
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

10.2 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
Learning objective.
- Describe the basic steps in the marketing research process and the purpose of each step.
The basic steps used to conduct marketing research are shown in Figure 10.6 “Steps in the Marketing Research Process” . Next, we discuss each step.
Figure 10.6 Steps in the Marketing Research Process
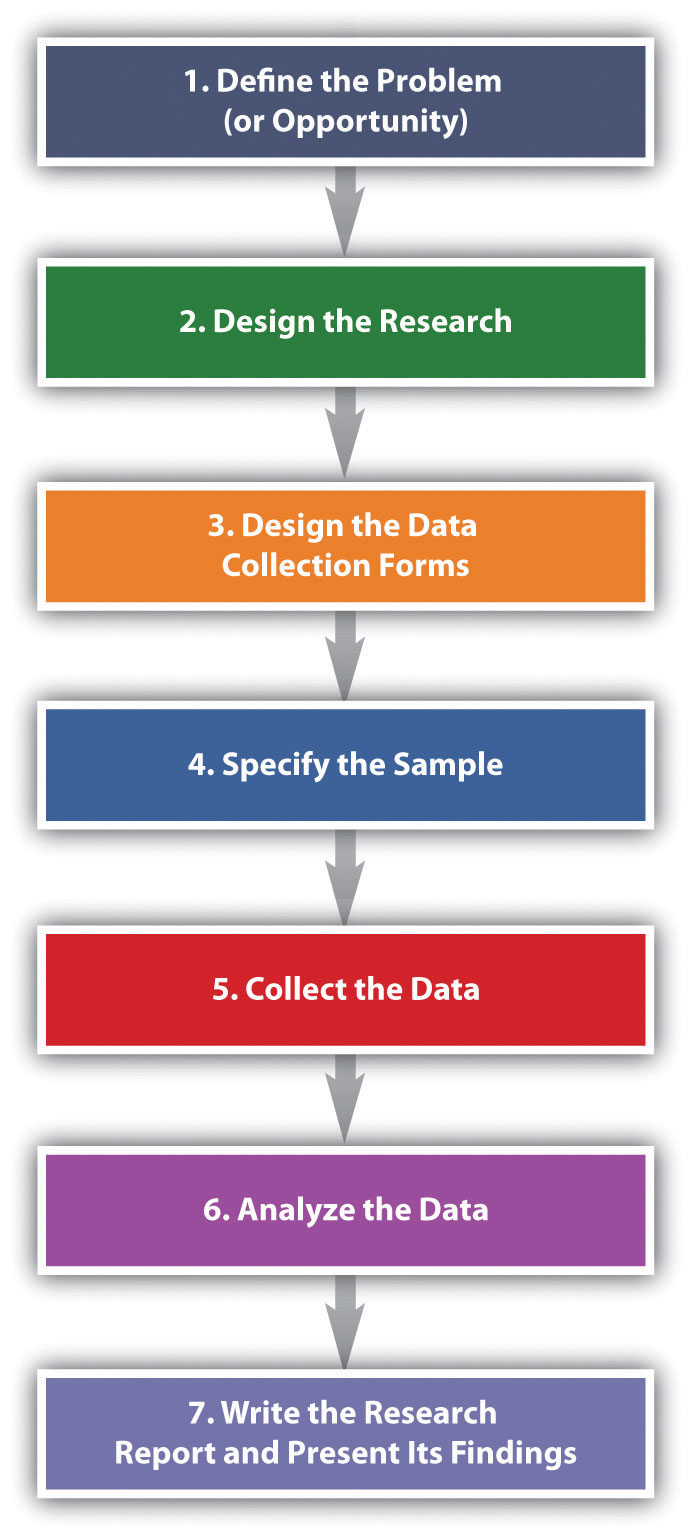
Step 1: Define the Problem (or Opportunity)
There’s a saying in marketing research that a problem half defined is a problem half solved. Defining the “problem” of the research sounds simple, doesn’t it? Suppose your product is tutoring other students in a subject you’re a whiz at. You have been tutoring for a while, and people have begun to realize you’re darned good at it. Then, suddenly, your business drops off. Or it explodes, and you can’t cope with the number of students you’re being asked help. If the business has exploded, should you try to expand your services? Perhaps you should subcontract with some other “whiz” students. You would send them students to be tutored, and they would give you a cut of their pay for each student you referred to them.
Both of these scenarios would be a problem for you, wouldn’t they? They are problems insofar as they cause you headaches. But are they really the problem? Or are they the symptoms of something bigger? For example, maybe your business has dropped off because your school is experiencing financial trouble and has lowered the number of scholarships given to incoming freshmen. Consequently, there are fewer total students on campus who need your services. Conversely, if you’re swamped with people who want you to tutor them, perhaps your school awarded more scholarships than usual, so there are a greater number of students who need your services. Alternately, perhaps you ran an ad in your school’s college newspaper, and that led to the influx of students wanting you to tutor them.
Businesses are in the same boat you are as a tutor. They take a look at symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes. If you approach a marketing research company with either scenario—either too much or too little business—the firm will seek more information from you such as the following:
- In what semester(s) did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what subject areas did your tutoring revenues fall (or rise)?
- In what sales channels did revenues fall (or rise): Were there fewer (or more) referrals from professors or other students? Did the ad you ran result in fewer (or more) referrals this month than in the past months?
- Among what demographic groups did your revenues fall (or rise)—women or men, people with certain majors, or first-year, second-, third-, or fourth-year students?
The key is to look at all potential causes so as to narrow the parameters of the study to the information you actually need to make a good decision about how to fix your business if revenues have dropped or whether or not to expand it if your revenues have exploded.
The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective. The research objective is the goal(s) the research is supposed to accomplish. The marketing research objective for your tutoring business might read as follows:
To survey college professors who teach 100- and 200-level math courses to determine why the number of students referred for tutoring dropped in the second semester.
This is admittedly a simple example designed to help you understand the basic concept. If you take a marketing research course, you will learn that research objectives get a lot more complicated than this. The following is an example:
“To gather information from a sample representative of the U.S. population among those who are ‘very likely’ to purchase an automobile within the next 6 months, which assesses preferences (measured on a 1–5 scale ranging from ‘very likely to buy’ to ‘not likely at all to buy’) for the model diesel at three different price levels. Such data would serve as input into a forecasting model that would forecast unit sales, by geographic regions of the country, for each combination of the model’s different prices and fuel configurations (Burns & Bush, 2010).”
Now do you understand why defining the problem is complicated and half the battle? Many a marketing research effort is doomed from the start because the problem was improperly defined. Coke’s ill-fated decision to change the formula of Coca-Cola in 1985 is a case in point: Pepsi had been creeping up on Coke in terms of market share over the years as well as running a successful promotional campaign called the “Pepsi Challenge,” in which consumers were encouraged to do a blind taste test to see if they agreed that Pepsi was better. Coke spent four years researching “the problem.” Indeed, people seemed to like the taste of Pepsi better in blind taste tests. Thus, the formula for Coke was changed. But the outcry among the public was so great that the new formula didn’t last long—a matter of months—before the old formula was reinstated. Some marketing experts believe Coke incorrectly defined the problem as “How can we beat Pepsi in taste tests?” instead of “How can we gain market share against Pepsi?” (Burns & Bush, 2010)
New Coke Is It! 1985
(click to see video)
This video documents the Coca-Cola Company’s ill-fated launch of New Coke in 1985.
1985 Pepsi Commercial—“They Changed My Coke”
This video shows how Pepsi tried to capitalize on the blunder.
Step 2: Design the Research
The next step in the marketing research process is to do a research design. The research design is your “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather and from whom, how and when you will collect the data, and how you will analyze it once it’s been obtained. Let’s look at the data you’re going to gather first.
There are two basic types of data you can gather. The first is primary data. Primary data is information you collect yourself, using hands-on tools such as interviews or surveys, specifically for the research project you’re conducting. Secondary data is data that has already been collected by someone else, or data you have already collected for another purpose. Collecting primary data is more time consuming, work intensive, and expensive than collecting secondary data. Consequently, you should always try to collect secondary data first to solve your research problem, if you can. A great deal of research on a wide variety of topics already exists. If this research contains the answer to your question, there is no need for you to replicate it. Why reinvent the wheel?
Sources of Secondary Data
Your company’s internal records are a source of secondary data. So are any data you collect as part of your marketing intelligence gathering efforts. You can also purchase syndicated research. Syndicated research is primary data that marketing research firms collect on a regular basis and sell to other companies. J.D. Power & Associates is a provider of syndicated research. The company conducts independent, unbiased surveys of customer satisfaction, product quality, and buyer behavior for various industries. The company is best known for its research in the automobile sector. One of the best-known sellers of syndicated research is the Nielsen Company, which produces the Nielsen ratings. The Nielsen ratings measure the size of television, radio, and newspaper audiences in various markets. You have probably read or heard about TV shows that get the highest (Nielsen) ratings. (Arbitron does the same thing for radio ratings.) Nielsen, along with its main competitor, Information Resources, Inc. (IRI), also sells businesses scanner-based research . Scanner-based research is information collected by scanners at checkout stands in stores. Each week Nielsen and IRI collect information on the millions of purchases made at stores. The companies then compile the information and sell it to firms in various industries that subscribe to their services. The Nielsen Company has also recently teamed up with Facebook to collect marketing research information. Via Facebook, users will see surveys in some of the spaces in which they used to see online ads (Rappeport, Gelles, 2009).
By contrast, MarketResearch.com is an example of a marketing research aggregator. A marketing research aggregator is a marketing research company that doesn’t conduct its own research and sell it. Instead, it buys research reports from other marketing research companies and then sells the reports in their entirety or in pieces to other firms. Check out MarketResearch.com’s Web site. As you will see there are a huge number of studies in every category imaginable that you can buy for relatively small amounts of money.
Figure 10.7
Market research aggregators buy research reports from other marketing research companies and then resell them in part or in whole to other companies so they don’t have to gather primary data.
Source: http://www.marketresearch.com .
Your local library is a good place to gather free secondary data. It has searchable databases as well as handbooks, dictionaries, and books, some of which you can access online. Government agencies also collect and report information on demographics, economic and employment data, health information, and balance-of-trade statistics, among a lot of other information. The U.S. Census Bureau collects census data every ten years to gather information about who lives where. Basic demographic information about sex, age, race, and types of housing in which people live in each U.S. state, metropolitan area, and rural area is gathered so that population shifts can be tracked for various purposes, including determining the number of legislators each state should have in the U.S. House of Representatives. For the U.S. government, this is primary data. For marketing managers it is an important source of secondary data.
The Survey Research Center at the University of Michigan also conducts periodic surveys and publishes information about trends in the United States. One research study the center continually conducts is called the “Changing Lives of American Families” ( http://www.isr.umich.edu/home/news/research-update/2007-01.pdf ). This is important research data for marketing managers monitoring consumer trends in the marketplace. The World Bank and the United Nations are two international organizations that collect a great deal of information. Their Web sites contain many free research studies and data related to global markets. Table 10.1 “Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources” shows some examples of primary versus secondary data sources.
Table 10.1 Examples of Primary Data Sources versus Secondary Data Sources
Gauging the Quality of Secondary Data
When you are gathering secondary information, it’s always good to be a little skeptical of it. Sometimes studies are commissioned to produce the result a client wants to hear—or wants the public to hear. For example, throughout the twentieth century, numerous studies found that smoking was good for people’s health. The problem was the studies were commissioned by the tobacco industry. Web research can also pose certain hazards. There are many biased sites that try to fool people that they are providing good data. Often the data is favorable to the products they are trying to sell. Beware of product reviews as well. Unscrupulous sellers sometimes get online and create bogus ratings for products. See below for questions you can ask to help gauge the credibility of secondary information.
Gauging the Credibility of Secondary Data: Questions to Ask
- Who gathered this information?
- For what purpose?
- What does the person or organization that gathered the information have to gain by doing so?
- Was the information gathered and reported in a systematic manner?
- Is the source of the information accepted as an authority by other experts in the field?
- Does the article provide objective evidence to support the position presented?
Types of Research Design
Now let’s look specifically at the types of research designs that are utilized. By understanding different types of research designs, a researcher can solve a client’s problems more quickly and efficiently without jumping through more hoops than necessary. Research designs fall into one of the following three categories:
- Exploratory research design
- Descriptive research design
- Causal research design (experiments)
An exploratory research design is useful when you are initially investigating a problem but you haven’t defined it well enough to do an in-depth study of it. Perhaps via your regular market intelligence, you have spotted what appears to be a new opportunity in the marketplace. You would then do exploratory research to investigate it further and “get your feet wet,” as the saying goes. Exploratory research is less structured than other types of research, and secondary data is often utilized.
One form of exploratory research is qualitative research. Qualitative research is any form of research that includes gathering data that is not quantitative, and often involves exploring questions such as why as much as what or how much . Different forms, such as depth interviews and focus group interviews, are common in marketing research.
The depth interview —engaging in detailed, one-on-one, question-and-answer sessions with potential buyers—is an exploratory research technique. However, unlike surveys, the people being interviewed aren’t asked a series of standard questions. Instead the interviewer is armed with some general topics and asks questions that are open ended, meaning that they allow the interviewee to elaborate. “How did you feel about the product after you purchased it?” is an example of a question that might be asked. A depth interview also allows a researcher to ask logical follow-up questions such as “Can you tell me what you mean when you say you felt uncomfortable using the service?” or “Can you give me some examples?” to help dig further and shed additional light on the research problem. Depth interviews can be conducted in person or over the phone. The interviewer either takes notes or records the interview.
Focus groups and case studies are often utilized for exploratory research as well. A focus group is a group of potential buyers who are brought together to discuss a marketing research topic with one another. A moderator is used to focus the discussion, the sessions are recorded, and the main points of consensus are later summarized by the market researcher. Textbook publishers often gather groups of professors at educational conferences to participate in focus groups. However, focus groups can also be conducted on the telephone, in online chat rooms, or both, using meeting software like WebEx. The basic steps of conducting a focus group are outlined below.
The Basic Steps of Conducting a Focus Group
- Establish the objectives of the focus group. What is its purpose?
- Identify the people who will participate in the focus group. What makes them qualified to participate? How many of them will you need and what they will be paid?
- Obtain contact information for the participants and send out invitations (usually e-mails are most efficient).
- Develop a list of questions.
- Choose a facilitator.
- Choose a location in which to hold the focus group and the method by which it will be recorded.
- Conduct the focus group. If the focus group is not conducted electronically, include name tags for the participants, pens and notepads, any materials the participants need to see, and refreshments. Record participants’ responses.
- Summarize the notes from the focus group and write a report for management.
A case study looks at how another company solved the problem that’s being researched. Sometimes multiple cases, or companies, are used in a study. Case studies nonetheless have a mixed reputation. Some researchers believe it’s hard to generalize, or apply, the results of a case study to other companies. Nonetheless, collecting information about companies that encountered the same problems your firm is facing can give you a certain amount of insight about what direction you should take. In fact, one way to begin a research project is to carefully study a successful product or service.
Two other types of qualitative data used for exploratory research are ethnographies and projective techniques. In an ethnography , researchers interview, observe, and often videotape people while they work, live, shop, and play. The Walt Disney Company has recently begun using ethnographers to uncover the likes and dislikes of boys aged six to fourteen, a financially attractive market segment for Disney, but one in which the company has been losing market share. The ethnographers visit the homes of boys, observe the things they have in their rooms to get a sense of their hobbies, and accompany them and their mothers when they shop to see where they go, what the boys are interested in, and what they ultimately buy. (The children get seventy-five dollars out of the deal, incidentally.) (Barnes, 2009)
Projective techniques are used to reveal information research respondents might not reveal by being asked directly. Asking a person to complete sentences such as the following is one technique:
People who buy Coach handbags __________.
(Will he or she reply with “are cool,” “are affluent,” or “are pretentious,” for example?)
KFC’s grilled chicken is ______.
Or the person might be asked to finish a story that presents a certain scenario. Word associations are also used to discern people’s underlying attitudes toward goods and services. Using a word-association technique, a market researcher asks a person to say or write the first word that comes to his or her mind in response to another word. If the initial word is “fast food,” what word does the person associate it with or respond with? Is it “McDonald’s”? If many people reply that way, and you’re conducting research for Burger King, that could indicate Burger King has a problem. However, if the research is being conducted for Wendy’s, which recently began running an advertising campaign to the effect that Wendy’s offerings are “better than fast food,” it could indicate that the campaign is working.
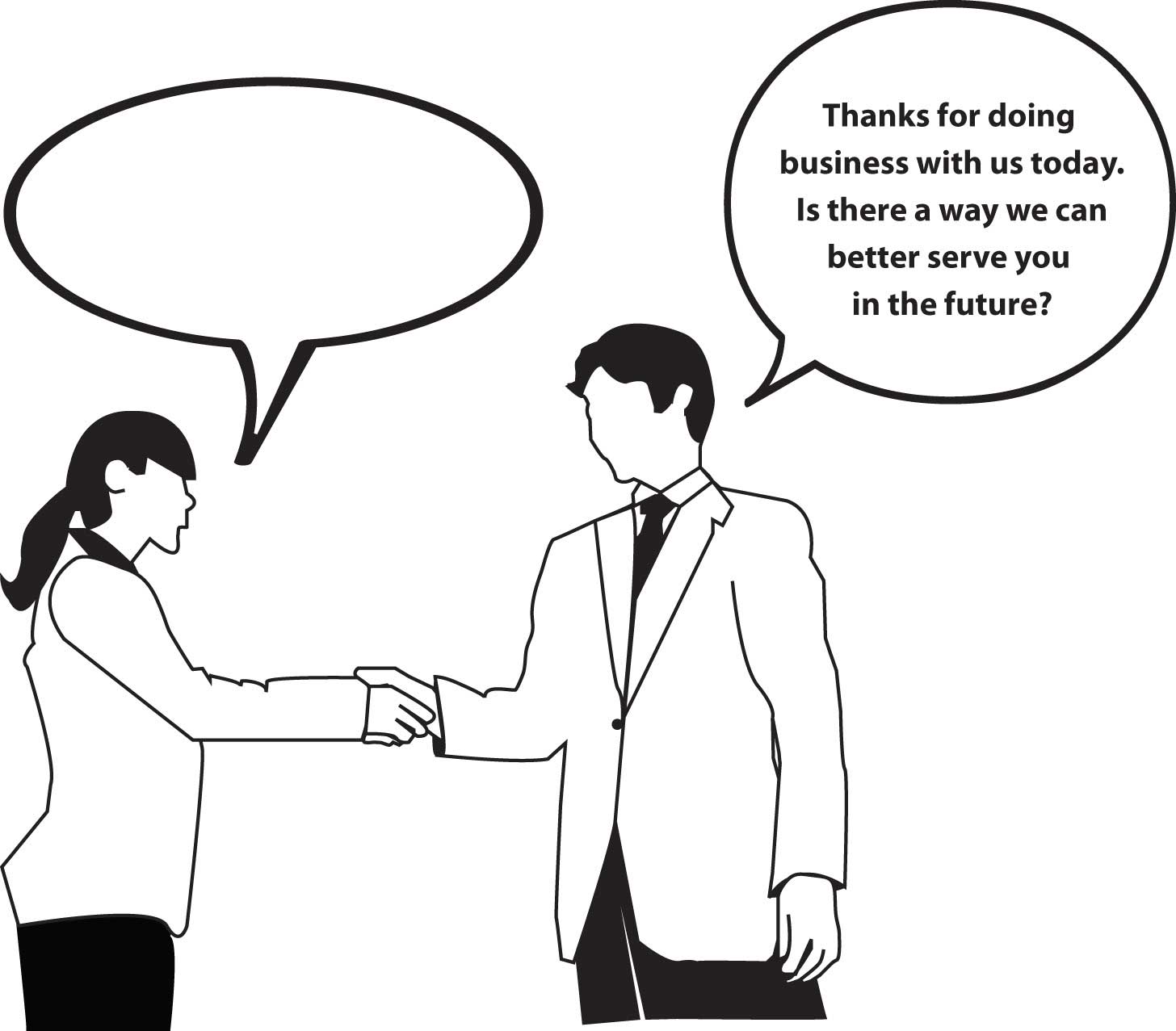
Completing cartoons is yet another type of projective technique. It’s similar to finishing a sentence or story, only with the pictures. People are asked to look at a cartoon such as the one shown in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . One of the characters in the picture will have made a statement, and the person is asked to fill in the empty cartoon “bubble” with how they think the second character will respond.
Figure 10.8 Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique

In some cases, your research might end with exploratory research. Perhaps you have discovered your organization lacks the resources needed to produce the product. In other cases, you might decide you need more in-depth, quantitative research such as descriptive research or causal research, which are discussed next. Most marketing research professionals advise using both types of research, if it’s feasible. On the one hand, the qualitative-type research used in exploratory research is often considered too “lightweight.” Remember earlier in the chapter when we discussed telephone answering machines and the hit TV sitcom Seinfeld ? Both product ideas were initially rejected by focus groups. On the other hand, relying solely on quantitative information often results in market research that lacks ideas.
The Stone Wheel—What One Focus Group Said
Watch the video to see a funny spoof on the usefulness—or lack of usefulness—of focus groups.
Descriptive Research
Anything that can be observed and counted falls into the category of descriptive research design. A study using a descriptive research design involves gathering hard numbers, often via surveys, to describe or measure a phenomenon so as to answer the questions of who , what , where , when , and how . “On a scale of 1–5, how satisfied were you with your service?” is a question that illustrates the information a descriptive research design is supposed to capture.
Physiological measurements also fall into the category of descriptive design. Physiological measurements measure people’s involuntary physical responses to marketing stimuli, such as an advertisement. Elsewhere, we explained that researchers have gone so far as to scan the brains of consumers to see what they really think about products versus what they say about them. Eye tracking is another cutting-edge type of physiological measurement. It involves recording the movements of a person’s eyes when they look at some sort of stimulus, such as a banner ad or a Web page. The Walt Disney Company has a research facility in Austin, Texas, that it uses to take physical measurements of viewers when they see Disney programs and advertisements. The facility measures three types of responses: people’s heart rates, skin changes, and eye movements (eye tracking) (Spangler, 2009).
Figure 10.9
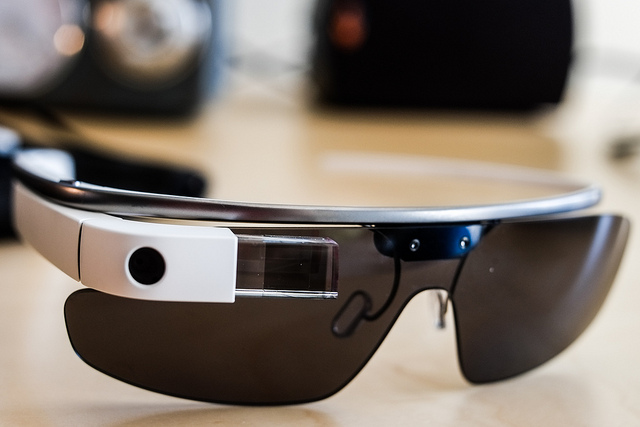

A woman shows off her headgear for an eye-tracking study. The gear’s not exactly a fashion statement but . . .
lawrencegs – Google Glass – CC BY 2.0.
A strictly descriptive research design instrument—a survey, for example—can tell you how satisfied your customers are. It can’t, however, tell you why. Nor can an eye-tracking study tell you why people’s eyes tend to dwell on certain types of banner ads—only that they do. To answer “why” questions an exploratory research design or causal research design is needed (Wagner, 2007).
Causal Research
Causal research design examines cause-and-effect relationships. Using a causal research design allows researchers to answer “what if” types of questions. In other words, if a firm changes X (say, a product’s price, design, placement, or advertising), what will happen to Y (say, sales or customer loyalty)? To conduct causal research, the researcher designs an experiment that “controls,” or holds constant, all of a product’s marketing elements except one (or using advanced techniques of research, a few elements can be studied at the same time). The one variable is changed, and the effect is then measured. Sometimes the experiments are conducted in a laboratory using a simulated setting designed to replicate the conditions buyers would experience. Or the experiments may be conducted in a virtual computer setting.
You might think setting up an experiment in a virtual world such as the online game Second Life would be a viable way to conduct controlled marketing research. Some companies have tried to use Second Life for this purpose, but the results have been somewhat mixed as to whether or not it is a good medium for marketing research. The German marketing research firm Komjuniti was one of the first “real-world” companies to set up an “island” in Second Life upon which it could conduct marketing research. However, with so many other attractive fantasy islands in which to play, the company found it difficult to get Second Life residents, or players, to voluntarily visit the island and stay long enough so meaningful research could be conducted. (Plus, the “residents,” or players, in Second Life have been known to protest corporations invading their world. When the German firm Komjuniti created an island in Second Life to conduct marketing research, the residents showed up waving signs and threatening to boycott the island.) (Wagner, 2007)
Why is being able to control the setting so important? Let’s say you are an American flag manufacturer and you are working with Walmart to conduct an experiment to see where in its stores American flags should be placed so as to increase their sales. Then the terrorist attacks of 9/11 occur. In the days afterward, sales skyrocketed—people bought flags no matter where they were displayed. Obviously, the terrorist attacks in the United States would have skewed the experiment’s data.
An experiment conducted in a natural setting such as a store is referred to as a field experiment . Companies sometimes do field experiments either because it is more convenient or because they want to see if buyers will behave the same way in the “real world” as in a laboratory or on a computer. The place the experiment is conducted or the demographic group of people the experiment is administered to is considered the test market . Before a large company rolls out a product to the entire marketplace, it will often place the offering in a test market to see how well it will be received. For example, to compete with MillerCoors’ sixty-four-calorie beer MGD 64, Anheuser-Busch recently began testing its Select 55 beer in certain cities around the country (McWilliams, 2009).
Figure 10.10
Select 55 beer: Coming soon to a test market near you? (If you’re on a diet, you have to hope so!)
Martine – Le champagne – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Many companies use experiments to test all of their marketing communications. For example, the online discount retailer O.co (formerly called Overstock.com) carefully tests all of its marketing offers and tracks the results of each one. One study the company conducted combined twenty-six different variables related to offers e-mailed to several thousand customers. The study resulted in a decision to send a group of e-mails to different segments. The company then tracked the results of the sales generated to see if they were in line with the earlier experiment it had conducted that led it to make the offer.
Step 3: Design the Data-Collection Forms
If the behavior of buyers is being formally observed, and a number of different researchers are conducting observations, the data obviously need to be recorded on a standardized data-collection form that’s either paper or electronic. Otherwise, the data collected will not be comparable. The items on the form could include a shopper’s sex; his or her approximate age; whether the person seemed hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried; and whether or not he or she read the label on products, used coupons, and so forth.
The same is true when it comes to surveying people with questionnaires. Surveying people is one of the most commonly used techniques to collect quantitative data. Surveys are popular because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, the questionnaire for the survey needs to be carefully designed.
Questionnaire Design
Most questionnaires follow a similar format: They begin with an introduction describing what the study is for, followed by instructions for completing the questionnaire and, if necessary, returning it to the market researcher. The first few questions that appear on the questionnaire are usually basic, warm-up type of questions the respondent can readily answer, such as the respondent’s age, level of education, place of residence, and so forth. The warm-up questions are then followed by a logical progression of more detailed, in-depth questions that get to the heart of the question being researched. Lastly, the questionnaire wraps up with a statement that thanks the respondent for participating in the survey and information and explains when and how they will be paid for participating. To see some examples of questionnaires and how they are laid out, click on the following link: http://cas.uah.edu/wrenb/mkt343/Project/Sample%20Questionnaires.htm .
How the questions themselves are worded is extremely important. It’s human nature for respondents to want to provide the “correct” answers to the person administering the survey, so as to seem agreeable. Therefore, there is always a hazard that people will try to tell you what you want to hear on a survey. Consequently, care needs to be taken that the survey questions are written in an unbiased, neutral way. In other words, they shouldn’t lead a person taking the questionnaire to answer a question one way or another by virtue of the way you have worded it. The following is an example of a leading question.
Don’t you agree that teachers should be paid more ?
The questions also need to be clear and unambiguous. Consider the following question:
Which brand of toothpaste do you use ?
The question sounds clear enough, but is it really? What if the respondent recently switched brands? What if she uses Crest at home, but while away from home or traveling, she uses Colgate’s Wisp portable toothpaste-and-brush product? How will the respondent answer the question? Rewording the question as follows so it’s more specific will help make the question clearer:
Which brand of toothpaste have you used at home in the past six months? If you have used more than one brand, please list each of them 1 .
Sensitive questions have to be asked carefully. For example, asking a respondent, “Do you consider yourself a light, moderate, or heavy drinker?” can be tricky. Few people want to admit to being heavy drinkers. You can “soften” the question by including a range of answers, as the following example shows:
How many alcoholic beverages do you consume in a week ?
- __0–5 alcoholic beverages
- __5–10 alcoholic beverages
- __10–15 alcoholic beverages
Many people don’t like to answer questions about their income levels. Asking them to specify income ranges rather than divulge their actual incomes can help.
Other research question “don’ts” include using jargon and acronyms that could confuse people. “How often do you IM?” is an example. Also, don’t muddy the waters by asking two questions in the same question, something researchers refer to as a double-barreled question . “Do you think parents should spend more time with their children and/or their teachers?” is an example of a double-barreled question.
Open-ended questions , or questions that ask respondents to elaborate, can be included. However, they are harder to tabulate than closed-ended questions , or questions that limit a respondent’s answers. Multiple-choice and yes-and-no questions are examples of closed-ended questions.
Testing the Questionnaire
You have probably heard the phrase “garbage in, garbage out.” If the questions are bad, the information gathered will be bad, too. One way to make sure you don’t end up with garbage is to test the questionnaire before sending it out to find out if there are any problems with it. Is there enough space for people to elaborate on open-ended questions? Is the font readable? To test the questionnaire, marketing research professionals first administer it to a number of respondents face to face. This gives the respondents the chance to ask the researcher about questions or instructions that are unclear or don’t make sense to them. The researcher then administers the questionnaire to a small subset of respondents in the actual way the survey is going to be disseminated, whether it’s delivered via phone, in person, by mail, or online.
Getting people to participate and complete questionnaires can be difficult. If the questionnaire is too long or hard to read, many people won’t complete it. So, by all means, eliminate any questions that aren’t necessary. Of course, including some sort of monetary incentive for completing the survey can increase the number of completed questionnaires a market researcher will receive.
Step 4: Specify the Sample
Once you have created your questionnaire or other marketing study, how do you figure out who should participate in it? Obviously, you can’t survey or observe all potential buyers in the marketplace. Instead, you must choose a sample. A sample is a subset of potential buyers that are representative of your entire target market, or population being studied. Sometimes market researchers refer to the population as the universe to reflect the fact that it includes the entire target market, whether it consists of a million people, a hundred thousand, a few hundred, or a dozen. “All unmarried people over the age of eighteen who purchased Dirt Devil steam cleaners in the United States during 2011” is an example of a population that has been defined.
Obviously, the population has to be defined correctly. Otherwise, you will be studying the wrong group of people. Not defining the population correctly can result in flawed research, or sampling error. A sampling error is any type of marketing research mistake that results because a sample was utilized. One criticism of Internet surveys is that the people who take these surveys don’t really represent the overall population. On average, Internet survey takers tend to be more educated and tech savvy. Consequently, if they solely constitute your population, even if you screen them for certain criteria, the data you collect could end up being skewed.
The next step is to put together the sampling frame , which is the list from which the sample is drawn. The sampling frame can be put together using a directory, customer list, or membership roster (Wrenn et. al., 2007). Keep in mind that the sampling frame won’t perfectly match the population. Some people will be included on the list who shouldn’t be. Other people who should be included will be inadvertently omitted. It’s no different than if you were to conduct a survey of, say, 25 percent of your friends, using friends’ names you have in your cell phone. Most of your friends’ names are likely to be programmed into your phone, but not all of them. As a result, a certain degree of sampling error always occurs.
There are two main categories of samples in terms of how they are drawn: probability samples and nonprobability samples. A probability sample is one in which each would-be participant has a known and equal chance of being selected. The chance is known because the total number of people in the sampling frame is known. For example, if every other person from the sampling frame were chosen, each person would have a 50 percent chance of being selected.
A nonprobability sample is any type of sample that’s not drawn in a systematic way. So the chances of each would-be participant being selected can’t be known. A convenience sample is one type of nonprobability sample. It is a sample a researcher draws because it’s readily available and convenient to do so. Surveying people on the street as they pass by is an example of a convenience sample. The question is, are these people representative of the target market?
For example, suppose a grocery store needed to quickly conduct some research on shoppers to get ready for an upcoming promotion. Now suppose that the researcher assigned to the project showed up between the hours of 10 a.m. and 12 p.m. on a weekday and surveyed as many shoppers as possible. The problem is that the shoppers wouldn’t be representative of the store’s entire target market. What about commuters who stop at the store before and after work? Their views wouldn’t be represented. Neither would people who work the night shift or shop at odd hours. As a result, there would be a lot of room for sampling error in this study. For this reason, studies that use nonprobability samples aren’t considered as accurate as studies that use probability samples. Nonprobability samples are more often used in exploratory research.
Lastly, the size of the sample has an effect on the amount of sampling error. Larger samples generally produce more accurate results. The larger your sample is, the more data you will have, which will give you a more complete picture of what you’re studying. However, the more people surveyed or studied, the more costly the research becomes.
Statistics can be used to determine a sample’s optimal size. If you take a marketing research or statistics class, you will learn more about how to determine the optimal size.
Of course, if you hire a marketing research company, much of this work will be taken care of for you. Many marketing research companies, like ResearchNow, maintain panels of prescreened people they draw upon for samples. In addition, the marketing research firm will be responsible for collecting the data or contracting with a company that specializes in data collection. Data collection is discussed next.
Step 5: Collect the Data
As we have explained, primary marketing research data can be gathered in a number of ways. Surveys, taking physical measurements, and observing people are just three of the ways we discussed. If you’re observing customers as part of gathering the data, keep in mind that if shoppers are aware of the fact, it can have an effect on their behavior. For example, if a customer shopping for feminine hygiene products in a supermarket aisle realizes she is being watched, she could become embarrassed and leave the aisle, which would adversely affect your data. To get around problems such as these, some companies set up cameras or two-way mirrors to observe customers. Organizations also hire mystery shoppers to work around the problem. A mystery shopper is someone who is paid to shop at a firm’s establishment or one of its competitors to observe the level of service, cleanliness of the facility, and so forth, and report his or her findings to the firm.
Make Extra Money as a Mystery Shopper
Watch the YouTube video to get an idea of how mystery shopping works.
Survey data can be collected in many different ways and combinations of ways. The following are the basic methods used:
- Face-to-face (can be computer aided)
- Telephone (can be computer aided or completely automated)
- Mail and hand delivery
- E-mail and the Web
A face-to-face survey is, of course, administered by a person. The surveys are conducted in public places such as in shopping malls, on the street, or in people’s homes if they have agreed to it. In years past, it was common for researchers in the United States to knock on people’s doors to gather survey data. However, randomly collected door-to-door interviews are less common today, partly because people are afraid of crime and are reluctant to give information to strangers (McDaniel & Gates, 1998).
Nonetheless, “beating the streets” is still a legitimate way questionnaire data is collected. When the U.S. Census Bureau collects data on the nation’s population, it hand delivers questionnaires to rural households that do not have street-name and house-number addresses. And Census Bureau workers personally survey the homeless to collect information about their numbers. Face-to-face surveys are also commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers.
A plus of face-to-face surveys is that they allow researchers to ask lengthier, more complex questions because the people being surveyed can see and read the questionnaires. The same is true when a computer is utilized. For example, the researcher might ask the respondent to look at a list of ten retail stores and rank the stores from best to worst. The same question wouldn’t work so well over the telephone because the person couldn’t see the list. The question would have to be rewritten. Another drawback with telephone surveys is that even though federal and state “do not call” laws generally don’t prohibit companies from gathering survey information over the phone, people often screen such calls using answering machines and caller ID.
Probably the biggest drawback of both surveys conducted face-to-face and administered over the phone by a person is that they are labor intensive and therefore costly. Mailing out questionnaires is costly, too, and the response rates can be rather low. Think about why that might be so: if you receive a questionnaire in the mail, it is easy to throw it in the trash; it’s harder to tell a market researcher who approaches you on the street that you don’t want to be interviewed.
By contrast, gathering survey data collected by a computer, either over the telephone or on the Internet, can be very cost-effective and in some cases free. SurveyMonkey and Zoomerang are two Web sites that will allow you to create online questionnaires, e-mail them to up to one hundred people for free, and view the responses in real time as they come in. For larger surveys, you have to pay a subscription price of a few hundred dollars. But that still can be extremely cost-effective. The two Web sites also have a host of other features such as online-survey templates you can use to create your questionnaire, a way to set up automatic reminders sent to people who haven’t yet completed their surveys, and tools you can use to create graphics to put in your final research report. To see how easy it is to put together a survey in SurveyMonkey, click on the following link: http://help.surveymonkey.com/app/tutorials/detail/a_id/423 .
Like a face-to-face survey, an Internet survey can enable you to show buyers different visuals such as ads, pictures, and videos of products and their packaging. Web surveys are also fast, which is a major plus. Whereas face-to-face and mailed surveys often take weeks to collect, you can conduct a Web survey in a matter of days or even hours. And, of course, because the information is electronically gathered it can be automatically tabulated. You can also potentially reach a broader geographic group than you could if you had to personally interview people. The Zoomerang Web site allows you to create surveys in forty different languages.
Another plus for Web and computer surveys (and electronic phone surveys) is that there is less room for human error because the surveys are administered electronically. For instance, there’s no risk that the interviewer will ask a question wrong or use a tone of voice that could mislead the respondents. Respondents are also likely to feel more comfortable inputting the information into a computer if a question is sensitive than they would divulging the information to another person face-to-face or over the phone. Given all of these advantages, it’s not surprising that the Internet is quickly becoming the top way to collect primary data. However, like mail surveys, surveys sent to people over the Internet are easy to ignore.
Lastly, before the data collection process begins, the surveyors and observers need to be trained to look for the same things, ask questions the same way, and so forth. If they are using rankings or rating scales, they need to be “on the same page,” so to speak, as to what constitutes a high ranking or a low ranking. As an analogy, you have probably had some teachers grade your college papers harder than others. The goal of training is to avoid a wide disparity between how different observers and interviewers record the data.
Figure 10.11

Training people so they know what constitutes different ratings when they are collecting data will improve the quality of the information gathered in a marketing research study.
Ricardo Rodriquez – Satisfaction survey – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
For example, if an observation form asks the observers to describe whether a shopper’s behavior is hurried, moderately hurried, or unhurried, they should be given an idea of what defines each rating. Does it depend on how much time the person spends in the store or in the individual aisles? How fast they walk? In other words, the criteria and ratings need to be spelled out.
Collecting International Marketing Research Data
Gathering marketing research data in foreign countries poses special challenges. However, that doesn’t stop firms from doing so. Marketing research companies are located all across the globe, in fact. Eight of the ten largest marketing research companies in the world are headquartered in the United States. However, five of these eight firms earn more of their revenues abroad than they do in the United States. There’s a reason for this: many U.S. markets were saturated, or tapped out, long ago in terms of the amount that they can grow. Coke is an example. As you learned earlier in the book, most of the Coca-Cola Company’s revenues are earned in markets abroad. To be sure, the United States is still a huge market when it comes to the revenues marketing research firms generate by conducting research in the country: in terms of their spending, American consumers fuel the world’s economic engine. Still, emerging countries with growing middle classes, such as China, India, and Brazil, are hot new markets companies want to tap.
What kind of challenges do firms face when trying to conduct marketing research abroad? As we explained, face-to-face surveys are commonly used in third world countries to collect information from people who cannot read or lack phones and computers. However, face-to-face surveys are also common in Europe, despite the fact that phones and computers are readily available. In-home surveys are also common in parts of Europe. By contrast, in some countries, including many Asian countries, it’s considered taboo or rude to try to gather information from strangers either face-to-face or over the phone. In many Muslim countries, women are forbidden to talk to strangers.
And how do you figure out whom to research in foreign countries? That in itself is a problem. In the United States, researchers often ask if they can talk to the heads of households to conduct marketing research. But in countries in which domestic servants or employees are common, the heads of households aren’t necessarily the principal shoppers; their domestic employees are (Malhotra).
Translating surveys is also an issue. Have you ever watched the TV comedians Jay Leno and David Letterman make fun of the English translations found on ethnic menus and products? Research tools such as surveys can suffer from the same problem. Hiring someone who is bilingual to translate a survey into another language can be a disaster if the person isn’t a native speaker of the language to which the survey is being translated.
One way companies try to deal with translation problems is by using back translation. When back translation is used, a native speaker translates the survey into the foreign language and then translates it back again to the original language to determine if there were gaps in meaning—that is, if anything was lost in translation. And it’s not just the language that’s an issue. If the research involves any visual images, they, too, could be a point of confusion. Certain colors, shapes, and symbols can have negative connotations in other countries. For example, the color white represents purity in many Western cultures, but in China, it is the color of death and mourning (Zouhali-Worrall, 2008). Also, look back at the cartoon-completion exercise in Figure 10.8 “Example of a Cartoon-Completion Projective Technique” . What would women in Muslim countries who aren’t allowed to converse with male sellers think of it? Chances are, the cartoon wouldn’t provide you with the information you’re seeking if Muslim women in some countries were asked to complete it.
One way marketing research companies are dealing with the complexities of global research is by merging with or acquiring marketing research companies abroad. The Nielsen Company is the largest marketing research company in the world. The firm operates in more than a hundred countries and employs more than forty thousand people. Many of its expansions have been the result of acquisitions and mergers.
Step 6: Analyze the Data
Step 6 involves analyzing the data to ensure it’s as accurate as possible. If the research is collected by hand using a pen and pencil, it’s entered into a computer. Or respondents might have already entered the information directly into a computer. For example, when Toyota goes to an event such as a car show, the automaker’s marketing personnel ask would-be buyers to complete questionnaires directly on computers. Companies are also beginning to experiment with software that can be used to collect data using mobile phones.
Once all the data is collected, the researchers begin the data cleaning , which is the process of removing data that have accidentally been duplicated (entered twice into the computer) or correcting data that have obviously been recorded wrong. A program such as Microsoft Excel or a statistical program such as Predictive Analytics Software (PASW, which was formerly known as SPSS) is then used to tabulate, or calculate, the basic results of the research, such as the total number of participants and how collectively they answered various questions. The programs can also be used to calculate averages, such as the average age of respondents, their average satisfaction, and so forth. The same can done for percentages, and other values you learned about, or will learn about, in a statistics course, such as the standard deviation, mean, and median for each question.
The information generated by the programs can be used to draw conclusions, such as what all customers might like or not like about an offering based on what the sample group liked or did not like. The information can also be used to spot differences among groups of people. For example, the research might show that people in one area of the country like the product better than people in another area. Trends to predict what might happen in the future can also be spotted.
If there are any open-ended questions respondents have elaborated upon—for example, “Explain why you like the current brand you use better than any other brand”—the answers to each are pasted together, one on top of another, so researchers can compare and summarize the information. As we have explained, qualitative information such as this can give you a fuller picture of the results of the research.
Part of analyzing the data is to see if it seems sound. Does the way in which the research was conducted seem sound? Was the sample size large enough? Are the conclusions that become apparent from it reasonable?
The two most commonly used criteria used to test the soundness of a study are (1) validity and (2) reliability. A study is valid if it actually tested what it was designed to test. For example, did the experiment you ran in Second Life test what it was designed to test? Did it reflect what could really happen in the real world? If not, the research isn’t valid. If you were to repeat the study, and get the same results (or nearly the same results), the research is said to be reliable . If you get a drastically different result if you repeat the study, it’s not reliable. The data collected, or at least some it, can also be compared to, or reconciled with, similar data from other sources either gathered by your firm or by another organization to see if the information seems on target.
Stage 7: Write the Research Report and Present Its Findings
If you end up becoming a marketing professional and conducting a research study after you graduate, hopefully you will do a great job putting the study together. You will have defined the problem correctly, chosen the right sample, collected the data accurately, analyzed it, and your findings will be sound. At that point, you will be required to write the research report and perhaps present it to an audience of decision makers. You will do so via a written report and, in some cases, a slide or PowerPoint presentation based on your written report.
The six basic elements of a research report are as follows.
- Title Page . The title page explains what the report is about, when it was conducted and by whom, and who requested it.
- Table of Contents . The table of contents outlines the major parts of the report, as well as any graphs and charts, and the page numbers on which they can be found.
- Executive Summary . The executive summary summarizes all the details in the report in a very quick way. Many people who receive the report—both executives and nonexecutives—won’t have time to read the entire report. Instead, they will rely on the executive summary to quickly get an idea of the study’s results and what to do about those results.
Methodology and Limitations . The methodology section of the report explains the technical details of how the research was designed and conducted. The section explains, for example, how the data was collected and by whom, the size of the sample, how it was chosen, and whom or what it consisted of (e.g., the number of women versus men or children versus adults). It also includes information about the statistical techniques used to analyze the data.
Every study has errors—sampling errors, interviewer errors, and so forth. The methodology section should explain these details, so decision makers can consider their overall impact. The margin of error is the overall tendency of the study to be off kilter—that is, how far it could have gone wrong in either direction. Remember how newscasters present the presidential polls before an election? They always say, “This candidate is ahead 48 to 44 percent, plus or minus 2 percent.” That “plus or minus” is the margin of error. The larger the margin of error is, the less likely the results of the study are accurate. The margin of error needs to be included in the methodology section.
- Findings . The findings section is a longer, fleshed-out version of the executive summary that goes into more detail about the statistics uncovered by the research that bolster the study’s findings. If you have related research or secondary data on hand that back up the findings, it can be included to help show the study did what it was designed to do.
- Recommendations . The recommendations section should outline the course of action you think should be taken based on the findings of the research and the purpose of the project. For example, if you conducted a global market research study to identify new locations for stores, make a recommendation for the locations (Mersdorf, 2009).
As we have said, these are the basic sections of a marketing research report. However, additional sections can be added as needed. For example, you might need to add a section on the competition and each firm’s market share. If you’re trying to decide on different supply chain options, you will need to include a section on that topic.
As you write the research report, keep your audience in mind. Don’t use technical jargon decision makers and other people reading the report won’t understand. If technical terms must be used, explain them. Also, proofread the document to ferret out any grammatical errors and typos, and ask a couple of other people to proofread behind you to catch any mistakes you might have missed. If your research report is riddled with errors, its credibility will be undermined, even if the findings and recommendations you make are extremely accurate.
Many research reports are presented via PowerPoint. If you’re asked to create a slideshow presentation from the report, don’t try to include every detail in the report on the slides. The information will be too long and tedious for people attending the presentation to read through. And if they do go to the trouble of reading all the information, they probably won’t be listening to the speaker who is making the presentation.
Instead of including all the information from the study in the slides, boil each section of the report down to key points and add some “talking points” only the presenter will see. After or during the presentation, you can give the attendees the longer, paper version of the report so they can read the details at a convenient time, if they choose to.
Key Takeaway
Step 1 in the marketing research process is to define the problem. Businesses take a look at what they believe are symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes so as to precisely define the problem. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective, or goal, the research is supposed to accomplish. Step 2 in the process is to design the research. The research design is the “plan of attack.” It outlines what data you are going to gather, from whom, how, and when, and how you’re going to analyze it once it has been obtained. Step 3 is to design the data-collection forms, which need to be standardized so the information gathered on each is comparable. Surveys are a popular way to gather data because they can be easily administered to large numbers of people fairly quickly. However, to produce the best results, survey questionnaires need to be carefully designed and pretested before they are used. Step 4 is drawing the sample, or a subset of potential buyers who are representative of your entire target market. If the sample is not correctly selected, the research will be flawed. Step 5 is to actually collect the data, whether it’s collected by a person face-to-face, over the phone, or with the help of computers or the Internet. The data-collection process is often different in foreign countries. Step 6 is to analyze the data collected for any obvious errors, tabulate the data, and then draw conclusions from it based on the results. The last step in the process, Step 7, is writing the research report and presenting the findings to decision makers.
Review Questions
- Explain why it’s important to carefully define the problem or opportunity a marketing research study is designed to investigate.
- Describe the different types of problems that can occur when marketing research professionals develop questions for surveys.
- How does a probability sample differ from a nonprobability sample?
- What makes a marketing research study valid? What makes a marketing research study reliable?
- What sections should be included in a marketing research report? What is each section designed to do?
1 “Questionnaire Design,” QuickMBA , http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/research/qdesign (accessed December 14, 2009).
Barnes, B., “Disney Expert Uses Science to Draw Boy Viewers,” New York Times , April 15, 2009, http://www.nytimes.com/2009/04/14/arts/television/14boys.html?pagewanted=1&_r=1 (accessed December 14, 2009).
Burns A. and Ronald Bush, Marketing Research , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010), 85.
Malhotra, N., Marketing Research: An Applied Approach , 6th ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall), 764.
McDaniel, C. D. and Roger H. Gates, Marketing Research Essentials , 2nd ed. (Cincinnati: South-Western College Publishing, 1998), 61.
McWilliams, J., “A-B Puts Super-Low-Calorie Beer in Ring with Miller,” St. Louis Post-Dispatch , August 16, 2009, http://www.stltoday.com/business/next-matchup-light-weights-a-b-puts-super-low-calorie/article_47511bfe-18ca-5979-bdb9-0526c97d4edf.html (accessed April 13, 2012).
Mersdorf, S., “How to Organize Your Next Survey Report,” Cvent , August 24, 2009, http://survey.cvent.com/blog/cvent-survey/0/0/how-to-organize-your-next-survey-report (accessed December 14, 2009).
Rappeport A. and David Gelles, “Facebook to Form Alliance with Nielsen,” Financial Times , September 23, 2009, 16.
Spangler, T., “Disney Lab Tracks Feelings,” Multichannel News 30, no. 30 (August 3, 2009): 26.
Wagner, J., “Marketing in Second Life Doesn’t Work…Here Is Why!” GigaOM , April 4, 2007, http://gigaom.com/2007/04/04/3-reasons-why-marketing-in-second-life-doesnt-work (accessed December 14, 2009).
Wrenn, B., Robert E. Stevens, and David L. Loudon, Marketing Research: Text and Cases , 2nd ed. (Binghamton, NY: Haworth Press, 2007), 180.
Zouhali-Worrall, M., “Found in Translation: Avoiding Multilingual Gaffes,” CNNMoney.com , July 14, 2008, http://money.cnn.com/2008/07/07/smallbusiness/language_translation.fsb/index.htm (accessed December 14, 2009).
Principles of Marketing Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Marketing Management » Marketing Research – Definition, Importance and Process
Marketing Research – Definition, Importance and Process
Definition of marketing research.
Marketing research is a key to the evolution of successful marketing strategies and programmes. It is an important tool to study buyer behavior, changes in consumer lifestyles and consumption patterns, brand loyalty and forecast market changes. Research is also used to study competition and analyze the competitor product’s positioning and how to gain competitive advantage . Recently, marketing research is being used to help create and enhance brand equity .
According to Philip Kotler , Marketing research is systematic problem analysis, model building and fact finding for the purposes of important decision making and control in the marketing of goods and services.
The important decision making related to market strategy and other tasks related to marketing depends on findings or marketing research. Marketing research process reduces the chances of errors, miss conceptions and uncertainty from decision making process . It is therefore very important to conduct marketing research to identify any changes in market environment, and understand customers and market. It means that this is the process of strategically importance.
Importance of Marketing Research
Marketing research is a systematic collection and analysis of data about market and the important quality of market. Therefore, Market research is an extremely part of any business that wants to offer products or service that are focused and well targeted. It also affects the profit of a business and makes the best return on marketing investment. For example, a product’s price elasticity research can help you to find out the true or correct information that impact of an increased price on the sales and the profits of a product. This special importance give on profitability also helps the company’s focus to shift from widen the sales to increase the profits of a company and helps the company to survive longer.
Research is about finding and gathers the information to learn about something that is not fully known. Marketing research is allows company to discover the facts whether customers or consumers is satisfy with it. And it also provides crucial information that may be affecting the business. In addition, Market research will also minimize the risk as it can help to shape a new product or service, and identifying what is needed and ensure that the development of a product is high level focused towards needs and wants.
Furthermore, market research also helps to identify opportunities. For example, if there is a plan to operate a new service and would like to have enough information or experience of the people’s attitudes then the market research can give not only evaluating new idea but also identify the areas where a marketing needs to develop and improve. To survive in competition of markets is not easily especially markets has been throughout the world. Marketing research helps to find out the true or correct information and understand the competitor such as their identity, the marketing network, what is customer focus on and the range of level operations. Other than that, with market research can also helps to understand the consumer needs that have not been met. Target markets is also one of the important points that marketers should take notes with, from marketing research it helps to decide the target markets and provide customer information in terms of their location, age, gender and buying behavior.
Besides that, marketing research helps to create benchmarks and prepare the plans carefully and take necessary measures and give opinion of the amount, value or quality for its performance. Moreover, marketing research is system that has been give devise more effective strategies. The most useful of marketing research is help to identify the potential problems and give ample time to discover the facts and to calculate an effective solution.
Marketing Research Process
There are seven steps in marketing research process: define the research problem, determine the research design, choose the method for collecting primary data, design the sample, collect the data, analyze and interpret the data, prepare the research report. Though those steps, marketers will make conversant decisions or reduce the risk of their decisions.

1. PROBLEM DEFINITION
This is the starting point in the marketing research exercise. Invariably, in any enterprise, there are several marketing issues that may require examination, and invariably every decision maker perceives his information need as being the most important. In problem definition it is important to be specific, avoiding ambiguities and generalities. Care should also be taken, not to define problems in too narrow a field as that may distract the researcher’s perspective. This may even affect creativity in the research.
2. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
Once the problem is defined, the next logical step is to state what the researcher wants to achieve. This statement is called objectives. To be meaningful and help focus the researcher’s attention, these objectives should be specific, attainable & measurable. The purpose of these objectives is to act as a guide to the researcher and help him in maintaining a focus all through the research.
3. RESEARCH DESIGN
The third stage in the marketing research process is deciding on the research design. There are three types of research designs, namely:
- Exploratory: This kind of research is conducted when the researcher does not know how & why a certain phenomenon occurs, for example, how does the consumer evaluate the quality of a bank or a hotel or an airline? Since the prime goal of an exploratory research is to know the unknown, this research is unstructured. Focus groups, interviewing key customer groups, experts and even search for printed or published information are some common techniques.
- Descriptive: This research is carried out to describe a phenomenon or market characteristics. For example, a study to understand buyer behavior & describe characteristics of the target market is a descriptive research. Continuing the above example of service quality, a research done on how consumers evaluate the quality of competing service institutions can be considered as an example of descriptive research.
- Causative: This kind of research is done to establish a cause and effect relationship, for example the influence of income & lifestyle on purchase decision. Here the researcher may like to see the effect of rising income & changing lifestyle on consumption of select products.
4. SOURCES OF DATA
Once the research design has been decided upon, the next stage is that of selecting the sources of data. Essentially there are two sources of data or information- secondary & primary
- Secondary data: This refers to the information that has been collected earlier by someone else. Often this includes printed or published reports, news items, industry or trade statistics etc. this also includes internal documents like invoices, sales reports, payment history of customers etc. these are important to the researcher as they provide an insight to the problem. Often the preliminary investigation is restricted to secondary data.
- Primary data: To overcome the limitations of incompatibility, obsolescence and bias, the researcher turns to the primary data. This is also resorted to when the secondary data is incomplete. Primary sources refer to data collected directly from the market place- customers, traders & suppliers often are the major sources. They are often reliable data sources and help in overcoming limitations of secondary data. The problem in primary data is its cost, both In terms of money & time, and often a researcher bias also creeps in.
5. DATA COLLECTION
The researcher is now ready to take the plunge. But still he or she needs to be clear about the following.
Procedure for data collection.
Data can be collected through any or combination of the following techniques.
- Observation: This technique involves observing how a customer behaves in the shopping area, how he or she dresses up & what does the customer say when he or she sees the product.
- Experimentation: This is a technique that involves experimenting new product ideas, advertising copies & campaigns, sales promotion ideas & even pricing & distribution strategies with the target customer group. These experiments can be conducted in an uncontrolled environment or in a controlled & simulated market environment.
Tools for data collection
The researcher has to decide on the appropriate tool for data collection. These tools are:-
- Questionnaire — used for the survey method
- Interview schedule — used mainly for exploratory research
- Association test — primarily used in qualitative research, also called as TAT (Thematic Apperception Test)
6. DATA ANALYSIS
The next stage is that of data analysis .It is important to understand raw data has no usage in marketing research .hence appropriate analytical tools must be used. The most elementary is the arithmetic analysis using percentile and ratios. Statistical analysis like mean, median, mode, percentages, standard deviation and coefficient of correlations should be used wherever applicable
7. REPORT & PRESENTATION
The last stage is that of writing out a report and making a presentation to the Decision —maker. It is important that the report has summary, called the executive summary, giving a bird’s-eye view of the research. This is because most senior managers have little time for going through the entire report in depth. The executive summary can direct the reader’s attention to specific issues by turning to the relevant sections in the report and should not exceed thousand words.
The report should be structured and pages chronologically numbered generally, the structure of a good repot is somewhat like the following:
- Introduction to the problem
- Marketing research finding or survey findings
- Interpretation of research finding
- Policy implications
Related posts:
- Importance of Marketing Research in Marketing Process
- Market Research – Definition, Classification and Process
- International Marketing Research – Definition, Categories and Process
- Marketing Strategy: Definition and Process
- Methods of Marketing Research
- Are Market Research and Marketing Research the Same?
- Relationship Between Marketing Research and Marketing Strategy
- The Importance of Advertising in Marketing Communication
- Introduction to Marketing Research
- Motivation – Definition, Process, Types, Features and Importance
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- 2025 Experience Trends
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO

9 Key stages in your marketing research process
You can conduct your own marketing research. Follow these steps, add your own flair, knowledge and creativity, and you’ll have bespoke research to be proud of.
Marketing research is the term used to cover the concept, development, placement and evolution of your product or service, its growing customer base and its branding – starting with brand awareness , and progressing to (everyone hopes) brand equity . Like any research, it needs a robust process to be credible and useful.
Marketing research uses four essential key factors known as the ‘marketing mix’ , or the Four Ps of Marketing :
- Product (goods or service)
- Price ( how much the customer pays )
- Place (where the product is marketed)
- Promotion (such as advertising and PR)
These four factors need to work in harmony for a product or service to be successful in its marketplace.
The marketing research process – an overview
A typical marketing research process is as follows:
- Identify an issue, discuss alternatives and set out research objectives
- Develop a research program
- Choose a sample
- Gather information
- Gather data
- Organize and analyze information and data
- Present findings
- Make research-based decisions
- Take action based on insights
Step 1: Defining the marketing research problem
Defining a problem is the first step in the research process. In many ways, research starts with a problem facing management. This problem needs to be understood, the cause diagnosed, and solutions developed.
However, most management problems are not always easy to research, so they must first be translated into research problems. Once you approach the problem from a research angle, you can find a solution. For example, “sales are not growing” is a management problem, but translated into a research problem, it becomes “ why are sales not growing?” We can look at the expectations and experiences of several groups : potential customers, first-time buyers, and repeat purchasers. We can question whether the lack of sales is due to:
- Poor expectations that lead to a general lack of desire to buy, or
- Poor performance experience and a lack of desire to repurchase.
This, then, is the difference between a management problem and a research problem. Solving management problems focuses on actions: Do we advertise more? Do we change our advertising message? Do we change an under-performing product configuration? And if so, how?
Defining research problems, on the other hand, focus on the whys and hows, providing the insights you need to solve your management problem.
Step 2: Developing a research program: method of inquiry
The scientific method is the standard for investigation. It provides an opportunity for you to use existing knowledge as a starting point, and proceed impartially.
The scientific method includes the following steps:
- Define a problem
- Develop a hypothesis
- Make predictions based on the hypothesis
- Devise a test of the hypothesis
- Conduct the test
- Analyze the results
This terminology is similar to the stages in the research process. However, there are subtle differences in the way the steps are performed:
- the scientific research method is objective and fact-based, using quantitative research and impartial analysis
- the marketing research process can be subjective, using opinion and qualitative research, as well as personal judgment as you collect and analyze data
Step 3: Developing a research program: research method
As well as selecting a method of inquiry (objective or subjective), you must select a research method . There are two primary methodologies that can be used to answer any research question:
- Experimental research : gives you the advantage of controlling extraneous variables and manipulating one or more variables that influence the process being implemented.
- Non-experimental research : allows observation but not intervention – all you do is observe and report on your findings.
Step 4: Developing a research program: research design
Research design is a plan or framework for conducting marketing research and collecting data. It is defined as the specific methods and procedures you use to get the information you need.
There are three core types of marketing research designs: exploratory, descriptive, and causal . A thorough marketing research process incorporates elements of all of them.
Exploratory marketing research
This is a starting point for research. It’s used to reveal facts and opinions about a particular topic, and gain insight into the main points of an issue. Exploratory research is too much of a blunt instrument to base conclusive business decisions on, but it gives the foundation for more targeted study. You can use secondary research materials such as trade publications, books, journals and magazines and primary research using qualitative metrics, that can include open text surveys, interviews and focus groups.
Descriptive marketing research
This helps define the business problem or issue so that companies can make decisions, take action and monitor progress. Descriptive research is naturally quantitative – it needs to be measured and analyzed statistically , using more targeted surveys and questionnaires. You can use it to capture demographic information , evaluate a product or service for market, and monitor a target audience’s opinion and behaviors. Insights from descriptive research can inform conclusions about the market landscape and the product’s place in it.
Causal marketing research
This is useful to explore the cause and effect relationship between two or more variables. Like descriptive research , it uses quantitative methods, but it doesn’t merely report findings; it uses experiments to predict and test theories about a product or market. For example, researchers may change product packaging design or material, and measure what happens to sales as a result.
Step 5: Choose your sample
Your marketing research project will rarely examine an entire population. It’s more practical to use a sample - a smaller but accurate representation of the greater population. To design your sample, you’ll need to answer these questions:
- Which base population is the sample to be selected from? Once you’ve established who your relevant population is (your research design process will have revealed this), you have a base for your sample. This will allow you to make inferences about a larger population.
- What is the method (process) for sample selection? There are two methods of selecting a sample from a population:
1. Probability sampling : This relies on a random sampling of everyone within the larger population.
2. Non-probability sampling : This is based in part on the investigator’s judgment, and often uses convenience samples, or by other sampling methods that do not rely on probability.
- What is your sample size? This important step involves cost and accuracy decisions. Larger samples generally reduce sampling error and increase accuracy, but also increase costs. Find out your perfect sample size with our calculator .
Step 6: Gather data
Your research design will develop as you select techniques to use. There are many channels for collecting data, and it’s helpful to differentiate it into O-data (Operational) and X-data (Experience):
- O-data is your business’s hard numbers like costs, accounting, and sales. It tells you what has happened, but not why.
- X-data gives you insights into the thoughts and emotions of the people involved: employees, customers, brand advocates.
When you combine O-data with X-data, you’ll be able to build a more complete picture about success and failure - you’ll know why. Maybe you’ve seen a drop in sales (O-data) for a particular product. Maybe customer service was lacking, the product was out of stock, or advertisements weren’t impactful or different enough: X-data will reveal the reason why those sales dropped. So, while differentiating these two data sets is important, when they are combined, and work with each other, the insights become powerful.
With mobile technology, it has become easier than ever to collect data. Survey research has come a long way since market researchers conducted face-to-face, postal, or telephone surveys. You can run research through:
- Social media ( polls and listening )
Another way to collect data is by observation. Observing a customer’s or company’s past or present behavior can predict future purchasing decisions. Data collection techniques for predicting past behavior can include market segmentation , customer journey mapping and brand tracking .
Regardless of how you collect data, the process introduces another essential element to your research project: the importance of clear and constant communication .
And of course, to analyze information from survey or observation techniques, you must record your results . Gone are the days of spreadsheets. Feedback from surveys and listening channels can automatically feed into AI-powered analytics engines and produce results, in real-time, on dashboards.
Step 7: Analysis and interpretation
The words ‘ statistical analysis methods ’ aren’t usually guaranteed to set a room alight with excitement, but when you understand what they can do, the problems they can solve and the insights they can uncover, they seem a whole lot more compelling.
Statistical tests and data processing tools can reveal:
- Whether data trends you see are meaningful or are just chance results
- Your results in the context of other information you have
- Whether one thing affecting your business is more significant than others
- What your next research area should be
- Insights that lead to meaningful changes
There are several types of statistical analysis tools used for surveys. You should make sure that the ones you choose:
- Work on any platform - mobile, desktop, tablet etc.
- Integrate with your existing systems
- Are easy to use with user-friendly interfaces, straightforward menus, and automated data analysis
- Incorporate statistical analysis so you don’t just process and present your data, but refine it, and generate insights and predictions.
Here are some of the most common tools:
- Benchmarking : a way of taking outside factors into account so that you can adjust the parameters of your research. It ‘levels the playing field’ – so that your data and results are more meaningful in context. And gives you a more precise understanding of what’s happening.
- Regression analysis : this is used for working out the relationship between two (or more) variables. It is useful for identifying the precise impact of a change in an independent variable.
- T-test is used for comparing two data groups which have different mean values. For example, do women and men have different mean heights?
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) Similar to the T-test, ANOVA is a way of testing the differences between three or more independent groups to see if they’re statistically significant.
- Cluster analysis : This organizes items into groups, or clusters, based on how closely associated they are.
- Factor analysis: This is a way of condensing many variables into just a few, so that your research data is less unwieldy to work with.
- Conjoint analysis : this will help you understand and predict why people make the choices they do. It asks people to make trade-offs when making decisions, just as they do in the real world, then analyzes the results to give the most popular outcome.
- Crosstab analysis : this is a quantitative market research tool used to analyze ‘categorical data’ - variables that are different and mutually exclusive, such as: ‘men’ and ‘women’, or ‘under 30’ and ‘over 30’.
- Text analysis and sentiment analysis : Analyzing human language and emotions is a rapidly-developing form of data processing, assigning positive, negative or neutral sentiment to customer messages and feedback.
Stats IQ can perform the most complicated statistical tests at the touch of a button using our online survey software , or data from other sources. Learn more about Stats iQ now .
Step 8: The marketing research results
Your marketing research process culminates in the research results. These should provide all the information the stakeholders and decision-makers need to understand the project.
The results will include:
- all your information
- a description of your research process
- the results
- conclusions
- recommended courses of action
They should also be presented in a form, language and graphics that are easy to understand, with a balance between completeness and conciseness, neither leaving important information out or allowing it to get so technical that it overwhelms the readers.
Traditionally, you would prepare two written reports:
- a technical report , discussing the methods, underlying assumptions and the detailed findings of the research project
- a summary report , that summarizes the research process and presents the findings and conclusions simply.
There are now more engaging ways to present your findings than the traditional PowerPoint presentations, graphs, and face-to-face reports:
- Live, interactive dashboards for sharing the most important information, as well as tracking a project in real time.
- Results-reports visualizations – tables or graphs with data visuals on a shareable slide deck
- Online presentation technology, such as Prezi
- Visual storytelling with infographics
- A single-page executive summary with key insights
- A single-page stat sheet with the top-line stats
You can also make these results shareable so that decision-makers have all the information at their fingertips.

Step 9 Turn your insights into action
Insights are one thing, but they’re worth very little unless they inform immediate, positive action. Here are a few examples of how you can do this:
- Stop customers leaving – negative sentiment among VIP customers gets picked up; the customer service team contacts the customers, resolves their issues, and avoids churn .
- Act on important employee concerns – you can set certain topics, such as safety, or diversity and inclusion to trigger an automated notification or Slack message to HR. They can rapidly act to rectify the issue.
- Address product issues – maybe deliveries are late, maybe too many products are faulty. When product feedback gets picked up through Smart Conversations, messages can be triggered to the delivery or product teams to jump on the problems immediately.
- Improve your marketing effectiveness - Understand how your marketing is being received by potential customers, so you can find ways to better meet their needs
- Grow your brand - Understand exactly what consumers are looking for, so you can make sure that you’re meeting their expectations
Free eBook: Quantitative and qualitative research design
Scott Smith
Scott Smith, Ph.D. is a contributor to the Qualtrics blog.
Related Articles
October 22, 2024
Brand Experience
The 4 market research trends redefining insights in 2025
May 20, 2024
Best strategy & research books to read in 2024
May 13, 2024
Experience Management
X4 2024 Strategy & Research Showcase: Introducing the future of insights generation
June 27, 2023
The fresh insights people: Scaling research at Woolworths Group
June 20, 2023
Bank less, delight more: How Bankwest built an engine room for customer obsession
April 1, 2023
Academic Experience
How to write great survey questions (with examples)
March 21, 2023
Sample size calculator
November 18, 2022
Statistical analysis software: your complete guide to getting started
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Module 3: Market Research
The market research process.
Marketing research identifies opportunities, generates informed marketing actions, monitors marketing performance, and improves understanding of the marketing process.
There are three types of objectives that can be deployed in marketing research: exploratory research, descriptive research, and causal research.
1. Exploratory research
- Used to better define a problem or scout opportunities.
- In-depth interviews and discussions groups are commonly used.
2. Descriptive research
- Used to assess a situation in the marketplace (i.e., potential for a specific product or consumer attitudes).
- Methods include personal interviews and surveys.
3. Causal research
- Used for testing cause and effect relationships, typically through estimation.
The Marketing Research Process
The marketing research process involves six steps:
- Problem definition
- Development of an approach to the problem
- Research design formulation
- Data collection
- Data preparation and analysis
- Report preparation and presentation
Step 1: Problem Definition
The first step in any marketing research study is to define the problem, while taking into account the purpose of the study, the relevant background information, what information is needed, and how it will be used in decision making. This stage involves discussion with the decision makers, interviews with industry experts, analysis of secondary data, and, perhaps, some qualitative research, such as focus groups. There are three types of objectives that can be deployed in marketing research:
Step 2: Development of an Approach to the Problem
Step two includes formulating an objective or theoretical framework, analytical models, research questions, hypotheses, and identifying characteristics or factors that can influence the research design. This process is guided by discussions with management and industry experts , case studies and simulations, analysis of secondary data, qualitative research, and pragmatic considerations.
Step 3: Research Design Formulation
A research design is a framework or blueprint for conducting the marketing research project. It details the procedures necessary for obtaining the required information, and its purpose is to design a study that will test the hypotheses of interest, determine possible answers to the research questions, and provide the information needed for decision making. Decisions are also made regarding what data should be obtained from the respondents (e,g,, by conducting a survey or an experiment). A questionnaire and sampling plan also are designed in order to select the most appropriate respondents for the study. The following steps are involved in formulating a research design:
- Secondary data analysis (based on secondary research)
- Qualitative research
- Methods of collecting quantitative data (survey, observation, and experimentation)
- Definition of the information needed
- Measurement and scaling procedures
- Questionnaire design
- Sampling process and sample size
- Plan of data analysis
The research plan outlines sources of existing data and spells out the specific research approaches, contact methods, sampling plans, and instruments that researchers will use to gather data. This plan includes a written proposal that outlines the management problem, research objectives, information required, how the results will help management decisions, and the budget allocated for the research.
Step 4: Data Collection
Data collection is a crucial step in the research process because it enables the generation of insights that will influence the marketing strategy.
Field work, or data collection, involves a field force or staff that operates either in the field, as in the case of personal interviewing (focus group, in-home, mall intercept, or computer-assisted personal interviewing), from an office by telephone (telephone or computer-assisted telephone interviewing/CATI), or through mail (traditional mail and mail panel surveys with pre-recruited households). Proper selection, training, supervision, and evaluation of the field force helps minimize data-collection errors. I
An example of data collection is when a consumer goods company hires a market research company to conduct in-home ethnographies and in-store shop-alongs in an effort to collect primary research data.
Systematic planning is required at all stages of the marketing research process, especially in the data collection step. The procedures followed at each stage are methodologically sound, well documented, and, as much as possible, planned in advance. Marketing research uses the scientific method in that data are collected and analyzed to test prior notions or hypotheses.
Marketing research aims to provide accurate information that reflects a true state of affairs and thus, should be conducted impartially. While research is always influenced by the researcher’s philosophy, it should be free from the personal or political biases of the researcher or the management. This is especially important in the data collection phase. The data collected will be analysed and used to make marketing decisions. Hence, it is vital that the data collection process be free of as much bias as possible.
Primary Versus Secondary Research
There are many sources of information a marketer can use when collecting data. The Nielson Ratings is an audience measurement system that provides data on audience size and the composition of television markets in the United States. The Gallup Polls conduct public opinion polls with its results published daily in the form of data driven news. The U.S Census Bureau, directed by the U.S. Government is the principal agency that is responsible for producing data about American people and the economy. Population, housing and demographic characteristics are gathered to help plan and define transportation systems, police and fire precinct, election districts and schools.
Step 5: Data Preparation and Analysis
Data Analysis is an important step in the Marketing Research process where data is organized, reviewed, verified, and interpreted.
During this phase of the research process, data is carefully edited, coded, transcribed, and verified in order for it to be properly analyzed. Statistical market research tools are used. The validity of the results is also assessed to confirm how well the data measures what it is supposed to measure. Oftentimes, the research team will arrange a debriefing session with the client to review highlights from the data and brainstorm potential ideas on how the findings can be implemented . This typically happens when a client hires a market research company and they want to remain thoroughly involved in the research process.
Analysis of data is a process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of highlighting useful information, suggesting conclusions, and supporting decision making. Data analysis has multiple facets and approaches, encompassing diverse techniques under a variety of names in different business, science, and social science domains. Data mining is a particular data analysis technique that focuses on modeling and knowledge discovery for predictive rather than purely descriptive purposes. Marketers use databases to extract applicable information that identifies customer patterns, characteristics and behaviors.
Business intelligence covers data analysis that relies heavily on aggregation and focusing on business information. In statistical applications, some people divide data analysis into descriptive statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA), and confirmatory data analysis (CDA). EDA focuses on discovering new features in the data and CDA focuses on confirming or falsifying existing hypotheses. Predictive analytics focuses on application of statistical or structural models for predictive forecasting or classification. Text analytics applies statistical, linguistic, and structural techniques to extract and classify information from textual sources, a species of unstructured data. All are varieties of data analysis.
Step 6: Report Preparation & Presentation
During the Report Preparation & Presentation step, the entire project should be documented in a written report that addresses the specific research questions identified; describes the approach, the research design, data collection, and data analysis procedures adopted; and presents the results and the major findings. This permanent document is also helpful because it can be easily referenced by others who may not have been part of the research.
The findings should be presented in a comprehensible format so that they can be readily used in the decision making process. In addition, an oral presentation should be made to management using tables, figures, and graphs to enhance clarity and impact.
A successful presentation may include the following elements:
- Charts, graphs, and visual elements that help showcase important facts and make the presentation easily digestible and memorable
- Recommendations about how to apply the research
- Final conclusions (based on the insights gathered from data collected) that effectively meet the initial objectives of the research
A formal research report presentation typically includes the following:
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Research Objectives
- Research Methodology
- Highlights of Data Collected
- Findings/Insights
- Recommendations/Implications and Action Plan
- Appendix (including Respondent Screening Instrument and Questionnaire)
business intelligence
Any information that pertains to the history, current status or future projections of a business organization
Values of qualitative or quantitative variables belonging to a set of items; typically the results of measurements and can be visualised using graphs or images
A technique for searching large-scale databases for patterns; used mainly to find previously unknown correlations between variables that may be commercially useful.
Information regarding cultural phenomena
executive summary
A short document or section of a document that summarizes a longer report or proposal in such a way that readers can rapidly become acquainted with a large body of material without having to read it all.
A survey whereby respondents are intercepted in shopping in malls. The process involves stopping the shoppers, screening them for appropriateness, and either administering the survey on the spot or inviting them to a research facility located in the mall to complete the interview.
marketing research
The function that links the consumers, customers, and public to the marketer through information. This information is used to identify and define marketing opportunities and problems; generate, refine, and evaluate marketing actions; monitor marketing performance; and improve understanding of marketing as a process.
Not influenced by irrational emotions or prejudices
qualitative research
A method of inquiry employed in many different academic disciplines, traditionally in the social sciences but also in market research and further contexts.
scientific method
A body of techniques for acquiring new knowledge or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning.
secondary data
Information collected by someone other than the user of the data
secondary research
This process involves the summary, collation, and synthesis of existing research rather than primary research, where data is collected from subjects or experiments
Information from a predetermined set of questions that is given to a sample and is used to assess thoughts, opinions, and feeling
Carried out using a planned, ordered procedure
Candela Citations
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Marketing Research Process. Authored by : Boundless. Located at : https://www.boundless.com/marketing/textbooks/boundless-marketing-textbook/consumer-marketing-4/marketing-research-process-34/ . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image: Scheduling. Authored by : DSP-user. Located at : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planning#mediaviewer/File:Planboard_planning.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- CMI Marketing Research Mini Case Study. Authored by : Official CMI Channel. Located at : http://youtu.be/u4beu5bp2NU . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Privacy Policy

- Updated on July 7, 2020
- By Market Research Guy
- In Overviews
The Market Research Process: 6 Steps to Success
The market research process is a systematic methodology for informing business decisions. The figure below breaks the process down into six steps:
Step 1. Define the Objective & Your “Problem”
Perhaps the most important step in the market research process is defining the goals of the project. At the core of this is understanding the root question that needs to be informed by market research. There is typically a key business problem (or opportunity) that needs to be acted upon, but there is a lack of information to make that decision comfortably; the job of a market researcher is to inform that decision with solid data. Examples of “business problems” might be “How should we price this new widget?” or “Which features should we prioritize?”
By understanding the business problem clearly, you’ll be able to keep your research focused and effective. At this point in the process, well before any research has been conducted, I like to imagine what a “perfect” final research report would look like to help answer the business question(s). You might even go as far as to mock up a fake report, with hypothetical data, and ask your audience: “If I produce a report that looks something like this, will you have the information you need to make an informed choice?” If the answer is yes, now you just need to get the real data. If the answer is no, keep working with your client/audience until the objective is clear, and be happy about the disappointment you’ve prevented and the time you’ve saved.
Step 2. Determine Your “Research Design”
Now that you know your research object, it is time to plan out the type of research that will best obtain the necessary data. Think of the “research design” as your detailed plan of attack. In this step you will first determine your market research method (will it be a survey, focus group, etc.?). You will also think through specifics about how you will identify and choose your sample (who are we going after? where will we find them? how will we incentivize them?, etc.). This is also the time to plan where you will conduct your research (telephone, in-person, mail, internet, etc.). Once again, remember to keep the end goal in mind–what will your final report look like? Based on that, you’ll be able to identify the types of data analysis you’ll be conducting (simple summaries, advanced regression analysis, etc.), which dictates the structure of questions you’ll be asking.
Your choice of research instrument will be based on the nature of the data you are trying to collect. There are three classifications to consider:
Exploratory Research – This form of research is used when the topic is not well defined or understood, your hypothesis is not well defined, and your knowledge of a topic is vague. Exploratory research will help you gain broad insights, narrow your focus, and learn the basics necessary to go deeper. Common exploratory market research techniques include secondary research, focus groups and interviews. Exploratory research is a qualitative form of research.
Descriptive Research – If your research objective calls for more detailed data on a specific topic, you’ll be conducting quantitative descriptive research . The goal of this form of market research is to measure specific topics of interest, usually in a quantitative way. Surveys are the most common research instrument for descriptive research.
Causal Research – The most specific type of research is causal research, which usually comes in the form of a field test or experiment. In this case, you are trying to determine a causal relationship between variables. For example, does the music I play in my restaurant increase dessert sales (i.e. is there a causal relationship between music and sales?).
Step 3. Design & Prepare Your “Research Instrument”
In this step of the market research process, it’s time to design your research tool. If a survey is the most appropriate tool (as determined in step 2), you’ll begin by writing your questions and designing your questionnaire. If a focus group is your instrument of choice, you’ll start preparing questions and materials for the moderator. You get the idea. This is the part of the process where you start executing your plan.
By the way, step 3.5 should be to test your survey instrument with a small group prior to broad deployment. Take your sample data and get it into a spreadsheet; are there any issues with the data structure? This will allow you to catch potential problems early, and there are always problems.
Step 4. Collect Your Data
This is the meat and potatoes of your project; the time when you are administering your survey, running your focus groups, conducting your interviews, implementing your field test, etc. The answers, choices, and observations are all being collected and recorded, usually in spreadsheet form. Each nugget of information is precious and will be part of the masterful conclusions you will soon draw.
Step 5. Analyze Your Data
Step 4 (data collection) has drawn to a close and you have heaps of raw data sitting in your lap. If it’s on scraps of paper, you’ll probably need to get it in spreadsheet form for further analysis. If it’s already in spreadsheet form, it’s time to make sure you’ve got it structured properly. Once that’s all done, the fun begins. Run summaries with the tools provided in your software package (typically Excel , SPSS , Minitab , etc.), build tables and graphs, segment your results by groups that make sense (i.e. age, gender, etc.), and look for the major trends in your data. Start to formulate the story you will tell.
Step 6. Visualize Your Data and Communicate Results
You’ve spent hours pouring through your raw data, building useful summary tables, charts and graphs . Now is the time to compile the most meaningful take-aways into a digestible report or presentation. A great way to present the data is to start with the research objectives and business problem that were identified in step 1. Restate those business questions, and then present your recommendations based on the data, to address those issues.
When it comes time to presenting your results, remember to present insights , answers and recommendations , not just charts and tables. If you put a chart in the report, ask yourself “what does this mean and what are the implications?” Adding this additional critical thinking to your final report will make your research more actionable and meaningful and will set you apart from other researchers.
While it is important to “answer the original question,” remember that market research is one input to a business decision (usually a strong input), but not the only factor.
Here’s an Example
So, that’s the market research process. The figure below walks through an example of this process in action, starting with a business problem of “how should we price this new widget?”
Ok, if you think you understand this stuff here’s a brief quiz:
25 thoughts on “The Market Research Process: 6 Steps to Success”
this site seems to provide solutions to my problems.
Thank you very much i found this information very useful.
Quiet helpful, it was clear and concise
Awesome site, thanks so much, really saved me alot of time 🙂 BIG THANKS 🙂
I had way too much fun using this site, the referencing aspect of it was just invigorating. Hehe
Very good information indeed, it has refreshed my studies.
This site is one of its kind.Really impressed with the manner in which the data is arranged.Thanks Very Much.
Truly rewarding, but my concern, these are the same steps outlined in the marketing research process. Is there no difference between market-research and search marketing?
its very usefull
Is good for my work
This is, perhaps, the most coherent and practical, yet succinct and laconic, summary of the market research process that I have reviewed in quite some time. Thank you.
Wow been struggling to get this kind of information and i have been looking for it. Thank you so much.
This is comprehensive enough
I would like to thank you for the great info
Appreciate it
This is very good paper and I find key concept in this field
very useful
superb keep up the good work
Clear discussion of topic with good examples on subject matter.
you make me pass in my exams
I’ve been in FMCG sales for last 20 years and now started career in market research. This site is very helpful to clear my market research concepts.
thanks for all of those informations and examples it is nice
Very insightful and I have now obtained a much more confident understand of the marketing research steps. Thank you kindly.
very clear and step by step explanation.
Thanks for sharing such an informative blog
Leave a reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Market Research – Objectives, Types, Process, Techniques, Importance
Market research refers to systematic collection, recording and analysis of data, aimed towards solving a marketing problem. It is the process of collecting information or facts relevant to the market and analysing and interpreting that information to strategize business decisions.
According to Philip Kotler, “ Market Research is the systematic design, collection, Analysis, and reporting of data relevant to a specific marketing situation an organization is facing”
Market Research involves systematic problem analysis, model building and fact finding for the purpose of improved decision making and control in the marketing of goods and services.
Objectives of Market Research
- Discovering new markets for products
- Increasing the market share for existing products
- Forecasting the future demand for products
- Analysing the tastes and preferences of consumers
- Reducing the cost of marketing activities
- Improving the quality of products
- Formulating effective marketing policies
- Determining competitors strategy
- Studying the internal and external marketing environment
Types of Market Research
- Market / Customer Research
- Product, Price, Promotion Research
- Channel Research
- Sales Research
- Advertising Research
- Policy Research
Information collected through Market Research
- Total size of current market
- Total size of potential market
- Growth rate
- Consumer demographics
- Consumer taste & preferences
- Consumer satisfaction
- Consumer expectations
- Consumer buying behaviour
- Price sensitivity analysis
- Internal and external marketing environment
- SWOT of the firm and its competitors
- Market Demand
Professional academic writers from SmartWritingService a research paper writing service can write an academic project in marketing for you.
Developing Information for Market Research / Techniques of Market Research
Market Research involves collection of primary and secondary data through various methods of data collection. They are:
Primary Data
- Questionnaire
- Observation
- Experiments
Secondary Data
- Government publications
- Trade journals
- Internal records
- Yearly reports of banks and businesses
- Public records
- National 5 year plans
- Historical documents
- Unpublished documentaries, biographies, letters, diaries etc.
Other methods of Data collection
- Warranty cards
- Store audits
- Pantry audits
- Consumer Panels
- Mechanical devices
- Content analysis
- Quiz, test, assignments
- In-depth interviews
- Projective techniques – Word association test, Sentence completion test, Story completion test, Verbal projection test, Pictorial techniques
Process of Market Research

(1) Identification and definition of Research Problem – It involves –
- Identification of Research problem
- Laying down objectives of the study, and
- Determining the extent of information required.
(2) Conducting situational analysis and informal investigation – Situational Analysis involves collecting information regarding business environment, market situation, competitions and industry surrounding the problem in general. An informal investigation includes an investigation with the people outside the organisation like suppliers, wholesalers, consumers, advertising agencies etc. This is done to determine whether a detailed study in necessary and feasible or not.
(3) Planning and conducting formal investigation – It involves the following –
- Preparing a research design – exploratory, descriptive, casual
- Selecting the sources of information – Primary source or Secondary source
- Deciding methods of data collection – Survey, Observation, Experimentation etc.
- Planning the Sample Frames, Sample size and Questionnaire
- Collecting the data – Survey, Observation or Experimentation
(4) Analysing and Interpreting data – It involves classification, tabulation and interpretation of the data collected. Statistical techniques are used to draw conclusions and make recommendations. Efforts are made to generalize all the findings.
(5) Summarizing the findings and preparing a research report – The last step involves preparation of a written report that helps the management to make effective decisions based on the finding and recommendations of the report.
Guidelines for effective report –
- There must be objectivity and clarity in presentation of data
- It must be concise and precise
- Charts and illustrations must be only used if necessary
- The layout of the report must be – Preliminary pages, Main Body and End Matter
- Title of Report
- Date, Acknowledgement and Foreword
- Table of Contents
- Objectives of Study
- Introduction
- Summary of Findings
- Main Report/Body
- Suggestions and Recommendations
- Conclusion, Appendices, Bibliography
Importance of Marketing Research
- It helps in formulation of marketing plans, policies and strategy
- It helps in Problem solving and Decision making
- It acts as a controlling technique for marketing activities
- It helps to understand market complications and opportunities
- It aids in understanding consumer behaviour and consumption patterns
No Comments
I was very pleased to search out this web-site. I wanted to thanks for this wonderful learn!! I undoubtedly enjoyed every level of it and I have you ever bookmarked to check out new stuff you weblog post.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
© 2019 BBA|mantra | All Rights Reserved

COMMENTS
To illustrate the marketing research process, let's return to Uncle Dan and his ailing bookstore, Bookends. You need a lot of information if you're going to help Dan turn things around, so marketing research is a good idea. You begin by identifying the problem and then work to set down your research objectives and initial research questions:
Step 1 in the marketing research process is to define the problem. Businesses take a look at what they believe are symptoms and try to drill down to the potential causes so as to precisely define the problem. The next task for the researcher is to put into writing the research objective, or goal, the research is supposed to accomplish.
Marketing Research Process. There are seven steps in marketing research process: define the research problem, determine the research design, choose the method for collecting primary data, design the sample, collect the data, analyze and interpret the data, prepare the research report. ... these objectives should be specific, attainable ...
Marketing research objectives. Marketing research aims to identify challenges and opportunities to achieve marketing goals. Companies process data, analyze data, and interpret relevant facts to provide valuable information about it. Research results also help companies plan, evaluate, and develop marketing strategies and tactics.
The marketing research process - an overview. A typical marketing research process is as follows: Identify an issue, discuss alternatives and set out research objectives; Develop a research program; Choose a sample; Gather information; Gather data; Organize and analyze information and data; Present findings; Make research-based decisions
Marketing research identifies opportunities, generates informed marketing actions, monitors marketing performance, and improves understanding of the marketing process. There are three types of objectives that can be deployed in marketing research: exploratory research, descriptive research, and causal research. 1. Exploratory research
The market research process is a systematic methodology for informing business decisions. The figure below breaks the process down into six steps: The Market Research Process. Step 1. Define the Objective & Your "Problem" Perhaps the most important step in the market research process is defining the goals of the project.
Each type of market research offers distinct advantages and can be used depending on your company's goals, timelines, and budget. Learn more: What is Customer Experience (CX) Research? Market Research Process. Step 1. Define Research Objectives. The first step in market research is to clearly define the research objectives.
Market research refers to the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data and information about a particular market, industry, or target audience. The purpose of conducting market research is to gain insights into consumer behavior, market trends, competitor analysis, and other primary objectives.
Market Research - Objectives, Types, Process, Techniques, Importance Market research refers to systematic collection, recording and analysis of data, aimed towards solving a marketing problem. It is the process of collecting information or facts relevant to the market and analysing and interpreting that information to strategize business ...