effect size is the difference between the true value and the value specified in the null hypothesis.
Effect size = True value - Hypothesized value
For example, suppose the null hypothesis states that a population mean is equal to 100. A researcher might ask: What is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis if the true population mean is equal to 90? In this example, the effect size would be 90 - 100, which equals -10.
Factors That Affect Power
The power of a hypothesis test is affected by three factors.
- Sample size ( n ). Other things being equal, the greater the sample size, the greater the power of the test.
- Significance level (α). The lower the significance level, the lower the power of the test. If you reduce the significance level (e.g., from 0.05 to 0.01), the region of acceptance gets bigger. As a result, you are less likely to reject the null hypothesis. This means you are less likely to reject the null hypothesis when it is false, so you are more likely to make a Type II error. In short, the power of the test is reduced when you reduce the significance level; and vice versa.
- The "true" value of the parameter being tested. The greater the difference between the "true" value of a parameter and the value specified in the null hypothesis, the greater the power of the test. That is, the greater the effect size, the greater the power of the test.
Test Your Understanding
Other things being equal, which of the following actions will reduce the power of a hypothesis test?
I. Increasing sample size. II. Changing the significance level from 0.01 to 0.05. III. Increasing beta, the probability of a Type II error.
(A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) All of the above (E) None of the above
The correct answer is (C). Increasing sample size makes the hypothesis test more sensitive - more likely to reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false. Changing the significance level from 0.01 to 0.05 makes the region of acceptance smaller, which makes the hypothesis test more likely to reject the null hypothesis, thus increasing the power of the test. Since, by definition, power is equal to one minus beta, the power of a test will get smaller as beta gets bigger.
Suppose a researcher conducts an experiment to test a hypothesis. If she doubles her sample size, which of the following will increase?
I. The power of the hypothesis test. II. The effect size of the hypothesis test. III. The probability of making a Type II error.
The correct answer is (A). Increasing sample size makes the hypothesis test more sensitive - more likely to reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false. Thus, it increases the power of the test. The effect size is not affected by sample size. And the probability of making a Type II error gets smaller, not bigger, as sample size increases.
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

In Brief: Statistics in Brief: Statistical Power: What Is It and When Should It Be Used?
Frederick j dorey , phd.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Corresponding author.
Issue date 2011 Feb.
Although any report formally testing a hypothesis should include an associated p value and confidence interval, another statistical concept that is in some ways more important is the power of a study. Unlike the p value and confidence interval, the issue of power should be considered before even embarking on a clinical study.
What is statistical power, when should it be used, and what information is needed for calculating power?
Like the p value, the power is a conditional probability. In a hypothesis test, the alternative hypothesis is the statement that the null hypothesis is false. If the alternative hypothesis is actually true, the power is the probability that one will correctly reject the null hypothesis. The most meaningful application of statistical power is to decide before initiation of a clinical study whether it is worth doing, given the needed effort, cost, and in the case of clinical experiments, patient involvement. A hypothesis test with little power will likely yield large p values and large confidence intervals. Thus when the power of a proposed study is low, even when there are real differences between treatments under investigation, the most likely result of the study will be that there is not enough evidence to reject the H 0 and meaningful clinical differences will remain in question. In that situation a reasonable question to ask would be, was the study worth the needed time and effort to get so little additional information.
The usual question asked involving statistical power is: what sample size will result in a reasonable power (however defined) for the primary hypothesis being investigated. In many cases however, a more realistic question would be: what will the statistical power be for the important hypothesis tests, given the most likely sample size that can be obtained during the duration of the proposed study?
For any given statistical procedure and significance level, there are three statistical concepts closely related to each other. These are the sample size, effect size, and power. If you know any two of them, the third can be determined. To determine the effect size the investigator first must estimate the magnitude of the minimum clinically important difference (MCID) that the experiment is designed to detect. This value then is divided by an estimate of the variability of the data as interpretation of numbers only makes sense relative to the variability of the estimated parameters. Although investigators usually can provide a reasonable estimate of the MCID for a study, they frequently have little idea about the variability of their data. In many cases the standard deviation of the control group will provide a good estimate of that variability. As intuitively it should be easier to determine if two groups differ by a large rather than a small clinically meaningful difference, it follows that a larger effect size usually will result in more power. Also, a larger sample size results in more precision of the parameters being estimated thus resulting in more power as the estimates are more likely to be closer to the true values in the target population. (A more-detailed article by Biau et al. [ 1 ] discusses the relationships between power and sample size along with examples.)
For power calculations to be meaningful, it first is necessary to decide on the proper effect size. The effect size must be decided first because, for any proposed sample size, an effect size always can be chosen that will result in any desired power. In short, the goals of the experiment alone should determine the effect size. Once a study has been completed and analyzed, the confidence interval reveals how much, or little, has been learned and the power will not contribute any meaningful additional information. In a detailed discussion of post hoc power calculations in general, Hoenig and Heisey [ 2 ] showed that if a hypothesis test has been performed with a resulting p value greater than the 5% significance level, then the power for detecting the observed difference will only be approximately 50% or less. However, it can be verified easily with examples that hypothesis tests resulting in very small p values (such as 0.015) could still have a post hoc power even less than 70%; in such a case it is difficult to see how a post hoc power calculation will contribute any more information than what already is known.
There is a very nice relationship between the concepts of hypothesis testing and diagnostic testing. Let the null hypothesis represent the absence of a given disease, the alternative hypothesis represent the presence of the disease, and the rejection of the null hypothesis represent having a positive diagnostic test. With these assumptions, the power is simply equivalent to the sensitivity of the test (the probability the test is positive when the disease is present). In addition, the significance level is equivalent to one minus the specificity of the test, or in other words, the error you are willing to risk of falsely rejecting the null hypothesis simply corresponds to the probability of getting a positive test among patients without the disease.
Myths and Misconceptions
As discussed above the notion of power after the data have been collected does not provide very much additional information about the hypothesis test results. This is illustrated by considering the experiment of flipping a coin 10 times to see if the coin is fair, that is, the probability of heads is 0.5. Suppose you flip the coin 10 times and you get 10 heads. This experiment with only 10 flips has very little power for testing if the coin is fair. However the p value for obtaining 10 heads in 10 flips with a fair coin (the null hypothesis) is very small, so the null hypothesis certainly will be rejected. Thus, even though the experiment has little power, it does not change the fact that an experiment has been conducted and provided convincing evidence that the coin is biased in favor of heads. I do not recommend that you bet on tails.
Another myth is that the power always has to be at least 80% or greater. That might be a reasonable expectation for a clinical study potentially involving great inconvenience or risk to patients. However in a laboratory study or a retrospective correlation study, there is usually no necessity for the power to be that high.

Conclusions
The concept of statistical power should be used before initiating a study to help determine whether it is reasonable and ethical to proceed with a study. Calculation of statistical power also sometimes is useful post hoc when statistically insignificant but potentially clinically important trends are noted, say in the study of two treatments for cancer. Such post hoc tests can inform the reader or future researchers how many patients might be needed to show statistical differences. The power and effect size needed for a study to be reasonable also will depend on the medical question being asked and the information already available in the literature.
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
- 1. Biau DJ, Kernéis S, Porcher R. Statistics in brief: the importance of sample size in the planning and interpretation of medical research. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:2282–2288. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0346-9. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Hoenig JM, Heisey DM. The abuse of power: the pervasive fallacy of power calculations for data analysis. Am Stat. 2001;55:19–24. doi: 10.1198/000313001300339897. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (137.0 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
Quickonomics
Power Of A Test
Published Sep 8, 2024
Definition of Power of a Test
The power of a test in statistics is the probability that the test will reject a false null hypothesis. Essentially, it measures a test’s ability to detect an effect when there is one. The power of a test is denoted as 1 – β (beta), where β represents the probability of making a Type II error (failing to reject a false null hypothesis). A higher power means a lower chance of a Type II error, making the test more reliable in identifying true effects.
Imagine a pharmaceutical company that has developed a new drug intended to lower blood pressure. To test its effectiveness, the company conducts a clinical trial with two groups: a treatment group that receives the drug and a control group that receives a placebo. The null hypothesis (H 0 ) states that the drug has no effect on blood pressure, while the alternative hypothesis (H 1 ) states that the drug does lower blood pressure.
After conducting the trial, the company uses statistical tests to analyze the results. The power of this test is particularly important because it indicates the likelihood of correctly identifying the drug’s effect, if it exists. Ideally, the company would want a high power (e.g., 0.80 or 80%) to ensure that the test is robust and minimizes the risk of a Type II error. If the power is low, the trial might fail to detect a genuine effect, potentially leading to the incorrect conclusion that the drug is ineffective.
Factors Affecting the Power of a Test
1. sample size:.
The larger the sample size, the higher the power of the test. A larger sample provides more information and reduces variability, making it easier to detect an effect.
2. Significance Level (α):
The significance level, or alpha, is the probability of making a Type I error (rejecting a true null hypothesis). Higher α levels (e.g., 0.05 vs. 0.01) can increase the power of the test, but they also increase the risk of Type I errors.
3. Effect Size:
Effect size refers to the magnitude of the difference or relationship that the test is trying to detect. Larger effect sizes are easier to detect and thus increase the power of the test.
4. Variability:
Lower variability within the sample data increases the power of the test. High variability can obscure the effect, making it harder to detect.
Importance of Power
Understanding and calculating the power of a test is crucial for researchers and analysts in various fields, including medicine, finance, and social sciences. Here’s why:
- Minimizing Errors: High power reduces the risk of Type II errors, ensuring that real effects are not overlooked.
- Resource Allocation: Adequate power ensures that resources such as time and money are not wasted on inconclusive studies.
- Credibility: Studies with high power are more credible and their results more likely to be accepted by the scientific community and stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the recommended power level for statistical tests.
A commonly accepted threshold for an adequately powered test is 0.80 (or 80%). This means there is an 80% chance of detecting an effect if there is one, while accepting a 20% chance of a Type II error.
How can researchers increase the power of their tests?
Researchers can increase the power of their tests by:
- Increasing the sample size, which provides more data and reduces variability.
- Enhancing the study design to reduce noise and improve measurement precision.
- Increasing the effect size, if possible, by choosing a more potent intervention or more sensitive measurement method.
- Adjusting the significance level (α), although this must be done cautiously to balance Type I and Type II error rates.
Can a test have too much power?
Yes, a test can be excessively powerful, leading to the detection of trivial effects that are statistically significant but not practically meaningful. In such cases, the test might identify minute differences that have little to no real-world significance, potentially leading to misguided conclusions.
Why is power analysis important before conducting a study?
Power analysis helps researchers determine the adequate sample size needed to detect an effect of interest. By conducting a power analysis before a study, researchers can design their experiments more effectively, ensure efficient use of resources, and enhance the reliability of their findings. It also helps in justifying the sample size to stakeholders and funding bodies.
Calculating and understanding the power of a test is fundamental in statistical analysis, ensuring that studies are well-designed and their conclusions are valid and actionable. By considering factors such as sample size, significance level, and effect size, researchers can enhance the robustness of their findings and contribute more reliably to their fields.
To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Power of the Hypothesis Test. The power of a hypothesis test is the probability of making the correct decision if the alternative hypothesis is true. That is, the power of a hypothesis test is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis \(H_0\) when the alternative hypothesis \(H_A\) is the hypothesis that is true.
Illustration of the power of a statistical test, for a two sided test, through the probability distribution of the test statistic under the null and alternative hypothesis. α is shown as the blue area , the probability of rejection under null, while the red area shows power, 1 − β , the probability of correctly rejecting under the alternative.
Statistical power function distribution. In the context of hypothesis testing, the power function distribution is a graphical depiction of the power function of a statistical test for varying values of the population parameter. It provides a visual representation of the test’s power for these different population parameter values and can ...
Power of the Hypothesis Test. The power of a hypothesis test is the probability of making the correct decision if the alternative hypothesis is true. That is, the power of a hypothesis test is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis \(H_0\) when the alternative hypothesis \(H_A\) is the hypothesis that is true.
Sep 15, 2017 · Power is the probability of making a correct decision (to reject the null hypothesis) when the null hypothesis is false. Power is the probability that a test of significance will pick up on an effect that is present. Power is the probability that a test of significance will detect a deviation from the null hypothesis, should such a deviation exist.
What is the power of the hypothesis test if the true population mean were \(\mu=112\)? Answer Because we are setting \(\alpha\), the probability of committing a Type I error, to 0.05, we again reject the null hypothesis when the test statistic \(Z\ge 1.645\), or equivalently, when the observed sample mean is 106.58 or greater.
Changing the significance level from 0.01 to 0.05 makes the region of acceptance smaller, which makes the hypothesis test more likely to reject the null hypothesis, thus increasing the power of the test. Since, by definition, power is equal to one minus beta, the power of a test will get smaller as beta gets bigger.
The most meaningful application of statistical power is to decide before initiation of a clinical study whether it is worth doing, given the needed effort, cost, and in the case of clinical experiments, patient involvement. A hypothesis test with little power will likely yield large p values and large confidence intervals.
Sep 8, 2024 · Published Sep 8, 2024 Definition of Power of a Test The power of a test in statistics is the probability that the test will reject a false null hypothesis. Essentially, it measures a test’s ability to detect an effect when there is one. The power of a test is denoted […]
Feb 16, 2021 · Why does power matter in statistics? Having enough statistical power is necessary to draw accurate conclusions about a population using sample data. In hypothesis testing, you start with null and alternative hypotheses: a null hypothesis of no effect and an alternative hypothesis of a true effect (your actual research prediction).